Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Plastics & Elastomers Functions
- Technologies
Features & Benefits
- Materials Features
- Features
PELESTAT 230 has the following features:
- Imparts excellent antistatic and antifouling properties to polyolefin when the amount added is between 5 and 20 wt %.
- Imparts a permanent antistatic property to PE and PP for films and sheets while causing practically no lowering of the physical properties of the resins themselves.
- Exhibits a permanent antistatic property immediately after molding. The antistatic property in the resulting plastic minimally changes even after washing with water because it is a high-molecularweight antistatic agent. In addition, it works even in low humidity due to its low dependency on humidity.
- This product dry-blended with polyolefin can be directly molded into the final product without a kneading process because this product exhibits excellent dispersibility in polyolefin, particularly PE.
Applications & Uses
- Applications
- Compatible Polymers & Resins
- Plastics & Elastomers End Uses
- Plastics & Elastomers Processing Methods
- Application Methods
1. General Procedure
As shown in Figure 1, polyolefin and PELESTAT 230 are dry-blended using a blender.
This blend is then molded into the final product using an appropriate molder (e.g. injection
molding machine). Fillers and dispersants can be added during the dry-blending if necessary.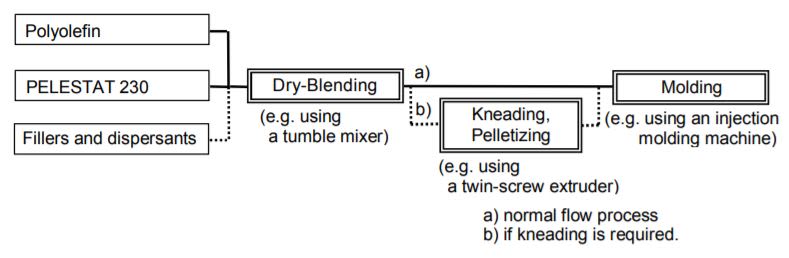
Figure 1. General Procedure for Application of PELESTAT 230
2. Amount to be Used
The standard amount of PELESTAT 230 is between 5 and 20 wt %.
Determine the optimal amount by referring to the results of its performance tests.3. Kneading Conditions
Use a high share rate kneader (e.g. twin-screw extruder) if the kneading process is
required. The standard kneading temperature is between 180°C and 230°C (356°F – 446°F). Determine the kneading temperature according to the resin applied.4. Drying of PELESTAT 230
- This product can be immediately used after the factory sealed package is opened because this product is packed under moisture-proof conditions.
- Drying is necessary when the factory sealed package is kept unsealed for several hours because this product has some hygroscopic properties.
The following are examples of the conditions for drying.
We recommend that you should use a hopper dryer or dehumidifying dryer during the molding process. (because there is a possibility that fisheyes, blisters and silver streaking will occur on molded products of PELESTAT 230 and resins if the water content of the mixture exceeds 500 ppm).Drying under reduced pressure Vacuum Below 1300 Pa (0.2 psi) Temperature 70°C – 80°C (158°F – 176°F) Duration 2 – 4 hours Hot-air drying Duration 4 – 6 hours Temperature 85°C – 95°C (185°F – 203°F) 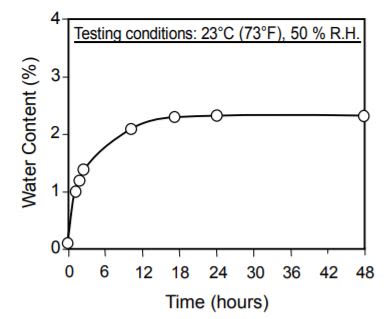
Time (hours)
Figure 2. Hygroscopic Properties of PELESTAT 230
Precaution Against Mishandling
- In the case of using resins at molding temperatures below 170°C (338°F), PELESTAT 230 may not fuse, possibly resulting in poor effectiveness. Furthermore, in case of using resins at molding temperatures above 240°C (464°F), this product may thermally decompose, possibly resulting in poor effectiveness.
The recommended molding temperature is between 170°C and 230°C (338°F – 446°F).
- Depending on the kind of resin, this product may have an influence on the resin's physical properties including mechanical properties. Test their influence on each other’s physical properties beforehand to ensure that there are no problems.
- Examples of Applications
PELESTAT 230 has been used as a permanent antistatic agent in polyolefin in the following
applications:- Blown films, sheets, trays, etc. for electric and electronic parts.
- House hold electrical goods, office equipment, etc.
- Floor materials, protector films, base materials for tapes, etc.
Properties
- Appearance
- Pale yellow pellet
- Typical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Melting Point | approx. 163 (325) | °C(°F) | — |
| Surface resistivity | approx. 5 × 10^7 | Ω | ASTM D 257 |
| Thermal Degradation Temperature | approx. 250 (482) | °C(°F) | — |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Patent Registered
US 6,552,131
Technical Details & Test Data
- Performance Tests
The examples on pages 4 to 8 are the results of performance tests using polyolefin mixed with PELESTAT 230. This product imparts a permanent antistatic property to polyolefin that cannot be attained by any other conventional blend-type, low-molecular-weight antistatic agent. Furthermore, this product minimally affects the physical properties of polyolefin because this product is highly compatible with it.
1. Application to low-density Polyethylene (LDPE)
A. Relationship Between Amount of PELESTAT 230 and Resulting Surface Resistivity
LDPE containing PELESTAT 230 is highly antistatic when the amount of this product added is between 5 and 20 wt %. Refer to Figure 3 and determine the optimal amount according to the desired surface resistivity.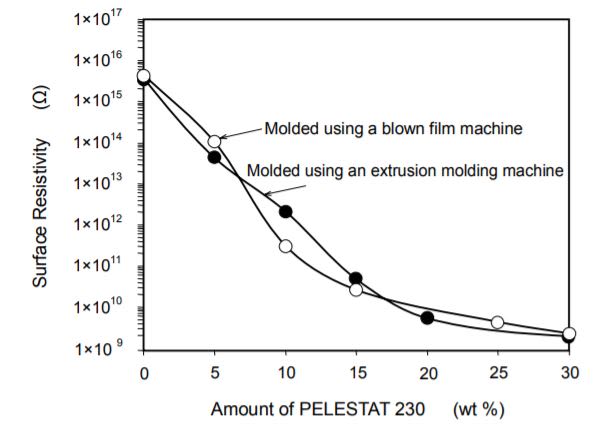
Amount of PELESTAT 230 (wt %)
Figure 3. Relationship Between Amount of PELESTAT 230 and Surface Resistivity
Materials and Methods:
Materials:
Blown film machine
A predetermined amount of PELESTAT 230 was dry-blended with the LDPE and the mixture was molded using a blown film machine [die temperature: approx. 180°C (356°F)] into films 50 μm (approx. 2.0 mils) in thickness.Extrusion molding machine
A predetermined amount of PELESTAT 230 was dry-blended with the LDPE and the mixture was molded using an extrusion molding machine [die temperature: approx. 200°C (392°F)] into sheets 100 μm (approx. 3.9 mils) in thickness.Method:
Each sample was kept at 23°C(73°F), 50 % R.H. for 24 hours. Then, the surface resistivity of each was measured using a megohmmeter according to ASTM D 257.B. Effect on Surface Resistivity When Washed with Water (Evaluation of Durability of Antistatic Effect) The surface resistivity of the LDPE blended with PELESTAT 230 minimally changes, remaining antistatic even when washed with water. This product imparts a permanent antistatic property that cannot be attained by any other conventional blend-type, low-molecular-weight antistatic agent, which loses its antistatic property after being washed with water approximately three times.
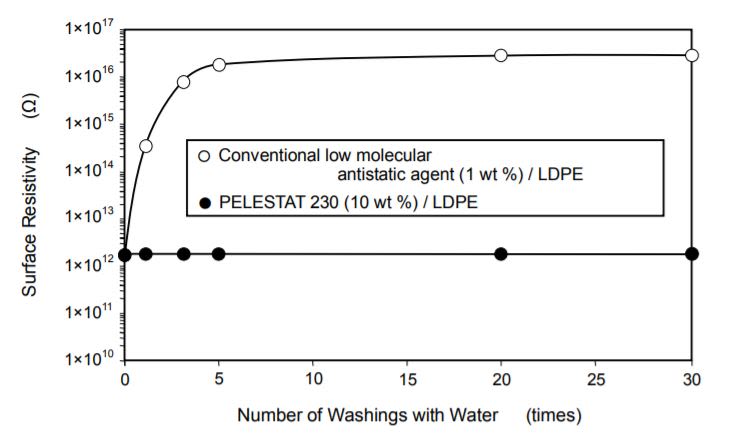
Number of Washings with Water (times)
Figure 4.Effect on Surface Resistivity When Washed with Water
Materials and Methods:
Materials:- PELESTAT 230 (10 wt %) / LDPE
- PELESTAT 230 (10 wt %) was dry-blended with the LDPE, and the mixture was then molded using an extruder [die temperature: approx. 200°C (392°F)] into sheets 100 μm (approx. 3.9 mils) in thickness.
- Conventional low-molecular-weight anionic antistatic agent (1 wt %) / LDPE A conventional blend-type, low-molecular-weight antistatic agent, a Sanyo Chemical product, was applied. It was dry-blended with the LDPE, and the mixture was kneaded using a twinscrew extruder at approx. 220°C (428°F). These samples were prepared by using the molding method described above.
Method:
Each sample was submerged in water and its surface was rubbed with a cotton cloth. The samples were dried under reduced pressure [133 Pa (0.02 psi)] at 70°C (158°F) for 2 hours and were kept at 23°C (73°F), 50 % R.H. for 24 hours.The surface resistivity was measured using a megohmmeter according to ASTM D 257. This process was repeated according to the number of washings with water as described in Figure 4.C. Effect of Humidity on Surface Resistivity
The surface resistivity of the LDPE blended with PELESTAT 230 minimally changes even in low humidity due to this product’s low dependency on humidity. Conversely, an LDPE blended with any other conventional low-molecular-weight antistatic agent loses its antistatic property in low humidity.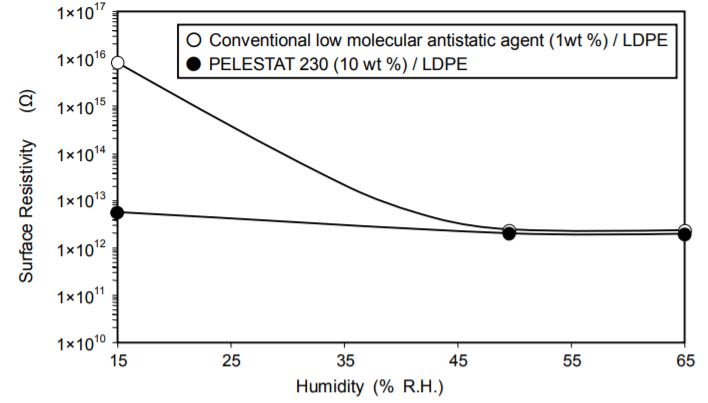
Figure 5. Effect of Humidity on Surface Resistivity
Materials and Methods:
Materials: See Figure 4.
Method:
Each sample was kept at 23°C (73°F) at a predetermined humidity for 24 hours. Then, the surface resistivity of each was measured using a megohmmeter according to ASTM D 257.D. Effect on Resin Physical Properties
As shown in Table 1, PELESTAT 230 minimally affects the LDPE physical properties.Property Method PELESTAT 230
10 wt %) / LDPELDPE Surface resistivity Ω ASTM D 257 3 × 10^11 > 10^16 Melt flow rate
10 min, 190°C, 21.18 N ) gASTM D 1238 3 2 Tensile strength MPa (psi) ASTM D 638 22 (3190) 20 (2900) Fracture elongation % ASTM D 638 600 580 Haze % JIS K 7105 35 34 Total light transmittance % JIS K 7105 86 86 Materials and Methods:
Materials:
Surface resistivity
PELESTAT 230 (10 wt %) was dry-blended with the LDPE and the mixture was molded using an extruder [die temperature: approx. 200°C (392°F)] into sheets 100 μm (approx. 3.9 mils) in thickness. LDPE was also molded under the same conditions.Melt flow rate
The above molded materials were cut into pellets, and used as samples.
Other mechanical properties Samples were prepared under the same conditions except that the predetermined size described in ASTM D 638 was applied to measure the tensile strength and fracture elongation.
Methods:
See the methods described in Table 1.
(The testing method for surface resistivity is described in Figure 3.)E. Dispersibility of PELESTAT 230 in LDPE
As shown in Figure 6, PELESTAT 230 is finely dispersed in the LDPE.
Figure 6. Transmission Electron Micrograph of Molding (TEM photo)
Composed of PELESTAT 230 (10 wt %) and LDPE[Explanation of Photograph]
Black stripes: PELESTAT 230 Figure 6 is a magnification (approx. 10,000 times) of a section of the PELESTAT 230 (10 wt %) / LDPE mixture described in Figure 4.2. Application to PP
A. Effect on Resin Physical Properties As shown in Table 2, PELESTAT 230 imparts a permanent antistatic property to the PP. The compatibility of this product with this resin is excellent, and the physical properties of this resin show minimal change.Property Method
ASTM No.PELESTAT 230
(10 wt %) / PPPP Surface resistivity Ω D257 5 × 10^11 > 10^16 Tensile strength MPa (psi) D638 55 (7975) 55 (7975) Fracture elongation % D638 700 700 Materials and Methods:
Materials:
PELESTAT 230 (10 wt %) / PP
Surface resistivity: Two kinds of materials were extruded [die temperature: approx. 220°C (428°F) according to the multi-layer T-die technique and molded into a
sheet, having three layers (layer ratio =1:8:1), 100 μm (approx. 3.9 mils) in
thickness. A mixture of PELESTAT 230 (10 wt %) and the PP was in the
surface layers, and PP by itself was in the core layer.
Others: Samples were prepared by the same method described above except that
the predetermined size described in ASTM was applied.PP: Samples were prepared under the same conditions described above except that PP was only used.
Methods:
See the ASTM No. described in Table 1.
(The testing method for surface resistivity is described in Figure 3.)
Safety & Health
- Hazards Description
PELESTAT 230 is a polyether-polyolefin block copolymer.
This product is insoluble in water. This product has no flash point (by COC) below 230°C (446°F). UN dangerous goods regulations are not applied to this product.
Vapor or fume from molten material causes eye and nose irritation.
Based on data from a similar product by Sanyo Chemical, this product may have low acute oral toxicity and may have no acute dermal irritation.
Acute oral toxicity (rat): LD50> 2,000 mg/kg (similar product)
Acute dermal irritation (rabbit): Non-irritant (similar product) This product is for industrial use only.