Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Chemical Name
- CAS No.
- 7440-02-0
- EC No.
- 231-111-4
- Technologies
- Contains
Pure Metals only: High purity ultra low carbon and sulfur.
- Identification
Temper
- Soft annealed
- Quarter hard
- Full hard
Surface
- Mill finish
- Mirror finish
- Brush finish
Features & Benefits
- Labeling Claims
- Base Chemicals Features
- Features & Benefits Of HPN™
- High-purity nickel, non-passivating.
- HPN™ anodes show a uniform dissolution behavior with a low tendency to pitting.
- HPN™ anodes dissolve completely without sludge formation.
- Due to the extremely high level of purity, no foreign elements can enter the anode material - Nickel bonds in abrasive layers with hard metal or diamond particles for grinding and entered the electrolysis process.
- Increased bath service life with economic and ecological advantages.
- HPN™ electrolytic layers are characterized by excellent properties (e.g. high ductility) and lower internal layer stresses. In selected electroplating applications (e.g embedding abrasive particles, electroforming, etc.) of significant benefit. - A particularly good and adhesive binding of abrasive grains or hard material particles can be achieved.
- Hpulcas GmbH supplies high-purity HPN™ nickel anodes in various customer-specific forms (sheet metal blanks, circular blanks, rods, wire grain or pellets).
- Sheet metal anodes up to a format of 600 mm x 2,000 mm with a maximum thickness of 10 mm, also as cuts and small batch sizes are available.
- Pure Nickel For The High-strength Integration Of Hard Materials
- Anodes made of conventional pure nickel tend to passivate during electrolytic dissolution.
- In order to improve the dissolution behavior of these anodes, either additives for depassivation (e.g. chlorides) must be added to the bath or sulfur must be added to the anodes for depolarization. Both have disadvantages. Chloride additives have an embrittling effect on the deposited nickel layers and are also relevant to work and environmental protection.
- When using sulfur-field-depolarized nickel, there is a risk of sulfur accumulation in the electrolyte. It is generally assumed that when the anode is dissolved, insoluble NiS compounds are formed and precipitated as anode slime. However, particularly if the bath is left standing for a long time, it cannot be ruled out that dissolved sulfur will be carried over to the cathode and embedded in the deposited nickel layer. Here, too, embrittlement of the layer is the result.
- Particularly at elevated operating temperatures, segregation of the sulfur along the grain boundaries can lead to a further loss of ductility in the nickel layer. In addition, the formation of sludge, even when using anode bags, generally shortens the service life of the bath and leads to nickel losses. Because the nickel bound in the sludge is no longer available for the deposition process at the cathode.
- With High Purity Nickel HPN™, hpulcas GmbH has developed a special pure nickel which on the one hand does not passivate and on the other hand reduces the entry of impurities into the electrolysis process to a minimum.
- The High Purity Nickel HPNTM has a purity of Ni 99.995%.
- This nickel is characterized by an extremely low sulfur content, which is between 0.1 and 0.5 ppm depending on the batch.
- Features & Advantages
- Highest purity of ≥ 99.98%. hpulcas™ determines the degree of purity of its input material by standard using GDMS (glow discharge mass spectroscopy) and the gas and carbon content additionally using IGA (instrumental gas analysis). A total of 78 elements are determined, with measurement limits being treated as impurity levels. The only trace elements whose content exceeds 1 ppm are oxygen, nitrogen, carbon and iron. You can find more information about our purity standards here. [Link to State of Purity whitepaper via request form]
- Due to the exceptionally high level of purity, HPN™ films exhibit consistent and reproducible physical properties
- The mechanical properties can be adjusted within wide limits during processing. Due to the high level of purity, very low hardness values of ≥ 65 HV can be achieved in the annealed condition.
- HPN™ foils can already be recrystallization annealed at low temperatures of ≥ 350 °C.
- HPN™ foils are highly corrosion resistant to sea water, non-oxidizing acids, alkalis and many organic substances.
- HPN™ foils are gas-tight up to small thicknesses.
Applications & Uses
- Applications
- Base Chemicals End Uses
- Manufacturing Process
- "Cathode plates" - from the nickel - electrolysis
- Hot rolling of plate
- Cold rolling of strip
- Welding and coiling
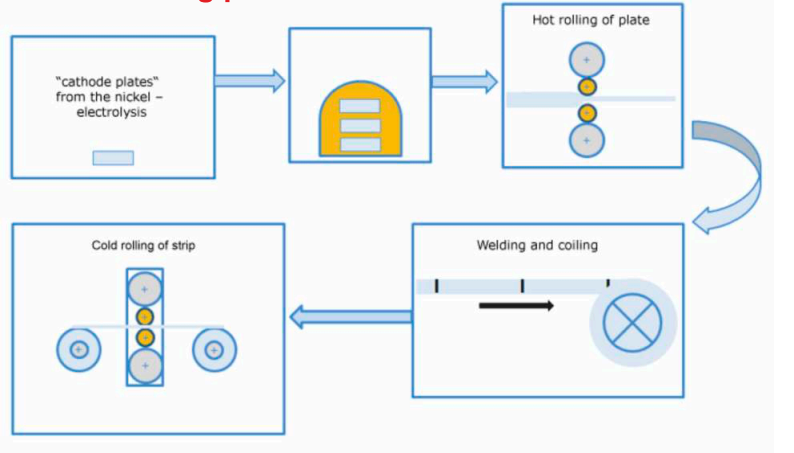
Strip is produced by joining plates frontally; wire is produced from sticks cut from plate and frontally welded. The grain structure of weld seams in strip and wire is aligned to the grain structure of the base material by a special process.- Applications
- Plate material: sputter targets, construction elements in the Chlor-alkali electrolysis, glass forming molds.
- Strip: in batteries as current collectors and terminals; in supercapacitors as electrode substrate.
- Wire: regulator coil in glow plugs of diesel engines; litz wire for current conduction under elevated temperatures and in aggressive environments.
Properties
- Mechanical Properties
- Typical Properties
- Properties
- Very low levels of C (20 ppm) and S (2 ppm) - These elements tend to segregate at grain boundaries resulting in hot shortening.
- Cleanliness - Absence of non-metallic inclusions as Al, Ti or Si oxides.
- Improved oxidation resistance - Development of a tightly adherent one-layer oxide scale instead of a twolayer customary one, which tends to flake off due to mismatch in thermal expansion.
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| R₀,₂ (Soft Annealed) | 100 - 200 | MPa | - |
| R₀,₂ (Half Hard) | min. 300 | MPa | - |
| R₀,₂ (Full Hard) | min. 500 | MPa | - |
| Rm (Soft Annealed) | 300 - 350 | MPa | - |
| Rm (Half Hard) | min. 450 | MPa | - |
| Rm (Full Hard) | 600 - 900 | MPa | - |
| Elongation (Soft Annealed) | min. 450 | % | - |
| Elongation (Half Hard) | min. 15 | % | - |
| Elongation (Full Hard) | min. 500 | % | - |
| Hardness (Soft Annealed) | max. 65 | HV | - |
| Hardness (Half Hard) | min. 100 | HV | - |
| Hardness (Full Hard) | min. 150 | HV | - |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Highest Degree Of Purity (Nickel) | 99.98 | % | - |
| Electrical Resistivity (20°C) | 7.1 | μ. ohm.cm | - |
| Thermal Conductivity (20°C) | 90.9 - 91 | W/m K | - |
| Formability (Young’s Modulus E=196 GPa) | 28427.0 | ksi | - |
| Softening Temperature | 350.0 | °C | - |
| Hardness | max. 65 | HV | - |
| Width (Foil) | 3 - 600 | mm | - |
| Thickness (Foil) | 0.05 - 2.5 | mm | - |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Standards
Assume fabrication by powder metallurgy - UNS NO 2270, 2.4050

