Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Product Type
- Technologies
- Product Families
Features & Benefits
- Labeling Claims
- Ready-to-Use Product Features
- Tedlar® for Architectural Sheet Metals
In coastal and tropical/sub-tropical natural environments with high temperature, high humidity and especially high salt spray, pollution brought by industrial development is gradually evolving into a highly corrosive atmospheric environment. Metals exposed to these environments for many years are highly susceptible to corrosive damage caused by moisture, oxygen and corrosive substances (such as impurities, acids, salt ions, dust and surface deposits).
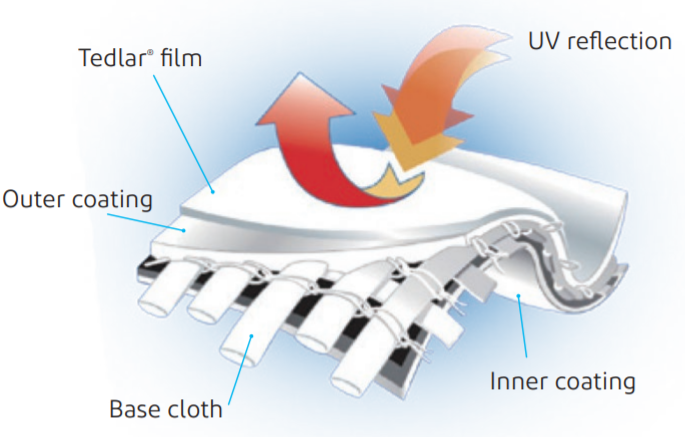
Tedlar® film consists of 100% fluorocarbon resin without the addition of plasticizers such as acrylic acid (also known as acrylic or polymethyl methacrylate [PMMA]). The chemical stability and aging resistance of fluorocarbon resins ensure the excellent weatherability of Tedlar® . In addition, Tedlar® film for buildings and construction has been subjected to biaxial stretching to improve mechanical, optical and barrier film properties. The surface of the film is resistant to pinholes, cracks and other abrasions, and provides long-term effective protection for the metal substrate.
The excellent weatherability and corrosion resistance of Tedlar® film laminated metal sheets have been proven in numerous practical application cases over the past 30 years.
- Tedlar® PVF Features in Architectural Applications
- Resistant to weather, ultraviolet (UV) rays, fading and corrosion
- Pliant and easily molded
- Impervious to harsh chemicals and pollution
- Easy to clean
- Resistant to mold, mildew and bacteria
- Environmentally safe
DuPont™ Tedlar® protective film helps extend the look and life of your design, even in the most extreme environments. From severe weather to harsh chemicals, Tedlar® protective film provides long-term durability and performance. Tedlar® protective film can easily be applied to a range of surfaces, providing the flexibility to design your way, and the surface performance to keep it that way.
Low maintenance costs : In addition to exceptional protection from the elements, Tedlar® provides an impervious barrier against stains and scuffs, making them easy to wipe away. And because it can stand up to the harshest industrial cleaning products, including bleach, Tedlar® protective film helps keep your designs looking their best.
Resistant to mold and mildew : Tedlar® protective films do not support mold or mildew growth, providing superior surface protection in even the most extreme and high-traffic environments. Additionally, Tedlar® won’t support bacterial growth, so it’s safe for you and for the environment.
Fade resistant: Tedlar® PVF is available in both transparent and opaque pigmented film. The color uniformity and fade resistance of pigmented Tedlar® protective film allows it to hold its color and maintain its original appearance for years. Transparent films allow long-term light transmission while greatly minimizing cracking, yellowing or fogging of the laminate.
Durable
Tedlar® film has delivered excellent weatherability and proven protection in a number of practical applications.
Japanese steel sheet plant
Founded in 1984, this steel sheet plant expanded its workshops in 2010 and installed Tedlar® film laminated steel sheets of the same color. As shown in the figure, the newly installed steel sheet has almost no difference in color and appearance compared with the steel sheet that has been used for 26 years.
In addition, although the plant is located in the coastal area, there is no obvious corrosion on the edges of the steel siding and at the screw holes, which indicates that the Tedlar® film provides effective protection for the steel sheet.
Chaoyang Park Tennis Center, Beijing, China
Laminated with Tedlar® film, this tennis center’s air bearing membrane roof has remained almost unchanged in color.
Okinawa Thermal Power Plant, Japan
Founded in 1986, this thermal power plant is located in the coastal area of Okinawa, less than 500 meters from the coastline. The high salt spray environment along the coast and the smoke in the power plant are very corrosive to buildings, especially metal sheets. After 27 years of erosion by wind and rain, the steel sheets protected by Tedlar® film revealed no signs of rusting at the edges and seams. Moreover, the film maintained an ultra-high color stability. After 27 years of use in the coastal environment, there is no obvious discoloration and chalking. There is almost no color difference compared with the sample left inside the plant in 1986.
Stylish
With ultra-low color differences, a smooth and fine texture and excellent formability, Tedlar® film is stylish and esthetically pleasing from installation until its removal. Its matte surface finish even prevents light pollution.
- Metal roofing panel : Tedlar® film’s lot-to-lot color reproducibility is controlled to a delta of <0.5.
- Even & delicate surface finish : With an even surface finish, Tedlar® film prevents uneven thickness and pinholes caused by factors in processing.
- Prevents light pollution : With a matte finish on the surface, Tedlar® film maintains an attractive esthetic without allowing light pollution.
- Ease of machining and shaping : Tedlar® film is pliable and ductile, allowing for excellent processability and application.
Building façade in Yokohama, Japan
In 1983, a building in Yokohama, Japan, installed a façade using Tedlar® PVF film. The film is matte, with an even and delicate surface finish. Compared to the Tedlar® standard color chart, the exterior wall surface has almost no difference in color after three decades of use.
Building in Tokyo, Japan
In 1986, a building in Tokyo, Japan, applied Tedlar® PVF to its exterior walls. Due to the complexity of the wall shape, Tedlar® film—with its easy-to-use machining and shaping properties—was the ideal choice. After more than three decades of use, the wall has almost no difference in color.
Easy to Clean
Non-sticky and stain resistant, Tedlar® film can withstand all types of dirt and grime. Chemically inert, the film can be cleaned with various cleaning agents and requires little maintenance.
Tedlar® is stain resistant and chemically inert, so it can be completely cleaned with a cleaning agent, even when exposed to stubborn stains such as spray paint or caulking compound. Other finishes, such as fluorocarbon paint, may be damaged in cleaning due to poor chemical inertness.
- Non-sticky and stain resistant : Tedlar® film resists all types of dirt, including bird droppings, water marks, paint, cooking fumes, grease, dust, acid rain and more.
- Chemically inert : Tedlar® film can stand up to a wide variety of detergents and strong solvents to remove stains such as asphalt, tar, grease, paint or caulking compound.
- Self-cleaning : Contaminants can be easily washed away by rain water, keeping the building’s appearance fresh and new, and reducing cleaning and maintenance costs.
Pedestrian bridge in Yokohama, Japan
Built in 1990, this pedestrian bridge in Yokohama, Japan, still remains esthetically pleasing after several decades of use. Tedlar® metal lamination was attached as a decorative panel to the side and bottom of the pedestrian bridge. Even today, the dust, moss and other stains on the Tedlar® surface are still very easy to clean, keeping the decorative surface clean and beautiful.
Safe & Environmentally Friendly
Tedlar® film is non-flammable and non-reactive, and it doesn’t support bacterial growth. Additionally, it produces minimal volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions during processing.
- Excellent fire resistance: Tedlar® film is a component of structures that pass safety requirements for aircraft-grade fire resistance and low smoke toxicity. It is also recognized as a non-flammable material in Japan (NM0717, NM1553). Lamination onto metal sheet provides excellent fire resistance and low smoke toxicity.
Applied to the interior of aircraft cabins - Exceptional bacteria resistance : Tedlar® film does not support the growth of bacteria, mold and mildew. It is especially suitable for places that require a high level of cleanliness, such as hospitals, hotels, restaurants and shopping malls.
Applied to sterile operating rooms in hospitals
- Colorful Enduring Empowering
Tedlar® PVF film provides a long-lasting finish to a wide variety of surfaces exposed to harsh environments. The color uniformity and fade resistance of Tedlar® allows it to hold its color and maintain its original appearance for decades.
- Flexible Product Adhesives
Over the last 25 years DuPont has developed a family of adhesives used for laminating Tedlar® PVF film to a wide range of substrates. These adhesives are characterized by excellent resistance to moisture and UV radiation.
DuPont flexible product adhesives are versatile acrylic adhesives developed specifically for laminating Tedlar® PVF film to a variety of substrates. With these adhesives, high-quality, long-lasting bonds can be achieved to meet demanding quality control specifications of manufacturers.
A blend of acrylic adhesive 68070 and Epon™ 828 is used to bond Tedlar® PVF film to aluminum and galvanized steel in various gages.
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Application Method
- Tedlar® PVF for Architectural Applications
- Wallcoverings
- Residential and commercial roofing, siding, trim and accents
- Formed or flat metal building panels
- Flexible laminates for air-inflated structures, canopies, awnings and stadium domes
- Indoor and outdoor fabrics
- Curtain walls
- Healthcare facility surfaces
- Pipe and vessel jacketing
- Flexible Adhesive Application
Heat the adhesive to room temperature and mix according to instructions. Dilute with toluene to desired viscosity. Apply adhesive using spray gun, brush, dipping, extrusion, rollers, doctor blade/wire wound rod, reverse roller coater, roller coater or gravure coating. Lamination can proceed as soon as the adhesive is dry. Toluene and/or methyl ethyl ketone (for cleanup only) may be used to clean up equipment.
Note: Trial laminations should be made to test adhesive suitability. Adhesives, especially non-DuPont, must be tested for the specific application. Some epoxies may not bond well to the Tedlar® PVF film. The harder polyester adhesives do not bond well to Tedlar® PVF film. Isocyanate curing agents generally enhance adhesion. Some phenolic materials or curing agents may cause staining of the Tedlar® PVF film.
Properties
- Physical Properties
- Thermal Properties
- Typical Properties
- Composition
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Coefficient of Friction (Film on Metal) | 0.18 - 0.21 | — | ASTM D1894 |
| Falling Sand Erosion (on PET Backing) | 04-Aug | L/µm | ASTM D968 |
| Falling Sand Erosion (on PET Backing) | 4-8 | L/µm | ASTM D968 |
| Impact Strength | 45 - 89 | J/mm | ASTM D3420 |
| Moisture Absorption (for most types) | max. 0.5 | % | Water Immersion |
| Optical Transmission of Clear Films | 93 | % | ASTM D1003 |
| Refractive Index of Clear Films | 1.46 | — | ASTM D542 |
| Shore Hardness | D60 - D70 | — | ASTM D2240 |
| Strain at Break | 90 - 250 | % | ASTM D882 |
| Tear Strength (Initial) | 100 - 200 | N/mm | ASTM D1004 |
| Tear Strength (Propagated) | 5.9 - 24 | N/mm | ASTM D1922 |
| Tensile Modulus | 2.1 - 2.6 | GPa | ASTM D882 |
| Ultimate Strength | 55 - 110 | MPa | ASTM D882 |
| Yield Strength | 34 - 41 | MPa | ASTM D882 |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 5 - 10 x 10^-5 | m/m·K | ASTM D696 |
| Lower Glass Transition Temperature | 15 to -20 | °C | Various |
| Peak Melting Temperature | 190 - 210 | °C | ASTM E1269 |
| Relative Thermal Index - Electrical Strength | 140 | °C | UL 746B |
| Relative Thermal Index - Mechanical Impact | 120 | °C | UL 746B |
| Relative Thermal Index - Mechanical Strength | 125 | °C | UL 746B |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 1.0 - 1.1 | kJ/kg*K | ASTM E1269 |
| Temperature Range (continuous use) | -70 to 105 | °C | — |
| Upper Glass Transition Temperature | 40 - 50 | °C | Various |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Lamination Temperature | 135 - 210 (275 - 410) | °C (°F) | — |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Toluene | 70 | % | — |
| Isopropanol | 30 | % | — |
Technical Details & Test Data
- Metal Lamination
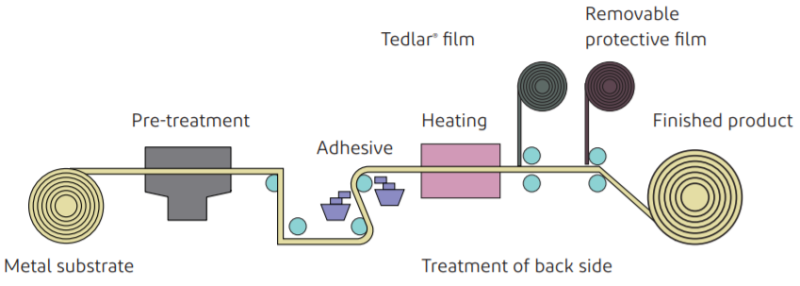
Product structure and processing flow
Tedlar® film is laminated onto a metal substrate using a special adhesive invented by DuPont based on a hot laminating process. The process and product structure are similar to those of a fluorocarbon coil coated metal sheet. The figure below illustrates the differences between Tedlar® film lamination and fluorocarbon baking coating.
Structural comparison of Tedlar® film laminated steel sheet vs. sheet with fluorocarbon baking coating
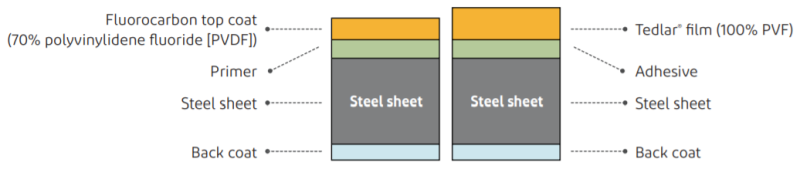
Metal Lamination Process of Tedlar® film
- Building Solutions
System solutions for building
Tedlar® film-based metal lamination
Tedlar® film-based metal lamination provides a guarantee of more than 30 years of service life for the roofing of any new project.
Product structure example
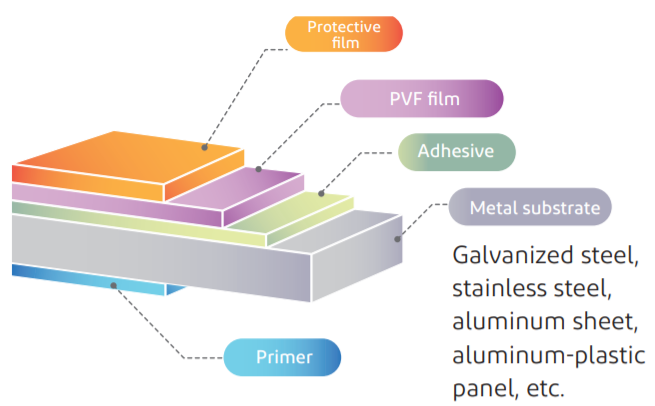
Tedlar® metal lamination product structure
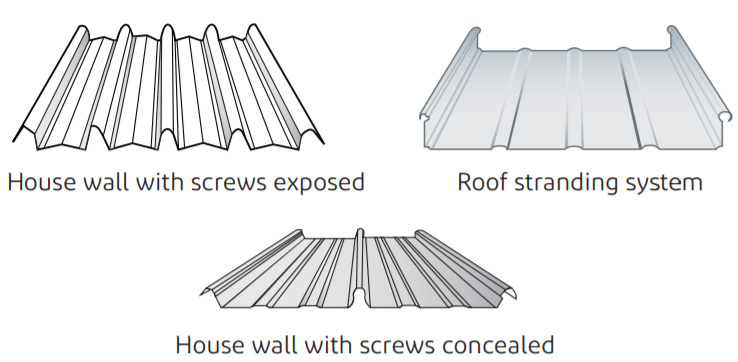
Metal roof panel structure diagram
Composite metal sheet with Tedlar® film interior finish
Tedlar® film interior finishes not only have the delicate texture of fabric, but also have excellent properties such as fire-, stain- and corrosion-resistance and ease of cleaning. Organic combination with steel sheet makes the Tedlar® interior finish suitable for medical environments.
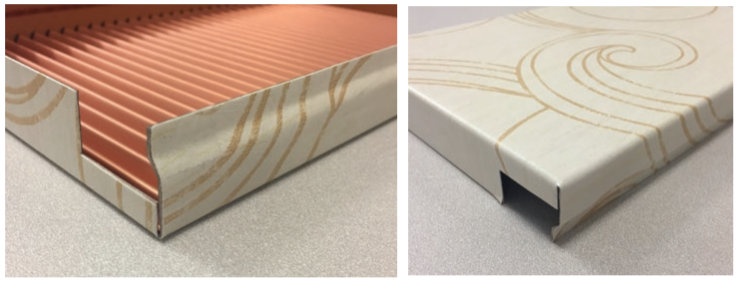
Membrane fabric materials laminated with Tedlar® film
Tedlar® film can be laminated with various coated fabrics to form membrane fabric structures at much lower construction costs than steel. With excellent weatherability and dirt-shedding properties, membrane fabric is a cost-effective material for buildings like stadiums, convention centers, commercial facilities and transportation hubs.
Composition of membrane fabric materials
- Improve the Corrosion Resistance and Service Life of Steel Sheets with Tedlar®

The picture above shows the rooftop of an industrial plant. The rooftop of the plant consists of two parts. The lower left is Tedlar® film laminated steel sheet installed in 1983, and the upper right roof is steel sheet coated with other material installed in the late 20th century. Although the roof sheets are the same shape and used in the same environment, the appearance of the steel sheet roofs coated with different materials shows a huge difference.
The steel sheet roof not laminated with Tedlar® has been severely rusted, while the Tedlar® film laminated steel sheet roof appears as durable as new after more than 30 years of use.
- Caulking Compound and Solvent Cleaning Test

- Chemical Resistance
Acid and alkali resistance – Test 1
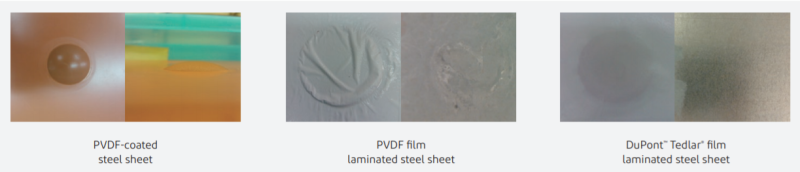
To test the acid and alkali resistance, experimenters placed drops of concentrated sulfuric acid (98%) on the surface of samples of Tedlar® and PVDF for 24 hours.
Acid and alkali resistance – Test 2
After Tedlar® film laminated steel sheet (gray) and PVDF fluorocarbon paint coated steel sheet (blue) have been soaked in 5% hydrochloric acid and 5% sodium hydroxide solution for 30 days at room temperature, obvious bubbling appears on the surface of the PVDF-coated steel sheet, which indicates that the substrate is severely corroded, while the Tedlar® film laminated steel sheet is free of bubbling, delamination, etc., indicating that the Tedlar® film-protected steel sheet has excellent resistance to acid and alkali.
30-day acid and alkali soaking test

Salt spray resistance test
Tedlar® film and PVDF coating were exposed to salt spray for 2,000 hours.

High-temperature acid gas resistance test
This case is a steel roofing sheet project of the synthesis workshop in a chemical plant. Because high-temperature acid gas produced in the synthesis workshop causes severe corrosion to the original steel roof panel, the building owner must replace the roof every two years, which not only affects normal operation of the plant, but also poses a large production safety hazard. The plant replaced some of its roofing with Tedlar® film laminated steel sheets in 2016. After two years, the normal roof was still corroded and had to be replaced regularly, but the new roof panel using the Tedlar® film laminated steel sheets had no corrosion and remained esthetically pleasing.
Original steel sheet roofing

Tedlar® film laminated steel sheet roofing at far right

Chemical resistance of Tedlar® film
Experimenters immersed Tedlar® film in the following chemicals. The checkmarks indicate no significant change in tensile strength and ultimate elongation.
1-year immersion at room temperature 2-hour immersion at boil 31-day immersion at 75°C (167°F) Acids Acetic acid (glacial) ✓ ✓ Hydrochloric acid (10% & 30%) ✓ Hydrochloric acid (10%) ✓ ✓ Nitric acid (20%) ✓ Nitric acid (10% & 40%) ✓ Phosphoric acid (20%) ✓ Sulfuric acid (20%) ✓ Sulfuric acid (30%) ✓ Bases Ammonium hydroxide (12% & 39%) ✓ Ammonium hydroxide (10%) ✓ Sodium hydroxide (10%) ✓ ✓ Sodium hydroxide (10% & 54%) ✓ Solvents Acetone ✓ ✓ Benzene ✓ ✓ Benzyl alcohol ✓ 1,4-Dioxane ✓ Ethyl acetate ✓ Ethyl alcohol ✓ n-Heptane ✓ Kerosene ✓ Methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) ✓ Toluene ✓ Trichloroethylene ✓ Miscellaneous Phenol ✓ Phenol (5%) ✓ Sodium chloride (10%) ✓ Sodium sulfide (9%) ✓ Tricresyl phosphate ✓ - Weather Resistance
Accelerated aging and UV exposure test
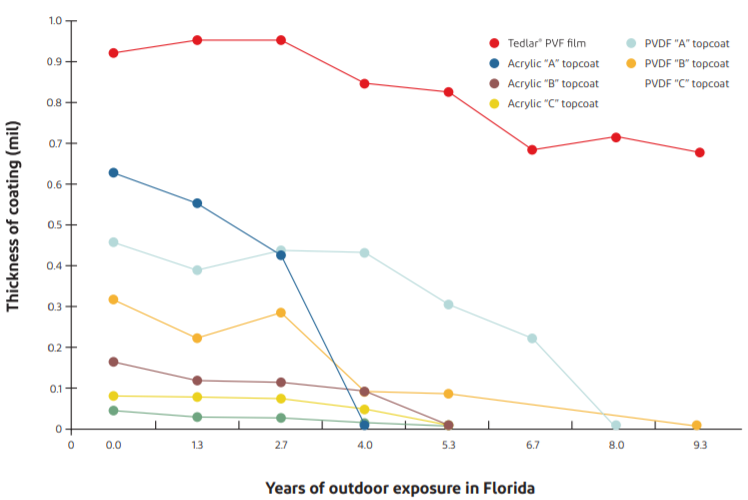
As test results show, compared with the surface protection coatings such as acrylic and PVDF, Tedlar® film can better resist UV and acid rain, prevent dust buildup, and retain its thickness, color and gloss for a longer time, thus maintaining the building’s original appearance for longer.
Thickness
 Gloss
Gloss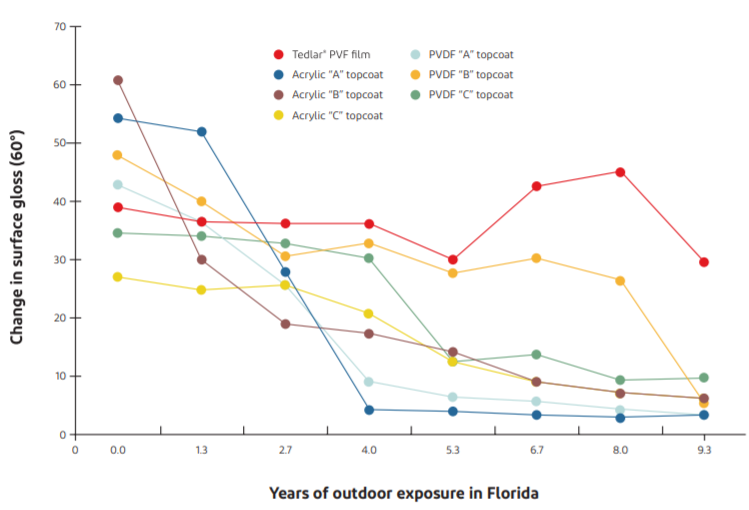
Color
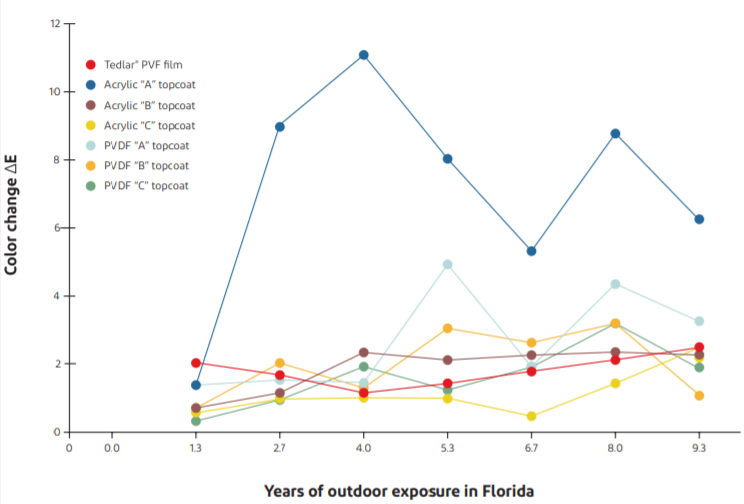
15-year Florida weather exposure test
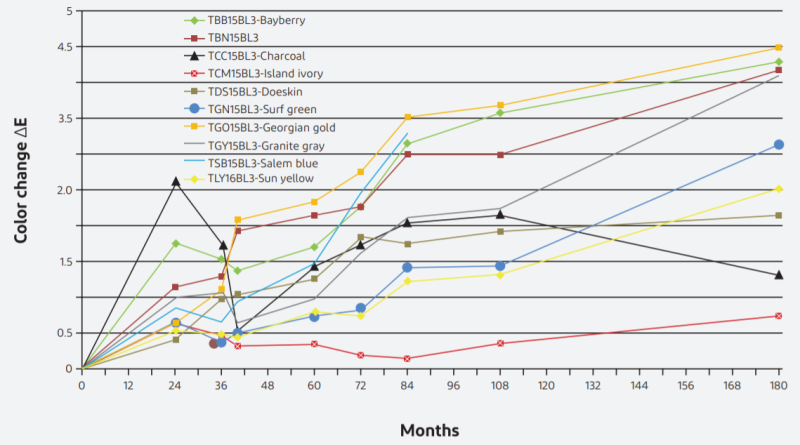
Florida’s outdoor exposure field is recognized in the industry as a standard test site for assessing the weatherability of coatings. Ten-year Florida exposure is an important indicator of the American Architectural Manufacturers Association (AAMA) 2605, which is the highest weatherability rating for PVDF. Not only has Tedlar® film passed the 15-year Florida exposure test (color difference E < 4.5), but its color stability and weatherability rating is 50% higher than ordinary PVDF.
Tedlar® Florida weathering data: color change
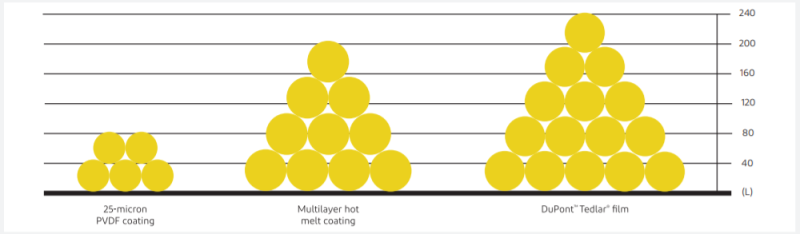
- Abrasion Resistance & Processability
Abrasion resistance test
Falling sand abrasion tests (ASTM D968) were conducted for 25-micron PVDF coating, 100-micron multilayer hot melt coating and Tedlar® film. The results show that the abrasion resistance of 37.5-micron Tedlar® film surpasses that of PVDF, but is identical to that of 100-micron multilayer hot melt coating.
0T bending test
A 180° 0T bending test (seen here at 40x magnification) shows that the PVDF-coated steel sheet has obvious cracks, while the Tedlar® film laminated steel plate shows no cracks. With film elongation up to 100%, Tedlar® has outstanding processability.
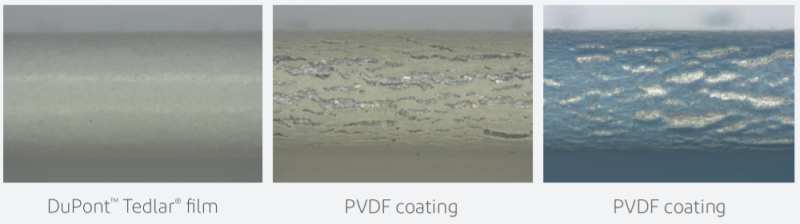
Processability Test
Tedlar® has an elongation of more than 100% and doesn’t crack after 0T bending, thus protecting the sheet from corrosion. It allows for complex sheet shaping during processability, with no discoloration at the bend. Additionally, there is no rusting on the punched steel sheet after a 2000-hour salt spray test.

- Tedlar® PVF Film Passes SGS Test
Test items Test methods Test contents Test results Remarks Weathering test (4000 hours) Weathering test CNS 15200-7-7 (2013) Appearance No cracking, blistering, etc. 1. Condition basis: refer to ASTM G154-12a Cycle 1
2. Illuminance: 0.89 W/m2 /nm
3. Light source type: UVA 340
4. Cycle conditions: 8h UV at 6°C BPT; 4h condensation at 50°C BPT
5. The sample is subject to 0T bending and 9.5 mm cupping before testingGloss CNS 10756-1 60° gloss retention (%) 100% Fading (color difference) ASTM D2244-11 4000 hours ∆E: 0.33 Chalking test ASTM D4214-07 Powdering degree Level 10 Damp heat resistance test (4000 hours) Damp heat resistance test CNS 11607 Appearance No cracking, blistering, etc. 1. Moisture and heat resistance test conditions: temperature: 50 ± 2°C, humidity: 95 ± 5% RH
2. The sample is subject to 0T bending and 9.5 mm cupping before testingGloss test CNS 10756-1 60° gloss retention (%) 98% Rusting grade rating ASTM D1654-92 Rusting grade Level 10 Salt spray test (4000 hours) Salt spray test CNS 8886 (2002) Appearance No cracking, blistering, etc. Salt spray test conditions
1. Experimental salt: analytical reagent
2. Saline concentration: 5 w/v% NaCl
3. Experimental water: pure water
4. Spray exposure zone temperature (°C): 35.0 ± 1.0
5. Spray amount (ml/h/80 cm2 ): 1.7 (avg.)
6. Supply air pressure (kgf/cm2 ): 1.0 (avg.)
7. Cleaning method: before the test— rinse with 38°C warm water, then wipe and dry
8. Solution pH: 6.8 (avg.)
9. Sample placement: vertical placement with an inclination of 15 degrees
10. Sample protection method: rubber seal on four sides
11. The sample is subject to 0T bending and 9.5 mm cupping before testingRusting grade rating ASTM D1654-92 Rusting grade Level 10 Acid and alkali resistance test Acid resistance test CNS 10757 (1995) 20% H2 SO4 , room temperature, 360 hours Immersion in acid solution without abnormality Alkali resistance test CNS 10757 (1995) 25% H2 SO4 , room temperature, 360 hours Immersion in acid solution without abnormality 1. The sample is subject to 0T bending and 9.5 mm cupping before testing Chemical resistance AAMA 2605-13 Nitric acid, after 30 minutes
Nitric acid, after 168 minutes
No significant change in color
No significant change in color
Physical property test Impact test CNS 10757 (1995) 160in.-lb No cracking, peeling, etc. Bending test ASTM D4145-83 (2002) 0T (no cracking, peeling, etc.) Cupping test CNS 10757 (1995) 10.49 mm Abrasion resistance (falling sand abrasion method) ASTM D968-05 (2010) Abrasion resistance (L/mil)(falling sand amount L) 127
191- Product Limitations
- Tedlar® adhesives are best used within two years from date of manufacture. See guidance on Adhesive Storage.
- 68070 has been observed to interact with some components in a flame-retardant vinyl causing yellowing.
- 68070/Epon™ 828 mixtures only have an 8-hour pot life. 68080 is incompatible with 68070.
- Ketone solvents should be avoided in diluting the adhesives as yellow discoloration will result.
Caution: DuPont does not warrant the “lamination.” The performance of the “system” is the sole responsibility of the applicator. DuPont will provide consultation and our best information in assisting the customer to achieve satisfactory lamination.
- Laminate Adhesive Selection Guide
Metals 68070/Epoxy Thermoplastics: Polycarbonate 68080 or 68070 ABS 68080 or 68070 PVC Film 68070/Epoxy, 68080 - Lamination Guidelines
Adhesives, thinned to a desired viscosity with toluene, can be applied to the film using a variety of coating methods. The coated film is normally passed through an oven where the solvent is evaporated to obtain a non-blocking adhesive coating. Thorough drying is essential as residual solvent may cause blocking in the roll. Drying temperatures of 77–104°C (170–220°F) coordinated with proper film web speed and tension are presently being used with success. Excessive machine direction (MD) film stretching and transverse direction (TD) film shrinkage can result from improperly controlled oven temperature and film web tension.
- Laminating DuPont™ Tedlar® PVF Film to Aluminum
Lamination is accomplished by cleaning the metal, depositing a controlled conversion coating on the metal, coating the metal with a solvent-based adhesive, evaporating the solvent, heating the metal to 195–205°C (383–401°F) to activate the adhesive, combining with Tedlar® PVF film in nip rolls and quenching the laminate.
Materials
Film – Tedlar® PVF film type TWH15BL3 and colors
Adhesive – DuPont™ 68070, Epon™ 828
Metal – AluminumAdhesive Mixing and Application
The adhesive is prepared by the following formula by weight:
Adhesive 68070 29 Epon™ 828 1 While stirring the 68070, slowly add Epon™ 828. Blend the mixture for approximately 5 minutes with a suitable mechanical mixer. Adjust adhesive coater to lay down 37–50 µm (1.5 to 2.0 mil) wet adhesive equivalent to 6–7.5 µm (0.23 to 0.30 mil) of dry adhesive. Adjust viscosity by diluting with toluene.
During normal operation, the rate of solvent evaporation is slight enough to have no effect on the percent solids. If prolonged halts in coating occur, the viscosity must be checked and adjusted with toluene to the original value. Pot life of the mixed adhesive is 8 hours.
The solvent is removed and adhesive activated in an oven of such length that the metal is in the oven from 30 to 90 seconds. The metal temperature must be 195–205°C (383–401°F) at the end of the oven followed by immediate lamination.
Lamination
The laminating equipment consists of a pair of combining or “nip” rolls that are unaffected by the operating temperature of 175°C (347°F). A nip pressure of 87–175 N/cm (50–100 lb/in) of width must be used. A film wrap of at least 90° on the upper nip roll must be used to prevent wrinkling.
- Laminating DuPont™ Tedlar® PVF Film to Galvanized Steel
Lamination is accomplished by cleaning the metal, depositing a controlled conversion coating on the metal, coating the metal with a solvent-based adhesive, evaporating the solvent, heating the metal to activate the adhesive, combining with Tedlar® PVF film in nip rolls and quenching the laminate.
Materials
Film – Tedlar® PVF film type TWH15BL3 and colors
Adhesive – DuPont™ 68070, Epon™ 828
Metal – Hot dipped galvanized steel, generally G-90, is used.The steel must have good forming quality and preferably minimum spangle, temper rolled, lock forming quality or extra smooth spangle. The metal must be free of white rust to enable proper surface treatment and adhesion. Prior to lamination the metal being used must have all mill oils removed.
The optimum thickness metal to be laminated is 18 gage (0.0516”).
Laminates on metal, 22 gage (0.0366”) or lighter, may be made on any standard type of galvanized, including commercial quality, regular spangle. Better forming quality is preferred.
Metals heavier than 22 (0.0366”) gage must be minimum spangle or spangle-free surface. Commercial quality, regular spangle steel is not acceptable in gages heavier than 22 gage (0.0366”). Care should be taken when laminating metal heavier than 22 gage (0.0366”) and formed to a radius of less than 3 mm (1/8”) to prevent splitting.
Adhesive Mixing and Application
The adhesive is prepared by the following formula by weight
Adhesive 68070 29 Adhesive Epon™ 828 1 While stirring the 68070, slowly add Epon™ 828. Blend the mixture for approximately 5 minutes with a suitable mechanical mixer. Adjust the coater to lay down 37–50 µm (1.5–2.0 mil) wet adhesive equivalent to 6–7.5 µm (0.23–0.30 mil) of dry adhesive.
During normal operation, the rate of solvent evaporation is slight enough to have no effect on the percent solids. If prolonged halts in coating occur, the viscosity must be checked and adjusted with toluene to the original value. The pot life of the mixed adhesive is 8 hours.
The solvent is removed and adhesive melted in an oven of such length that the metal is in the oven from 30 to 90 seconds. The metal temperature must be 195–205°C (383–401°F) at the end of the oven followed by immediate lamination.
Lamination
The lamination equipment consists of a pair of combining or “nip” rolls that are unaffected by the operating temperature of 175°C (347°F). A nip pressure of 10–20 kg/cm (50–100 lb/in) of width must be used. A film wrap of at least 90° on the upper nip roll must be used to prevent wrinkling.
- Laminating DuPont™ Tedlar® PVF Film to PVC for Outdoor Applications
Since there are many formulations of PVC, optimum laminating conditions may vary with the PVC formulation. The following is given as a suggested starting point for lamination studies and has given good results with a number of PVC films.
Materials
For opaque laminates, pigmented Tedlar® PVF film, such as TWH15BL3 white film, can be used. Under the pigmented films, a higher proportion of epoxy can be used, and a 68070/ Epon™ 828 ratio of 18/1 by volume (14/1 by weight) can be used.
Adhesive Application
Apply 7.5–12.7 µm (0.3 to 0.5 mil) (measured on dry resin) of adhesive to the DuPont™ Tedlar® PVF film or PVC. Dry the adhesive at 66–71°C (150–160°F), film temperature. After drying, the adhesive will appear practically dry to touch and only slightly tacky. If the PVC is coated, note that the adhesive solvent contains toluene, which attacks vinyl, but under the above conditions it will probably be flashed off so fast that this will not cause trouble. Note also that ketones should not be used for dilution as they can cause yellowing of the 68070 adhesive.
Lamination
Combine the Tedlar® PVF film and PVC in a nip roll, with a glue line temperature of at least 79°C (175°F) but preferably not over 121°C (250°F). Some people have accomplished such laminations with roll temperatures of about 121°C (250°F).
- Laminating DuPont™ Tedlar® PVF Film to Thermoplastic Sheet
Materials
Film – Any Tedlar® PVF film
Adhesive – DuPont™ 68070 or 68080
Plastic – Polystyrene, Polymethacrylate, Polycarbonate, Acrylonitrilebutadiene-styrene (ABS)Adhesive Application
Adhesive % Solids ft2 /mil/gal Recommended Thickness 68070 34 460 6–7.5 dry µm
(0.2–0.3 dry mil)Apply the adhesive, thinned with toluene to a desired viscosity, to the film using adhesive coating equipment. Pass the coated film through an oven evaporating the solvent obtaining a non-blocking adhesive coating.
Thorough drying is essential as residual solvent may cause blocking in the roll. Drying temperatures of 77–104°C (170–220°F) coordinated with proper film web speed and tension are presently being used with success. Excessive MD film stretching and TD film shrinkage can result from improperly controlled oven temperature and film web tension.
Lamination
Laminating adhesive-coated Tedlar® PVF film to thermoplastic sheet is easily accomplished at the extruder. The operation consists of combining the film with the hot sheet at the first nip of the take-off stack. Stack temperatures of 149°C (300°F) or higher are necessary to heat activate the adhesive and adequately bond the film. The unwind roll of Tedlar® PVF film should be positioned so that the film wraps the top roll 30° or more and tension across the sheet is uniform. Press Operations: 1-1/2 minutes, minimum lamination temperatures: 135–149°C (275–300°F), 100–150 psi; cool to 38°C (100°F) before removing from press.
Safety & Health
- Safety Precautions
Tedlar® 68070 is FLAMMABLE AND CONTAIN HARMFUL VAPORS. Store containers away from heat, sparks, and open flames. Keep containers closed when not in use.
Storage & Handling
- Shelf Life
- 2 years
- Adhesive Storage
Tedlar® adhesives are best used within two years from date of manufacture. Best used dates are guidelines to insure the material maintains its viscosity and appearance. In the event material has exceeded two years from date of manufacture, it may be assessed for use in the following manner:
- Insure the material is at room temperature
- Insure the material is mixed (10 – 15 minutes gentle agitation on drum roller is suitable)
- Collect a small sample of adhesive in a clear vessel to inspect visually for presence of non-soluble gel particles (do not use adhesive if non-soluble gel particles are visible)
- Adhesive may be adjusted to the desired viscosity by thinning with toluene
Protect the adhesives from temperature and humidity extremes. If adhesives are exposed to temperatures below 4°C (40°F), they must be brought to room temperature, 22°C (70°F), and thoroughly mixed as separate units. Additional mixing is required when blending the compounds.





