Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Name
- Pharma & Nutraceuticals Functions
- CAS No.
- 9012-36-6
- EC No.
- 232-731-8
- Technologies
Features & Benefits
- Benefit Claims
- Benefits
Gels made with MS-12 have higher gel strength than competitive products. The gel is exceptionally firm but still flexible when handled, minimizing the danger of cracking or breaking.
MS-12 has the same melting and gelling temperature as regular agaroses, allowing faster and easier preparation of gels. MS-12 also gives excellent resolution at concentrations of ≤1 %.
MS-12 Agarose is recommended for all analytical applications, especially when DNA is recovered for subsequent use in enzymatic procedures.
Applications & Uses
- Markets
Properties
- Typical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Ash Content | max. 0.35 | % | — |
| Clarity (at 1.5%) | max. 5 | NTU | — |
| End-Expiratory Occlusion | max. 0.12 | — | — |
| Gel Strength (at 1.5%) | min. 2000 | g/cm2 | — |
| Gelling Temperature (at 4%) | max. 40 | °C | — |
| Melting Temperature (at 4%) | max. 93 | °C | — |
| Moisture Content | max. 10 | % | — |
| Sulfate Content | max. 0.11 | % | — |
Technical Details & Test Data
- Test Data
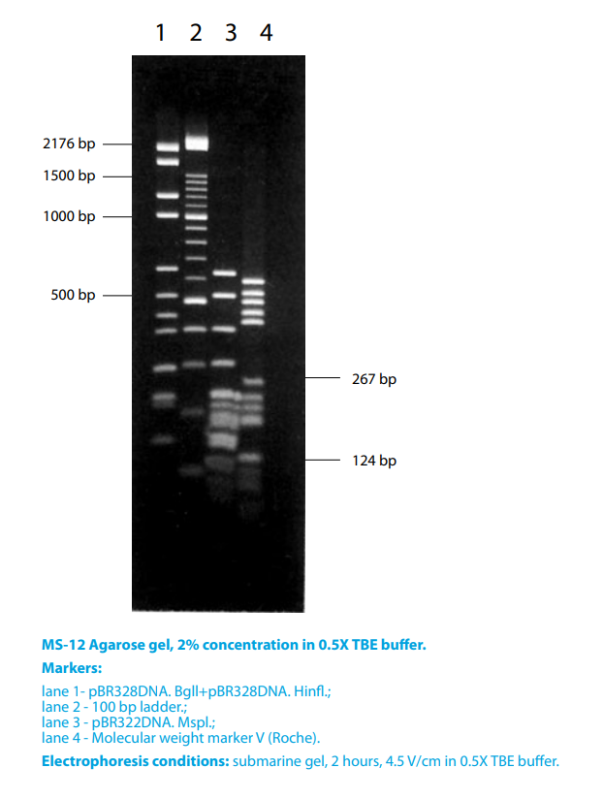
- Functional Tests
- DNA resolution: bands appear sharp and finely resolved.
- DNAse/RNAse activity: none detected.
- Gel background: very low after EtBr staining.
- Blotting: very good transference for DNA fragments 154 – 2176 bp in 4 % gels.
- DNA binding: very low.
- Ranges Of Separation For MOLECULAR SCREEN AGAROSES
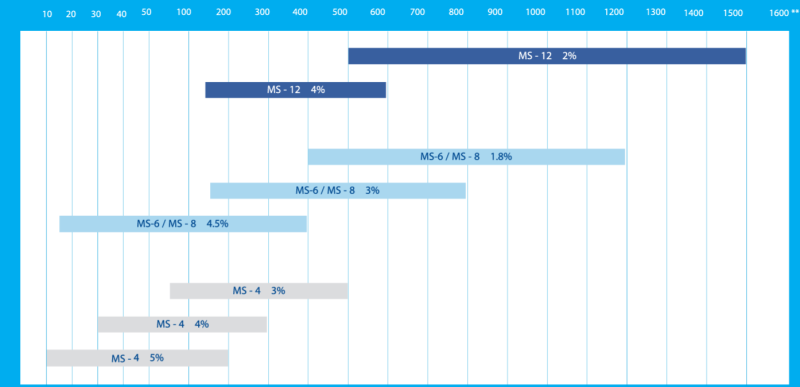
Range of separation depends upon the choice of buffer. The ranges were determined in presence of TAE buffer. Migration in the TBE buffer is slower; therefore lower concentrations can be used to obtain similar separation ranges.