Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Chemical Name
- Base Chemicals Functions
- Molecular Formula
- C3H4O2
- CAS No.
- 79-10-7
- EC No.
- 201-177-9
- Technologies
- Product Families
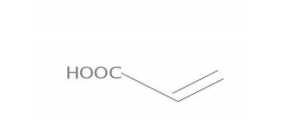
- Structure
Features & Benefits
- Labeling Claims
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Base Chemicals End Uses
- Use and Applications
Acrylic acid is used in the production of esters, polymers and specialty products. It can spontaneously polymerize evolving heat and pressure. Therefore it is usually supplied with an inhibitor to prevent unintended reactions. The chemicals produced using AA, are primarily used as reactive building blocks to produce polymers, coatings and inks, adhesives, sealants, textiles, plastics and elastomers. Specifically, AA is used in the following applications:
- Chemical intermediates: for a variety of chemical products
- Coatings: as a building block in the synthesis of polymers that are used in latex coatings, floor polishes, lacquers, sealers, textile sizing, textile and leather finishing products
- Polymerization and formulation: as a building block in the manufacture of thermoplastics, the production of resins, rubbers, sealants, and also to produce superabsorbent polymers for use in personal care products and soil conditioning
Acrylic acid is not sold for direct consumer use, but it is used as a raw material to make a variety of goods used by consumers or construction personnel and could be present in trace amounts as residual monomer in consumer products.
Properties
- Physical Form
- Odor
- Acrid, pungent
- Physico-Chemical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Density (20°C) | 1.051 | g/mL | — |
| Octanol-water Partition Coefficient (Log Pow) (25°C) | 0.46 | — | — |
| Melting Point (1013hpa) | 13 | °C | — |
| Flammability | Not flammable | — | — |
| Explosive Properties | Non explosive | — | — |
| Self-ignition Temperature (1013 hPa) | 438 | °C | — |
| Vapor Pressure (25°C) | 5.29 | hPa | — |
| Molecular Weight | 72.06 | — | — |
| Water Solubility (25°C) | 1000 | g/l | — |
| Flash Point (1013 hPa) | 48.5 | °C | — |
| Boiling Point (1013 hPa) | 141 | °C | — |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
- Regulatory Information
This substance is subject to a number of federal and international statutes and regulations. Selected U.S. regulatory information is available on the BAMM website. Other federal, state and local regulations may apply.
This substance has been registered under EU chemical control law known as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemical substances), and is listed on various chemical inventories. It has been reviewed under the OECD SIDS (Screening Information Data Set) program.
While the toxicological data are not specific to a particular region, the regulatory frameworks differ between countries and regions. The Global Harmonized System (GHS) attempts to standardize hazard communication so that the intended audience (workers, consumers, transport workers, and emergency responders) can better understand the hazards of the chemicals in use. Under the GHS, substances are classified according to their physical, health, and environmental hazards.
Hazard statements:
H226: Flammable liquid and vapor.
H302: Harmful if swallowed.
H312: Harmful in contact with skin.
H314: Causes severe skin burns and eye damage.
H332: Harmful if inhaled.
H400: Very toxic to aquatic life.
H411: Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Safety & Health
- Human Health Safety Assessment
Acrylic acid has a very strong, unpleasant odor that may be bothersome. However, the smell of AA does not necessarily indicate a health hazard. It has a low odor threshold which serves as a good warning property.
Like any reactive chemical, AA can create hazards if not handled properly. The main hazard is irritation. It causes severe burns to skin, eyes and the respiratory tract. It has a low toxicity (lethality) if it is swallowed, inhaled or applied to the skin. Animal studies have not indicated that it causes cancer or reproductive toxicity.
- Environmental Safety Assessment
Acrylic acid is a liquid which is unlikely to persist in the environment. In surface water, sewage treatment plants and soil, rapid degradation is expected. It is not expected to bind extensively to soil or sediment. If released to air, it will undergo degradation within days. It is not expected to accumulate in the food chain, i.e., the bioconcentration potential is low. It biodegrades rapidly in the environment. AA is very toxic to aquatic life. AA is toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects (fish, algae, invertebrates).
- Exposure
Human health
Acrylic acid is used in the production of industrial and consumer products. Based on these uses, the public could be exposed through:
- Workplace exposure – Exposure can occur either in an AA manufacturing facility or in the various industrial or manufacturing facilities that use it. It is produced, distributed, stored and consumed in closed systems. Those working with AA in manufacturing operations could be exposed during maintenance, sampling, testing, manual transfer, or other procedures.
- Consumer exposure to products containing acrylic acid – AA is not sold for direct consumer use, but it is used as a raw material to make a variety of goods used by consumers or construction personnel and could be present in trace amounts as residual monomer in consumer products, including paints
Environment
Potential releases into the environment are limited and for the most part occur only during production and processing, typically via wastewater and exhaust gasses. If accidentally released to surface water, it rapidly biodegrades and will not persist in the environment and will not accumulate in the food chain.
- Risk Management Recommendations
Industrial Manufacturing and Processing
In industrial manufacturing and processing applications, it is always important to obtain a current Safety Data Sheet from your supplier, follow the guidance provided and comply with applicable regulations.
Acrylic acids, acrylates and products containing them should always be handled in well ventilated areas. Each manufacturing facility should have a thorough training program for employees, appropriate work processes, and safety equipment in place to limit unnecessary exposure.
In the event of a spill, the focus is on containing the spill to prevent contamination of soil, ditches, sewers, or surface or ground water. Only trained and properly protected personnel should be involved in clean-up operations.
Professional Applications
Before using any chemical product, the user should be properly trained in safe handling procedures for that product. This means that they should always contact the supplier of the product being used to obtain the most current safe handling advice and follow all instructions and warnings.
Consumer Applications
It is important to read and follow all warnings and instructions on the product label or packaging

