Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Chemical Name
- Base Chemicals Functions
- Molecular Formula
- C7H12O2
- CAS No.
- 141-32-2
- EC No.
- 205-480-7
- Technologies
- Product Families
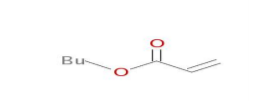
- Structure
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Base Chemicals End Uses
- Use and Applications
Acrylate esters, the family of chemicals to which nBA belongs, are used primarily as reactive building blocks to produce coatings and inks, adhesives, sealants, textiles, and plastics. The acrylate esters typically are present only in trace amounts (as residual monomer) in the finished product. Specifically, nBA is used in the following applications:
- Adhesives: for use in construction and pressure-sensitive adhesives as a co-monomer
- Chemical intermediates: for a variety of chemical products
- Coatings: monomers used to produce polymers for architectural, decorative, industrial, paper and roof coatings
- Leather: to produce different polymer finishes, particularly nubuck and suede
- Plastics: for the manufacture of a variety of plastics
- Fibers: in the manufacture of fibers of both woven and non-woven textiles as a copolymer of e.g. acrylonitrile and nBA. The fibers are in turn used for e.g. the manufacture of textiles.
n-Butyl acrylate is not sold for direct consumer use, but is used as a raw material to make a variety of goods used by consumers or construction personnel, including those listed above. nBA can be present in trace amounts as residual monomer in consumer products, including paints.
Properties
- Physical Form
- Odor
- Acrid
- Physico-Chemical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Density (20°C) | 0.9 | g/cm3 | — |
| Melting Point (atmospheric pressure) | -64.6 | °C | — |
| Flammability | Flammable upon ignition. | — | — |
| Boiling Point (atmospheric pressure) | 147 | °C | — |
| Explosive Properties | Non explosive | — | — |
| Self-ignition Temperature (1013 hPa) | 292 | °C | — |
| Vapor Pressure (22.5°C) | 5 | hPa | — |
| Molecular Weight | 128.169 | — | — |
| Water Solubility (20°C) | 1.7 | g/l | — |
| Flash Point (atmospheric pressure) | 37 | °C | — |
| Octanol-water partition coefficient (Log Pow) (25°C) | 2.38 | — | — |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
- Regulatory Information
This substance is subject to a number of federal and international statutes and regulations. Selected U.S. regulatory information is available on the BAMM website. Other federal, state and local regulations may apply.
This substance has been registered under EU chemical control law known as REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemical substances), and is listed on various chemical inventories. It has been reviewed under the OECD SIDS (Screening Information Data Set) program.
While the toxicological data are not specific to a particular region, the regulatory frameworks differ between countries and regions. The Global Harmonized System (GHS) attempts to standardize hazard communication so that the intended audience (workers, consumers, transport workers, and emergency responders) can better understand the hazards of the chemicals in use. Under the GHS, substances are classified according to their physical, health, and environmental hazards.
Hazard statements:
H226: Flammable liquid and vapor.
H303: May be harmful if swallowed.
H313: May be harmful in contact with skin.
H315: Causes skin irritation.
H317: May cause an allergic skin reaction.
H319: Causes serious eye irritation.
H332: Harmful if inhaled.
H335: May cause respiratory irritation.
H401: Toxic to aquatic life.
H412: Harmful to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
Safety & Health
- Human Health Safety Assessment
Acrylate esters, including butyl acrylate, have a very strong, unpleasant odor that may be bothersome. However, the smell of acrylates does not necessarily indicate a health hazard.
Like any reactive chemical, butyl acrylate can create hazards if not handled properly. The primary hazards with butyl acrylate are from contact of the skin or inhalation of its vapors, both being moderately toxic. nBA causes irritation to skin, eyes and the respiratory tract. Repeated skin contact may cause allergic reactions. Butyl acrylate has a low toxicity if swallowed. Animal studies have not indicated that butyl acrylate causes cancer or reproductive toxicity
- Environmental Safety Assessment
In contact with water, nBA will hydrolyze very slowly; also photodegradation in air will proceed slowly. In water, sewage treatment plants and soil rapid degradation is expected, since nBA was readily biodegradable in an OECD 310 -Screening test. Based on an experimental log Pow and calculated BCF, there is no indication of bioaccumulation potential. Adsorption of nBA to the solid soil phase is not expected. nBA is placed into a medium to high mobility class for adsorption and desorption to soils.
Acute toxicity data in freshwater organisms are available for all three trophic levels (fish, aquatic invertebrates and algae). Effect values were all in the same range of concentrations, i.e. between 1 and 10 mg/L, indicating a toxic effect to aquatic organisms.
- Exposure
Human health
Butyl acrylate is used in the production of industrial and consumer products.
- Workplace exposure – Exposure can occur either in a butyl acrylate manufacturing facility or in the various industrial or manufacturing facilities that use butyl acrylate. It is produced, distributed, stored and reacted in closed systems. Those working with butyl acrylate in manufacturing operations could be exposed during maintenance, sampling, testing, manual transfer, or other procedures. Workplace exposure is controlled by the use of proper industrial handling procedures and safety equipment.
- Consumer exposure to products containing butyl acrylate – Butyl acrylate is not sold for direct consumer use, but it is used as a raw material to make a variety of goods used by consumers or construction personnel and could be present in trace amounts as residual monomer in consumer products, including paints.
Environment
Potential releases into the environment are limited and for the most part occur only during production and processing, typically via wastewater and exhaust gasses. If accidentally released to surface water, it rapidly biodegrades and will not persist in the environment and will not accumulate in the food chain.
- Risk Management Recommendations
Industrial Manufacturing and Processing
In industrial manufacturing and processing applications, it is always important to obtain a current Safety Data Sheet from your supplier, follow the guidance provided and comply with applicable regulations.
Acrylic acids, acrylates and products containing them should always be handled in well ventilated areas. Each manufacturing facility should have a thorough training program for employees, appropriate work processes, and safety equipment in place to limit unnecessary exposure.
In the event of a spill, the focus is on containing the spill to prevent contamination of soil, ditches, sewers, or surface or ground water. Only trained and properly protected personnel should be involved in clean-up operations.
Professional Applications
Before using any chemical product, the user should be properly trained in safe handling procedures for that product. This means that they should always contact the supplier of the product being used to obtain the most current safe handling advice and follow all instructions and warnings.
Consumer Applications
It is important to read and follow all warnings and instructions on the product label or packaging

