Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Name
- Pharma & Nutraceuticals Functions
- CAS No.
- 9012-36-6
- EC No.
- 232-731-8
- Technologies
Features & Benefits
- Benefit Claims
- Features
- Lower gel strength than standard agaroses. Even so, gels can be handled easily.
- Higher clarity (gel transparency) than gels of standard agaroses.
- Greater sieving capacity.
- LM Agaroses are classified in three categories, depending on the degree of derivatization. Gelling/melting temperatures and gel strength are the most important differences
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- LM (LOW MELT): with the highest gelling/melting temperatures and gel strength.
- Electrophoresis of DNA fragments ≥1000 bp.
- Tissue and cell culture.
- Viral plaque assays.
Properties
- Typical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Ash Content | max. 0.4 | % | — |
| Clarity (at 1.5%) | max. 4 | NTU | — |
| DNA resolution (≥ 1000 bp) | Finely resolved | — | — |
| End-Expiratory Occlusion | max. 0.12 | — | — |
| Gel Background | Very low | — | — |
| Gel Strength (at 1.5%) | min. 500 | g/cm2 | — |
| Gelling Temperature (at 1.5%) | 24-28 | °C | — |
| Melting Temperature (at 1.5%) | max. 65.5 | °C | — |
| Moisture Content | max. 10 | % | — |
| Sulfate Content | max. 0.12 | % | — |
Technical Details & Test Data
- Ranges Of Separation For LM AND LM GQT AGAROSE
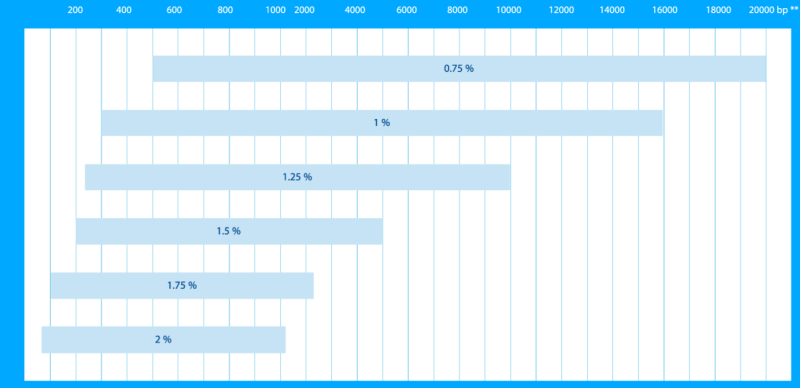
Range of separation depends upon the choice of buffer. The ranges were determined in presence of TAE buffer. Migration in the TBE buffer is slower; therefore lower concentrations can be used to obtain similar separation ranges.