Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Name
- Pharma & Nutraceuticals Functions
- CAS No.
- 9012-36-6
- EC No.
- 232-731-8
- Technologies
Features & Benefits
- Benefit Claims
- MS-4 type of agarose is unique to Hispanagar
At 3 % concentration, MS-4 Agarose gives a resolution of DNA fragments similar to gels made with polyacrylamide at concentrations of 8 %. While MS-4 may be dissolved carefully by microwaving, gels are best prepared by autoclaving.
- Features
- Excellent resolution of DNA fragments lower than 500 bp, especially smaller primer–sized fragments.
- Forms a very clear, transparent gel, even at concentrations of 5% or higher.
- Efficient mechanical handling at all concentrations.
- The chances of gels breaking or cracking when handled are greatly minimized.
Applications & Uses
- Markets
Properties
- Typical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Ash Content | max. 0.3 | % | — |
| Clarity (at 3%) | max. 6 | NTU | — |
| End-Expiratory Occlusion | max. 0.12 | — | — |
| Gel Strength (at 3%) | min. 500 | g/cm2 | — |
| Gelling Temperature (at 3%) | max. 31 | °C | — |
| Melting Temperature (at 3%) | max. 76 | °C | — |
| Moisture Content | max. 10 | % | — |
| Sulfate Content | max. 0.11 | % | — |
Technical Details & Test Data
- Test Data
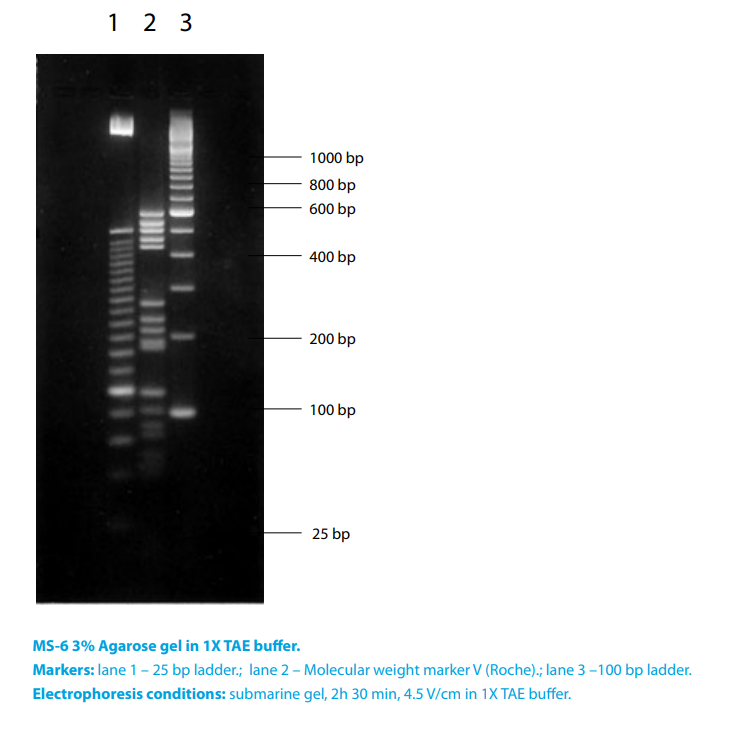
- Ranges Of Separation For MOLECULAR SCREEN AGAROSES
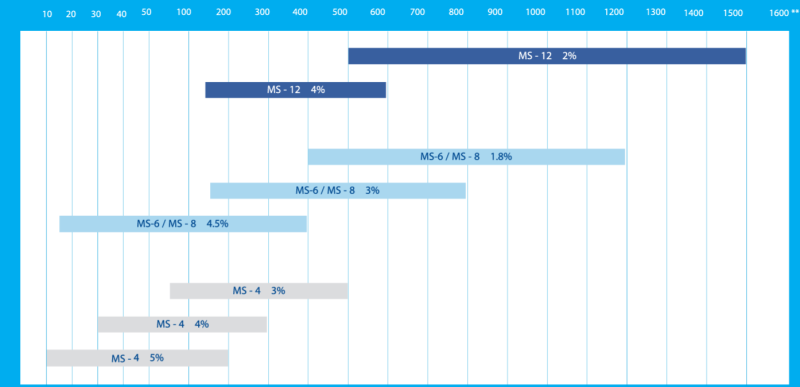
Range of separation depends upon the choice of buffer. The ranges were determined in presence of TAE buffer. Migration in the TBE buffer is slower; therefore lower concentrations can be used to obtain similar separation ranges.