Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Chemical Name
- Base Chemicals Functions
- CASE Ingredients Functions
- Fluids & Lubricants Functions
- CAS No.
- 25354-97-6
- EC No.
- 246-885-9
Features & Benefits
- Fluids & Lubricants Features
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Compatible Substrates & Surfaces
- Fluids & Lubricants Type
- Base Chemicals End Uses
- Fluids & Lubricants End Use
- Recommended Uses & Known Applications
ISOCARB acids are used as raw materials and intermediates in many specialized applications:
- Esters
- Betaines
- Ethoxylates
- Amides
Metalworking and lubrication:
- ISOCARB acids can be used as a corrosion inhibitor when formulating lubricating oils and greases in industrial and automotive applications.
- ISOCARB acids can be used, neutralized, as ingredient of soluble and synthetic metal-working fluids or in water-based degreasers due to their very good anticorrosion properties.
Healthcare and Pharma:
- ISOCARB acids can be used as building blocks for synthesis of functional cationic lipid components to be incorporated in lipid nano particles
- Intermediates
Inks, Paints & Coatings
Cosmetic Agents
Properties
- Physical Form
- Odor
- Odorless
- Insoluble in
- Water
- Thermal Properties
- Typical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Refractive Index (nD20) | approx. 1.4471 | — | DIN 51423 |
| Molecular weight | approx. 256 | g/mol | 600-19 |
| 2-Hexyldecansaure | min. 96.0 | wt% | 1050F-33 |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Ester Number | max. 1 | mg KOH/g | 600-33 |
| Water Content | max. 0.1 | wt. % | DIN 51777 |
| Color | max. 40 | — | EN ISO 6271-2 |
| Acid Number | 212 – 222 | mg KOH/g | 600-31 |
| Density (20°C) | 0.874 - 0.880 | g/ml | DIN 51757 |
| Melting Point | 16 - 18 | °C | 600-27 |
| Flash Point | 170 | °C | DIN 51758 |
| Viscosity (20°C) | approx. 62 | mPas | 600-25 |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Chemical Inventories
Technical Details & Test Data
- Viscosity And Density
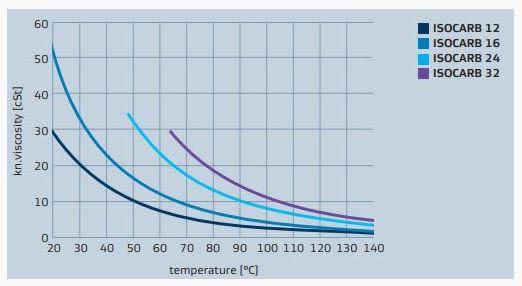
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s ability to resist flow under gravity. The kinematic viscosity of a fluid is defined as the ratio of absolute or dynamic viscosity to its density. The viscosity of a fluid is highly temperature dependant. For a liquid the kinematic viscosity will decrease with higher temperature, for a gas the kinematic viscosity will increase with higher temperature.
ISOCARB acid viscosity vs temperature
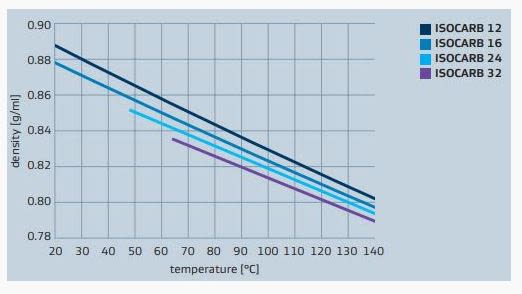
Density is a measure of how much mass is contained in a given unit volume. The formal definition of density is mass per unit volume. Usually the density is expressed in grams per ml. In general, density can be changed by changing either the pressure or the temperature. Increasing the pressure will always increase the density of a material. Increasing the temperature generally decreases the density, but there are notable exceptions to this generalization.
ISOCARB acid density vs temperature
Storage & Handling
- Storage And Handling
Safe handling advice
- Take measures to prevent the build up of electrostatic charge.
Storage/Transport pressure
- Ambient
Load/Unload temperature
- 74-94 °F