Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Ingredient Name
- Food Ingredients Functions
- Pharma & Nutraceuticals Functions
- Ingredients
- Cynara Extract
- Product Families
- Chemical Structure
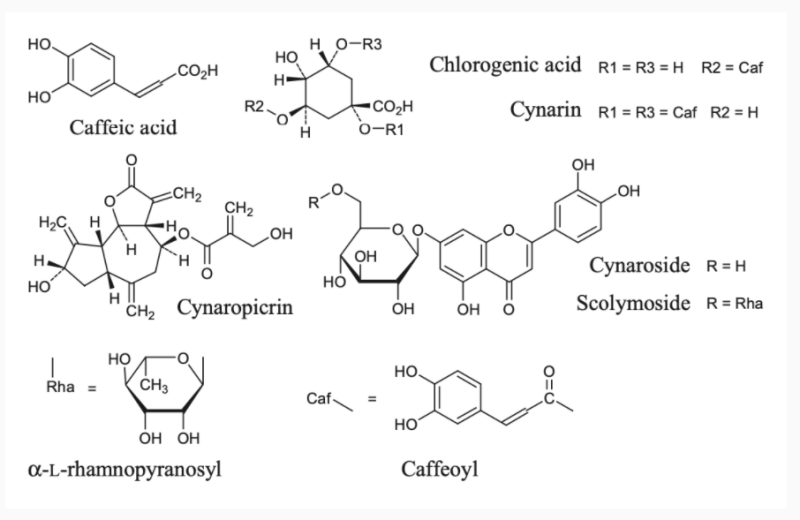
The extract of Cynara Cardunculus has many properties both when used on its own and when it is made with other extracts. Its benefits have been known for a long time: just think that in the monograph prepared by the WHO on medicinal plants there is a chapter dedicated to the dried basal leaves of Cynara cardunculus L. (Asteraceae). Of this perennial and thorny herbaceous plant, which produces different varieties of artichokes, the main beneficial properties are found in the dry leaves. The above monograph states that cinaropicrin is used for the treatment of digestive disorders (such as dyspepsia, feeling of fullness, flatulence, nausea, stomach pain and vomiting), in the additional treatment of mild to moderate hypercholesterolemia, for treatment of atherosclerosis and renal dysfunction (diuretic). Indicated for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome, in traditional medicine it has been used to treat anemia, diabetes, fever, gout, rheumatism and urinary calculi. Other benefits are added to the antiatherosclerotic and antihypercholesterolaemic activity. It is, for example, an antioxidant: a study measured the effects of the aqueous extracts and ethanol of the leaves on the intracellular oxidative stress stimulated by inflammatory mediators, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) in endothelial cells and in monocytes.
Features & Benefits
- Benefit Claims (Health)
- Food Ingredients Features
- Product Highlights
In various pharmacological test, artichoke leaf extracts have exhibited hepatoprotective, anticarcinogenic, antioxidative, antibacterial, anti-HIV, bile-expelling, and urinative activities as well as the ability to inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis and LDL oxidation.All these therapeutic indications cannot be ascribed to a single, but to several active compounds that together generate additive or synergistic pharmacologic effects (mono- and di- caffeoylquinic acids, flavonoids such as luteolin etc).As explained by Lattanzio, Kroon, Linsalata and Cardinali, over the last few years a renewed and growing interest in the artichoke, an old plant with new uses in functional foods, has been observed. Artichoke, Cynara cardunculus is an ancient herbaceous perennial plant, originating from the Mediterranean area, today widely cultivated all over the world. The botanical name is derived from the tradition of fertilizing the plant with ashes (Latin: cinis, cineris) and from the Greek skolymos, thistle, from the spines found on the bracts that enclose the flower heads forming the edible part of the plant.Artichoke is a species belonging to the Asteraceae family, which has been known since the 4th century B.C. as a food and remedy: this plant has been appreciated by the ancient Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans, who used it both as a food and as a medicine (for their beneficial effects against hepatobiliary diseases and as a digestive aid).
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Food & Nutrition Applications
Technical Details & Test Data
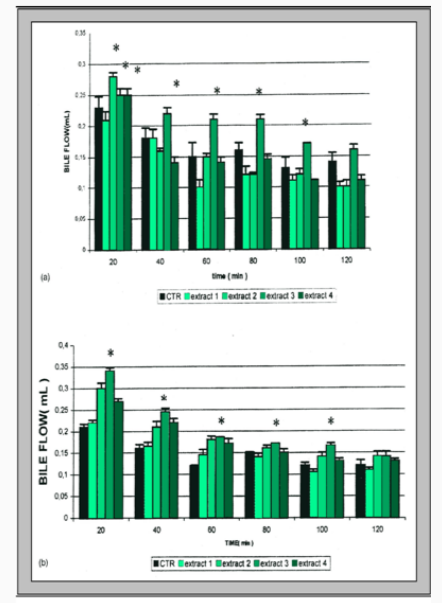
- CYC® Activities In Systemic Inflammation
- CYC® Anti-lipemic Properties
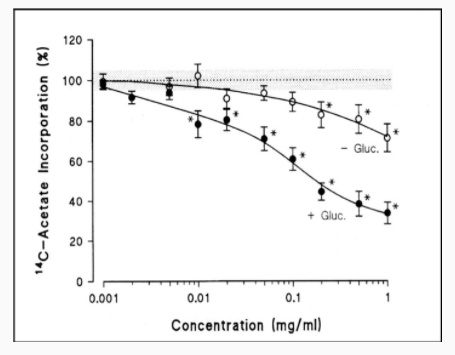
Effetto della cinarina sui lipidi totali e livelli di acidi grassi esterificati nei ratti trattati con etanolo (media+ sd)
Gruppo Lipidi Totali (mg/ml) Acidi grassi esterificatitotali (mg/ml)
Controllo 374.9±35 217±12 Etanolo 485.5±43* 439±33** Etanolo+Cinarina 310.2±81 170±21** - CYC® Hepato-protective Activities
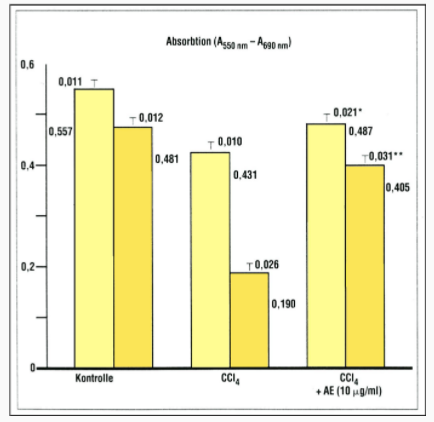
- CYC® Anti-proliferative Action
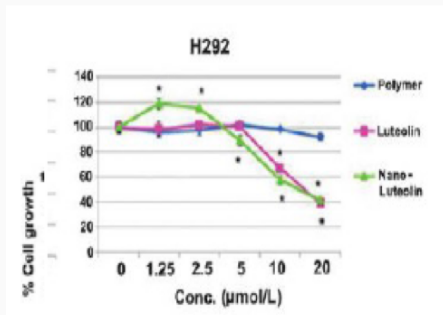
Relationship between cancer cell proliferation and luteolin and nano-luteolin concentration
Bioactive compounds
Tot. Polyphenols (mg/g) 20.82 Tot. Flavonoids (mg/g) 4.37
Antioxidant activity (EC50 mg/ml)10.14 Liver anti-carcinoma activity (GI 50 ug/mL) 52.06 Hepatotoxicity (GI 50 ug/mL)
71.73 Bioactive compounds, antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity of cynara scolymus extracts.
EC50 corresponds to the concentration of product that causes a 50% decrease in antioxidant activity.
GI50 corresponds to the concentration capable of inhibiting cell proliferation in human liver cells affected by carcinoma.
