Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Agrochemical Functions
- Technologies
Features & Benefits
- Agrochemicals Features
- Product Highlights
Functions of Iron
- Indispensable for chlorophyll production.
- Adequate iron, in plant-available form, is essential for protein synthesis.
- One of the essential elements required for biological nitrogen fixation.
- A central component of respiratory enzyme systems.
- Increases yield.
- Increases resistance to diseases.
Conditions Causing Iron Deficiency
- High lime (Ca) level in calcareous soil.
- High HCO3 (Bicarbonate) concentration in irrigation water.
- Lack of Fe nutrition
- Cold, wet conditions limit iron uptake, particularly in the early growth stages
- Inadequate soil aeration hinders mobility.
- Excessive phosphate applications or high phosphate levels in the soil.
- High manganese reduces iron uptake (excessive copper or molybdenum can also cause iron shortages).
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Applicable Crop
- Application Technique
- Applications
- Docto®Ferro 48 prevents and corrects iron deficiency for all fruit and vegetable crops in Fe poor soils.
- Application time: In arboriculture it must be applied in the beginning of the spring. In citrus fruits it must be also applied before the summer.
- In horticultural and ornamental crops, it must be applied regularly after transplanting.
- The effect begins to be detected from the first weeks of the application, obtaining a homogeneous new green color on the leaf. If necessary to be repeated after 10 days.
- Application directions: Directly in the soil dissolved in water, both in open systems: channel plowshare, injection, blanket and spraying, and in closed systems: dripping and band.
- Don´t expose the iron solution to light (light degradation) for long time (weeks).
- Fertigation: Never mix with strong acids (Chelate breakdown). Don’t mix with high doses of phosphate (Fe-phosphate precipitation). Don’t expose the iron solution to light.
- Soil application: After soil application, Docto®Ferro 48 should be incorporated immediately into the soil (rooting zone) by mechanical means or via irrigation.
- Docto® Ferro 48 Doses
Crop
Saplings 10 – 20 gr/tree Fruit Trees (Young Trees start fruiting) 20 – 50 gr/tree Fruit Trees (Normal Yield) 80 – 100 gr/tree Fruit Trees (High Yield) 100 – 150 gr/tree Citrus (Mature Trees) 150 – 200 gr/tree Vineyard ( vinestock) 10 – 20 gr Ornamental Plants (rose, clove etc.) 500 gr/da Annual/Perennial _x001f_owers, Pot plants (gerber daisy, chrysanthemum etc.) 600 gr/d Strawberry, Raspberry 100 – 150 gr/da Vegetables (greenhouse, _x001e_eld) 250 – 350 gr/da Field Plants 250 – 350 gr/da
Technical Details & Test Data
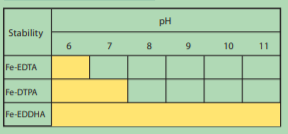
- Chemical stability in relation to pH
- Docto®Ferro 48 is a high quality EDDHA chelated iron (Fe). The ortho-ortho Fe concentration is 4.8% (=80%), which is 25% more efficient than normal 3,6%.
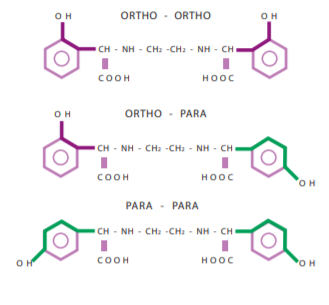
- Docto®Ferro 48 ortho-ortho is the most efficient iron chelate in the market. Other types of chelates are not efficient in high pH soils.
- The effective pH range of the product is between 4-12.
- It is effective even days after application.
- Docto®Ferro 48 is fully water soluble.
- Importance of ortho-ortho Isomer
The most efficient chelating agent in alkaline soils against Ferric chlorose is EDDHA, but only its ortho-ortho (o-EDDHA) isomer forms a stable chelate with iron and has got a fertilizing power in soils. During the chemical synthesis of the chelating agent EDDHA, three different isomers could be formed besides other by-products. Those are ortho-ortho, ortho-para and para-para. The relative position of the hydroxyl group and the amine chain in the benzene ring defines the type of isomer. The concentration of every isomer is defining the agronomical quality of the iron chelate. The higher amount of ortho-ortho isomer, the better the quality".