Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Product Type
- Technologies
- Product Families
Features & Benefits
- Ready-to-Use Product Features
- Product Highlights
Prepration: Thoroughly clean surfaces to be joined or patched. It is important to remove imbedded carbon and graphite dust that could interfere with good bonding to the substrate. Ultrasonic cleaning, a strong air blasé, rough machining, or use of a stiff brush and detergent followed by thorough rinsing are effective. Dust can be removed from small areas by pressing clear cellophane tape firmly against the surfaces to be joined and then removing. Completely dry the graphite at 212°F (100°C) or above and allow to cool to room temperature before applying cement. Mix contents of can thoroughly. Prior to using refrigerated Grade GC-5000F, sufficient time must be allowed for the cement to reach room temperature and a trowelable consistency. Apply cement to both faces, working it strongly into surfaces to be joined. Add excess cement to the center of the joint so that when the surfaces are mated and pressure applied, the cement squeezes to the edges, filling the joint. Remove excess cement. Best joints are usually less than 1/16th inch thick. Secure the joint in any manner to assure that it will not move during curing. Weights and clamps can be used but are not normally required.
Curing: The cemented joint must be cured at 266°F (130°C) for four hours to develop maximum strength. Oven heating, electric tape, infrared bulbs and radiant heaters are all satisfactory heating sources. Furnace linings and other large shapes are cured in place, normally with process heat. If the Grade GC-5000F is too thick or heating too rapid, the material may bubble and exude from the joint before it is set. When curing is complete, Grade GC-5000F may be brought rapidly to any desire operating temperature. As with all carbon or graphite structures, an inert or reducing atmosphere must be maintained above 662°F (350°C) to prevent oxidation in air.
Clean-Up: Tools and spills of the uncured cement can be cleaned with acetone or MEK. Once cured, the cement is insoluble in any liquid.
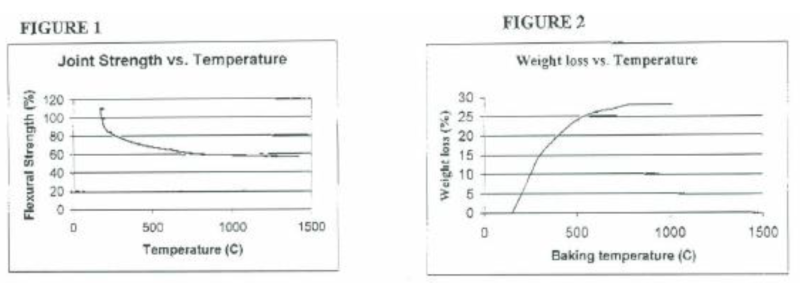
Strength: Joint Strength is maximum following the 266°F (130°C) cure. Baking to 752°F (400°C) results in removal of gasses, and structural change of the bond. Ultimately, an all-carbon bond develops which has lower strength than the 266°F (130°C) – cured joint. (See Figure 1). At temperatures above 1470°F (800°C), very little change in strength occurs.
Degassing During Bake-Out: When using Grade GC-5000F in furnaces operating at high temperatures in reducing atmospheres, it is often advisable to bake out the volatiles before use in a critical application. Figure 2 graphically illustrates the off-gas weight loss vs. Operating temperatures. Grade GC-5000F was cured at 266°F (130°C) for four hours and baked in an inert atmosphere to the temperatures indicated. This curve shows that volatile loss is essentially complete at 1292°F (700°C). At temperatures between 392°F and 752°F (200° and 400° C), where the major weight loss occurs, the off-gas content is comprised mainly of methane and other short chain hydrocarbons. Above 752°F (400° C) the off-gas is mostly hydrogen. Since the resultant joint is all carbon, there are no impurities with which to react at higher temperatures to produce gaseous reaction products.
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Uses
For bonding carbon brick, to make large monolithic graphite structures from smaller components, to repair cracked sintering trays, dies, jigs, fixtures, to secure lids to capsules, patch holes, fix spalls and scratches. Grade GC-5000F may also be used to cement insulation in place, affix sight tubes and pouring spouts, join rams and punches, set molds and dies, seal plugs, repair susceptors, join carbon foam, cloth and felt. Use as a binder for carbon cloth, yarn and fibers, fix broken resistance heating elements, etc.
Properties
- Physical Form
Safety & Health
- Safety
The uncured cement may cause skin irritation and eye burns. It is important to avoid contact with the skin or eyes. In case of contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of soap and water. For eyes, flush immediately with water and get medical attention. Do not inhale fumes when curing
Packaging & Availability
- Packaging Type
- Packaging
5 Gallon Pails
Grade GC-5000F Export
Grade GC-5000F is also manufactured in a two-component version suitable for overseas shipment. Each component is stable for at least one year in the original sealed containers. The components do not require refrigeration until mixed. For use, mix at room temperature 24 parts by weight of Grade GC-5000F Export Liquid with 76 parts by weight of Grade GC-5000F Export Powder until perfectly smooth and completely free of agglomerates. Let stand for 10 minutes and then remix for an additional 2 minutes. The resultant material should be used, handles and stored like regular Grade GC-5000F Graphite Cement.
Storage & Handling
- Storage
Keep refrigerated in tightly closed containers. The cement is time-temperature dependent. At 70° – 75°F (21° – 24° C) the cement will begin to harden in one month. When refrigerated at temperatures of 40°F (4°C) or less, shelf life of new unopened containers is at least one year. Once hardening begins, the cement should be discarded. Adding solvents cannot rejuvenate it.

