Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Name
- Product Type
- Agrochemical Functions
- Cleaning Ingredients Functions
- Industrial Additives Functions
- CAS No.
- 577-11-7
- EC No.
- 209-406-4
- Product Families
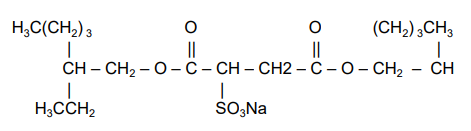
- Chemical Structure
Features & Benefits
- Biodegradability
STEPWET DOS 70 is biodegradable.
Applications & Uses
- Applications
- Applicable Processes
- Home Care Applications
- I&I Cleaning Applications
- Industrial Additives End Use
- Applications
STEPWET DOS 70 is a very good wetting agent for aqueous systems (even at low concentrations) and for mineral dispersions. STEPWET DOS 70 can be a useful emulsifier agent for oil in water emulsions. It is used in Emulsion Polymerisation and textile industry.
Properties
- Formulation Type
- Physical Form
- Appearance
- Clear liquid
- Typical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Density (at 25 °C) | 1.05 | g/ml | — |
| Moisture Content | 21.9 | % | — |
| Ethanol Content | 8 | % | — |
| Actives Content (MW 444) | 70 | % | — |
| Flash Point | 27 | °C | — |
| pH (in 5% aqueous) | 6 | — | — |
| Viscosity (at 20°C) | 200 | m.pq.s | — |
| Sodium Sulfate Content | max. 1.5 | % | — |
| Sodium Sulfate Content | max. 0.5 | % | — |
| Pour Point | max. 0 | °C | — |
| Regulated Volatile Organic Chemicals (Ethanol) | 8 | % | U.S. EPA |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Chemical Inventories
- Clearances
- All components of STEPWET DOS 70 are listed in the following countries; the registration numbers for the active ingredients are included in parentheses: Australia (AICS 577-11-7), Canada (DSL 577-11-7), China (IECSC 577-11-7), Europe (EINECS 209-406-4), Japan (ENCS 2-1623), Korea (ECL Serial No. KE-32402), New Zealand (NZIoC 577-11-7), Philippines (PICCS 577-11-7), and United States (TSCA 577-11-7). It is the responsibility of the formulator to review the chemical control regulations for each country where the end product is intended to be sold or used.
- STEPWET DOS 70 is listed on the French positive list for food contact (Ministerial order from September 25th, 1985).
- STEPWET DOS 70 is not derived from animal sources.
- STEPWET DOS 70 does not contain and is not derived from Genetically Modified Compounds.
Safety & Health
- Health Effects
STEPWET DOS 70 is slightly toxic orally (LD50 > 2000 mg/kg on rats).
Packaging & Availability
- Packaging Type
- Standard Packaging
STEPWET DOS 70 is available in drums (440 lb, 200 kg), tote (2200 lb, 1000 kg), and in bulk quantities.
Storage & Handling
- Storage & Handling
Normal safety precautions (i.e., gloves and safety goggles) should be employed when handing STEPWET DOS 70. Contact with eyes, nose or prolonged contact with skin should be avoided. Wash thoroughly after handling STEPWET DOS 70. It is recommended that STEPWET DOS 70 be stored in sealed containers kept in a well ventilated area away from sparks, fire and open flame. Avoid overheating or freezing. Equipment should be grounded when transferring or using material. Drums should be vented during heating to avoid excessive pressure build up.
Non-Bulk Storage Recommendations
STEPWET DOS 70 should be stored in closed containers and kept in a cool, dry place away from incompatible materials (see Section 10 of the SDS). If material is frozen it should be heated gently and stirred to ensure it is homogeneous before use. Product temperatures over 104°F (40°C) are not recommended.
Bulk Storage Recommendations
STEPWET DOS 70 should be stored in vessels of 316 stainless steel or glass fiber-reinforced polyester tanks. Many oven cured phenolic and epoxy/phenolic limings may also be used. Elevated storage temperature may be desirable to maintain ease of pumping. Temperatures up to 104°F (40°C) can be maintained for long periods of time without degradation of the product.
- Workplace Exposure
Occupational exposure can occur primarily through skin contact or via inhalation of vapors and mists. Engineering controls, personal protective equipment, and other workplace practices should be used to control these exposures.