Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Name
- Pharma & Nutraceuticals Functions
- Molecular formula
- (C₈H₁₃NO₅)ₙ
- CAS No.
- 1398-61-4
- EC No.
- 215-744-3
- Technologies
- Product Families
- Origin
Chitin was first isolated and characterized in 1811 by the chemist and botanist Henry Braconnot.
- Occurrence in Nature
- In the exoskeleton of animals such as shrimp, crabs, krill, squid and insects or in cell walls of fungi, yeast and other microorganisms.
- The amount of chitin in marine biomass alone is approx. 106 - 107 tons.
- A distinction is made between alpha, beta and gamma chitin, which have different mechanical properties depending on the arrangement of the polymer chains.
- Alpha: alternating antiparallel arrangement of polysaccharide chains (crustaceans)
- Beta: parallel chain arrangement (squid)
- Gamma: two parallel chains statistically alternating with an antiparallel chain (fungi)
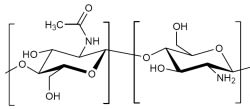
- Chemical Structure
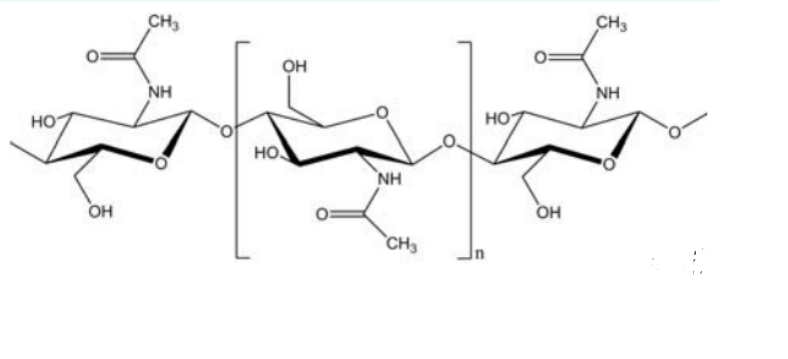
- Chemical Structure (50% deacetylizated)
Features & Benefits
- Product Highlights
Chitin is a nitrogenous polysaccharide. It belongs to the group of biopolymers. Monomers of chitin are called acetyl-glucosamine because the acetyl group is bonded to the nitrogen atom. Monomers are cross-linked in the polymer „beta-1,4 glycosidic“. This denotes to type and manner and structure in which the monomers are bonded with each other. There are three different kinds of structure in which chitin occurs in nature: as alpha,beta and gamma chitin. Chitins have those different arrangements of polymer chains which provthathem with differing properties and can be found in various organisms:
- Alpha chitin: in arthropods, crustaceans
- Beta chitin: in molluscs, such as squids
- Gamma chitin: a mixture of alpha and beta structures, notably in cephalopods
- Function of Chitin in Nature
- Supporting function (structural substance)
- Protection of soft parts (offers protection to inner organs)
- Prevention of loss of fluids
- Biodegradability
Biodegradable through the enzymes chitinases and lysozyme to chitobiose and through the chitobiases to monosaccharides.
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Potential Applications
Chitin can be applied either directly or further processed into various derivatives. Two of the most important derivatives are chitosan and glucosamine.
- Chitin Application in Cosmetics
As carboxymethyl chitin (moisturizers, changes flow properties), antistatic effect due to cationic properties (hair products).
- Chitin Application in Medicine/Pharmaceutics
- Wound and burn treatment
- Hemostatic for orthopedic treatment of broken bones
- Viscoelastic solutions for ophthamology and orthopedic surgery
- Abdominal adhesions treatment
- As antibacterial and antifungal agents and for treatment of mucous membranes
- In tumor therapies
- In micro surgery, neurosurgery
- For treatment of chronic wounds, ulcers and bleeding (chitin powder)
Properties
- Insoluble in
- Water, Organic Solvents, Weak Acids, Lye
- Soluble in
- Conc. Formic Acid, Methane Sulfonic Acid

