Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Ingredient Name
- Food Ingredients Functions
- Pharma & Nutraceuticals Functions
- Molecular Formula
- C15H10O5
- CAS No.
- 520-36-5
- Ingredients
- Apigenin
- Product Families
- Synonms
Apigenin; apigenine; apigenol; chamomile; C.I. natural yellow 1; 2-(p-hydroxyphenyl)-5,7- dihydroxy-chromone; spigenin; 4′,5,7- trihydroxyflavone
Features & Benefits
- Benefit Claims (Health)
- Food Ingredients Features
- Benefits
Anti-cancer, Anti-inflammatory
- Health Benefits
- Inhibit the growth of cancer cells.
- Lower blood pressure
- Protects the cardiovascular system
- Help sleep, calm nerves, eliminate irritability
- Resist inflammation
- Prevent osteoporosis
- Diuretic effect.
- Inhibit platelet aggregation.
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Food & Nutrition Applications
- Food Sources of Apigenin
Apigenin is one of the nutrients that abundantly present in green vegetables such as parsley, onions, maize, wheat sprouts, and in fruits, such as grapefruit, oranges, and so on.
However, One of the most frequent sources of apigenin is celery (Apium graveolens), a marsh plant in the family of Apiaceae that has been cultivated as a vegetable since antiquity. Apigenin is the most extracted nutrient in celery, containing 108 mg apigenin per kg.

Other sources for apigenin include beverages such as wine and beer brewed from natural ingredients in natural sources like Chamomilla Recutita.- How does Apigenin work?
Apigenin is one of the common dietary flavonoids, which is abundantly found in many fruits, vegetables, and medicinal herbs. It serves various physiological functions, such as antioxidant, potent anti-inflammatory, antiviral activities, antibacterial and blood pressure reduction.
Anti-tumor effect
Apigenin plays an essential role in cancer prevention by inducing apoptosis in various cell lines.
Ovarian cancer:
Some research was found that apigenin could inhibit the growth, proliferation, and transfer of ca-ov3 (human ovarian cancer cell); it induces apoptosis of ca-ov3 through keeping the cancer cells stasis in G2/M phase. The effect is related to time and dose.
Pancreatic cancer:
Apigenin can inhibit the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Apigenin starves the tumor by reducing the source of glucose, which is the food on which cancers cells live. Besides, Apigenin can improve the effectiveness of the chemotherapy drug- gemcitabine.
Chemo-sensitization
It was found that apigenin in low content had a low cytotoxic effect and could not induce human acute myeloid leukemia (hl-60) cells to apoptosis effectively. However, apigenin can enhance the inhibitory effect of cisplatin (DDP) on hl-60 cell proliferation while combining with different concentrations of DDP. So Apigenin may have chemotherapy-sensitization effect on hl-60; Low concentrations of apigenin can also reduce the resistance of hl-60 cells to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis, which may be related to the down-regulation of NF-κB and BCL-2. (NF-KB is a kind of protein complex that controls DNA transcription, the production of cytokines and cell survival; BCL-2 is encoded in the body through the BCL2 gene, it is the original member of the BCL-2 regulatory proteins family that can regulate cell death )
Liver protection
Apigenin can reduce liver injury induced by ischemia-reperfusion through antagonizing lipid peroxidation and scavenging free radicals. Apigenin can reduce liver injury caused by oxidative stress due to its potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Pharmacological experiments have proved that apigenin has an apparent protective effect on alcohol-induced liver/hepatocyte injury, and its primary mechanism is related to the inhibition of CYP2E1 expression in the liver/hepatocyte.
Prevent osteoporosis
Apigenin inhibits osteoblastogenesis, osteoclastogenesis, and also prevents bone loss. Apigenin protects bone tissue by reducing bone loss in the body. Some studies related to the MC3T3-E1, an osteoblast precursor cell line derived from Mus musculus (mouse) calvaria, found that apigenin can inhibit the TNF-α, IFN-γ, and then induced the secretion of several cytokines that promote osteoclast formation. Apigenin also inhibited the differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipose precursor cells into adipocytes strongly, therefore inhibiting the differentiation attendant inhibition adipocyte differentiation-induced IL-6, MCP-1, lectin product. Apigenin inhibits the differentiation of osteoclasts from RAW264.7 cell lines and then inhibits the formation of multinucleated osteoclasts. It can also induce osteoclast apoptosis and inhibit bone resorption.
Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant activity
Apigenin restrains the inflammation process, increases the IL-10 levels and normalizes the oxidative stress parameters Apigenin inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines and induces the anti-inflammatory cytokine production. Some literature suggests that apigenin alleviates tissue inflammation induced by oxidative stress in tissues by modulating various oxidative stress markers, interleukins, blood enzyme markers, and expression of several other related enzymes Regulation of endocrine Apigenin can regulate blood sugar, treat thyroid insufficiency and control lipid peroxidation It was found that apigenin could increase the levels of insulin and thyroxine in diabetic animals, and decrease the concentration of blood sugar and the activity of glucose-6-phosphorylase (G-6-Pase). Apigenin reversed the effects of increased serum cholesterol, increased liver lipid peroxidation (LPO) and decreased activities of antioxidants such as catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in alloxan-induced animals. In animals with regular blood sugar, apigenin can also reduce serum cholesterol and liver lipid peroxidation, and increase the activity of antioxidants in cells.
- Apigenin Dose
As we already know, apigenin is a potent natural flavonoid, and it has anti-cancer, antibacterial, anti-spasmodic, anti-inflammatory, and many other benefits. The dosage may differ for different purposes.
For anxiolytic effects, doses of apigenin from 3mg/kg to 10mg/kg is effective without sedation, and higher doses induce sedation in addition to reductions in anxiety.
For general health, doses at a range of 20-50mg together with amino acids and vitamins are preferred.
- Botanical source
Apium graveolens L.
Properties
- Typical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Molecular Weight | 270.24 | - | - |
| Specifications | 98.0 | % | - |
Technical Details & Test Data
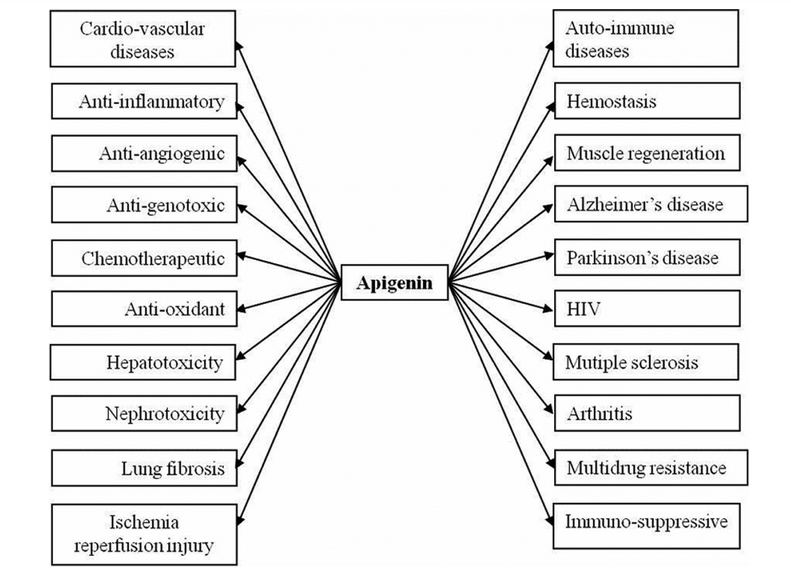
- Pharmacological properties of apigenin
Apigenin has been attached great importance in recent years, as a beneficial health promoter on account of its lower intrinsic toxicity and its health effects on regular versus cancer cells, compared with other structurally related flavonoids. There is a bulk of research evidence that has shown apigenin has great therapeutic potential for many diseases:
Packaging & Availability
- Packaging
25kg/drum, paper-drums and two plastic-bags inside
