Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- INCI Name
- Cosmetic Ingredients Functions
- Technologies
- Product Families
- Composition
Linear, high molecular weight, poly(ethylene oxide) polymers
Features & Benefits
- Benefit Claims
- Labeling Claims
- Key Attributes
- Excellent friction reduction
- Slippery and lubricious in-wash feel
- Smooth after feel
- Foam density improvement
- Synergistic boost in conditioning when used with UCARE™ and SoftCAT™ Conditioning Polymers
- Improved tactile properties of water phase and overall esthetics
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Bath & Shower Applications
- Hair Care Applications
- Skin Care Applications
- Recommended Applications
- Hair care
- Body washes
- Bar soaps
- Shaving products
- Skin care
- Formulating Tips
The relative ease of dissolving FOAMYSENSE™ Polymers directly in water depends on three factors: (a) rate of viscosity buildup (which is a function of solution concentration and molecular weight), (b) particle size, and (c) type of agitation employed. The underlying factor, once again, is to obtain good polymer dispersion before the solution viscosity builds to a point where it is no longer possible to disperse additional resin without high shear. This is best accomplished by adding the FOAMYSENSE™ Polymers at just the “right” rate of addition. If you add it too slowly, the viscosity will build too rapidly, and you will not be able to add the rest of the resin. On the other hand, if you add the resin too rapidly, it will clump up and not dissolve.
Solutions of FOAMYSENSE™ Polymers can be prepared by direct addition of the dry resin to water using a marine-type propeller. These stirrers create a large vortex with only moderate shear. Stir rapidly to create a vortex initially (about 600 rpm), sprinkle in FOAMYSENSE™ Polymers at just the “right” rate, and then decrease the rpm to about 60. Continue stirring for 30–60 minutes until the solution appears homogeneous. In this way, as the viscosity increases, the shear degradation will be minimal.
FOAMYSENSE™ Polymers can undergo chain cleavage via auto-oxidation. Therefore, these products will degrade to lower molecular weight hence lower solution viscosity. Variables such as time, elevated temperature, and exposure to oxygen can impact the rate at which these polymers degrade. The rate of degradation is also dependent on the grade. Higher molecular weight grades are more sensitive than the lower molecular weight grades. The rate of auto-oxidation can be minimized through the addition of antioxidants and by controlling storage conditions. FOAMYSENSE™ Polymers are supplied with a typical range of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) content from 50 to 1000 ppm.
Properties
- Physical Form
- Typical Properties
- Note
1 Based on rheological measurements. Molecular weights obtained by other methods, including light scattering and gel permeation chromatography, may not be directly compatible
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Viscosity (at 25°C, Brookfield RVT, Spindle 1, 50 rpm, 5% Aqueous Solution) | 30 - 50 | cPs | DOWM 101962 |
| pH (at 25°C, 5% aqueous solution) | 8 - 10 | — | DOWM 102175 |
| Particle Size (Through 10 Mesh, < 2000 microns) | min. 100 | % | DOWM 102261 |
| Particle Size (Through 20 Mesh, < 841 microns) | 96 - 100 | % | DOWM 102261 |
| Loss on Drying | 0 - 1 | wt % | DOWM 102188 |
| Alkaline Earth Metals (as CaO) | 0 - 1 | wt % | DOWM 102225 |
| Silicon Dioxide Content | 0.8 - 3 | wt % | DOWM 101992 |
| Butylated Hydroxytoluene | 100 - 1000 | ppm wt | DOWM 102192 |
| Ash Content | 0 - 9.99 | wt % | DOWM 101992 |
| Microbial Content | max. 1000 | CFU/g | — |
| Free Ethylene Oxide Content | max. 0.004 | wt % | — |
| Heavy Metals | max. 0.002 | wt % | — |
| Arsenic Content | max. 2 | ppm | — |
| Residue on Ignition | max. 3 | wt % | — |
| Molecular Weight ¹ | 100000 | g/mol | — |
| BHT | 100 - 1000 | ppm wt | DOWM 102192 |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
Technical Details & Test Data
- Mechanism of Action
- Lubricity : The turbulence of flowing water increases drag. Adding FOAMYSENSE™ Polymers to water decreases hydrodynamic drag by altering the dynamics at the interface between the water and the surface with which it is in contact. The linear structure of the FOAMYSENSE™ Polymers allows the molecule to stretch. When a solution containing FOAMYSENSE™ Polymers is subjected to greater and greater linear forces (known as laminar flow), the FOAMYSENSE™ Polymers extend and stretch in solution. The resultant increase in the length of the FOAMYSENSE™ Polymers removes energy from the flowing system to decrease the building turbulence that accompanies the mounting force of the flowing solution. The overall effect is that the entire solution flows more smoothly.
- Foam Stabilization : FOAMYSENSE™ Polymers, although nonionic, are slightly electronegative. This is due to the lone pair of electrons in the ether oxygen present in the chemical structure of FOAMYSENSE™ Polymers. This slight negativity allows the resin to associate with the counter ions (i.e. Na or NH3) of the surfactant and the hydrogens in the water molecules to strengthen the foam bubble structure, and thus provide additional stabilization. Since a single molecule of the FOAMYSENSE™ Polymers is interacting with many surfactant molecules present in the surface layer, it helps bind them together electrochemically.
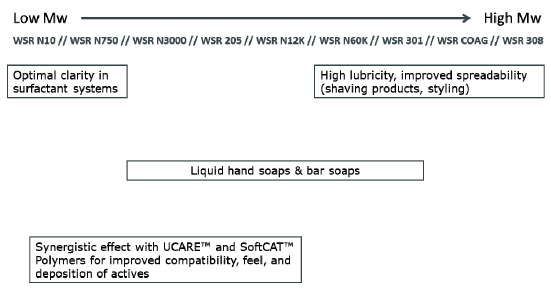
- Product Suggestions
Packaging & Availability
- Packaging Type
- Packaging Information
Product is sold in 140 lb bags.
Storage & Handling
- Usable Life and Storage
Product should be stored in a dry location at a temperature of less than 40°C (104°F).

