Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Name
- Ingredient Name
- Ingredient Origin
- CASE Ingredients Functions
- Industrial Additives Functions
- CAS No.
- 9005-38-3
- Ingredients
- Alginates
- Food Additive Number
- E 401, INS 401
- EC No.
- 618-415-6
- Technologies
Features & Benefits
- Labeling Claims
Applications & Uses
- Applications
Properties
- Odor
- Neutral
- Flavor
- Neutral
- Appearance
- Creamy-White to Yellowish, Powder
- Physico-Chemical Properties
- Microbiological Values
- Heavy Metals
- Note
*1 % solution, Brookfield Viscosimeter at 20 °C and 60 rpm
**monitoring
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Brookfield viscosity* | 350 - 550 | mPa.s | — |
| pH Value (1 % Solution) | 5.5 - 8.0 | — | — |
| Loss on Drying | max. 15 | % | — |
| Particle Size (Greater than 200 μm) | max. 5 | % | — |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| E. Coli** | Absent | Per 5 gram | — |
| Salmonella** | Absent | Per 10 gram | — |
| Total Plate Count** | max. 5 x 103 | cfu/g | — |
| Yeasts and moulds** | max. 5 x 102 | cfu/g | — |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Arsenic Content** | max. 3 | mg/kg | — |
| Cadmium Content ** | max. 1 | mg/kg | — |
| Lead Content** | max. 5 | mg/kg | — |
| Mercury Content** | max. 1 | mg/kg | — |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
Technical Details & Test Data
- JRS Hydrocolloids – Natural Barrier Alginate Gels
Natural Barrier Alginate Gels
All JRS alginate products are based on extraction of sustainable brown seaweed, mainly grown off the Breton coast.
In the JRS portfolio, three types of alginates are available. Pure alginic acid, which is water insoluble but hygroscopic. Second, water soluble sodium or potassium alginates, which are derived from alginic acid and the respective bases. Lastly, calcium alginates, again water insoluble but of hygroscopic nature.
The focus here is on sodium alginates as their aqueous solutions give rise to various applications.
JRS Alginates Core Benefits
Sodium alginates are mainly used in dosages between 0.7 and 4 % (w/w) to obtain aqueous solutions of different viscosity. An effective and controlled gelation is achieved through ion exchange reactions, where Na+ -ions are replaced by Ca (2+) -ions or other di- and higher valent ions. The gelation occurs very fast and produces thermal resistant gels stable between pH 4 and 8 (Pic.1).
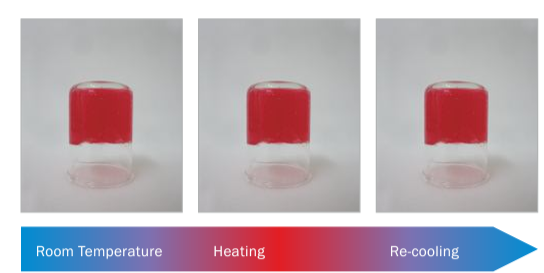
Pic. 1: Temperature resistant alginate gels.
Sodium alginates are also highly versatile film forming agents. Uniform coatings can be created with Naalginate solutions, to which higher valent ions are added, for example via spraying aqueous CaCl2 - solution onto the film. The obtained Ca-alginate films need to be dried carefully to yield transparent and thermostable foils. Plasticizers like glycerin or sorbitol must be added for introducing flexibility to the films.
Moreover, alginate films demonstrate optimal oil barrier properties.
JRS used a KIT Test based on TAPPI T559 with alginate films between 100 μm and 200 μm. None of the tested films showed any permeability towards oil, Toluene or n- Heptane. Furthermore, JRS alginate films showed good oxygen barrier properties, making the sprayable products promising candidates for natural barrier coatings.
Additionally, JRS sodium alginates are suited as thickener in water based paint and adhesive formulations.
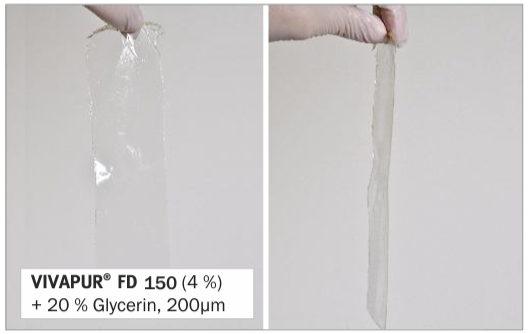
Pic. 1: Transparent and flexible alginate films with glycerin.
Storage & Handling
- Shelf Life
- 12 Months
- Storage
- Store in cool and dry conditions. Temperature max. 25 °C with a relative humidity < 60 %. In original and unopened bags, best before at least 12 months starting with production date.