Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Polymer Name
- Technologies
Features & Benefits
- Labeling Claims
- Materials Features
- Product Highlights
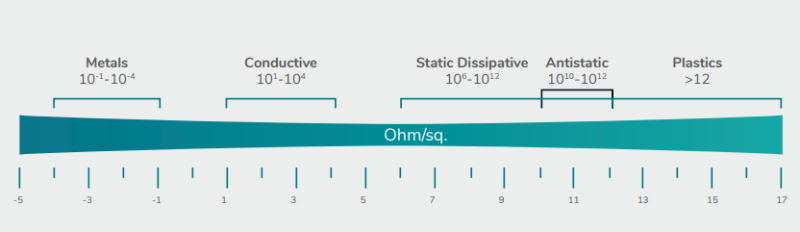
Our TPE compounds based on styrene block copolymers are excellent insulators as well as all plastic materials, however it is possible to exhaust the build-up of electrostatic charge thanks to specific additives. The problem of the accumulation of electrostatic charges has increasingly become an aspect of legislative relevance thus it is regulated by various sector directives, especially for Personal Protective Equipment for professional use (for example safety shoes).
Plastic materials are electrical insulators by their own nature. This feature is desired in most applications but it can generate problems when the final product undergoes rubbing stress. In such conditions the material accumulates electrostatic charges which are responsible for the "shock" received when touching an electrified object.
CONDUCTION METHODS IN THERMOPLASTIC MEDIA
The conductive properties of compounds depend strongly on the fillers choice and how they are dispersed within the thermoplastic matrix. The main methods for modifying electrical conductivity in a thermoplastic elastomer can be achieved through the addition of three different types of fillers:
1. Unmixable particles of conductive materials - The electrical conductivity occurs thanks to the contact of conductive particles that create a network within the thermoplastic material. Some examples of such particles are: conductive carbon black, metal microfibres, carbon nanotubes, etc.
2. Migrant Ionic and/or Hydrophilic Additives - These additives migrate on the surface of the material, activating an electrical surface conductivity through time. For this reason they are easily removable so the dissipative effect is destined to decrease over time. These additives are commonly referred to a "non-permanent antistatic additives".
3. Intrinsically Conductive Polymers (ICP) - The conduction mechanism is activated by a homogeneously dispersed polymer component in the thermoplastic matrix; this mechanism doesn’t depend on mechanical and environmental stresses applied to the material and it guarantees a much more stable electrical conductivity over time (permanent).
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Plastics & Elastomers End Uses
- Plastics & Elastomers Processing Methods
- Processing Tips
FOR INJECTION MOLDING MARFRAN® E CD can be easily processed by injection molding. The processing conditions of the TPE have a significant impact on the quality of the surface of the finished product. Beyond the following information, which can be considered as a guideline, it is always suggested to carry out various tests in order to identify the best conditions.
MARFRAN® E CDP Temperature profile of the cylinder (°C) 190 ÷ 220 Maximum processing temperature (°C) 240 Mold temperature (°C) 20 ÷ 30 Pre-drying MANDATORY 80°C for 4 h - Injection machine with standard three-zone screw for polyolefins.
- Injection pressure-speed: medium/high.
- Injection channels: with rounded and regular section; avoid sharp edges.
- Applications
MARFRAN® E CD combine easy processability, lightness and versatility of TPE compounds with the dissipation properties of electrical charges required by the market. The new MARFRAN® E CD are born as products oriented to the production of work shoes such as hospital clogs, but they can also be used in other injection molding applications.
Properties
- Typical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Hardness | 50.0 | Shore A | — |
| Food Contact Grade | Yes | — | — |
| Density | 940.0 | g/cm³ | — |
| Tensile Strength | 2.8 | MPa | — |
| Elongation at Break | 530.0 | % | — |
| Tear Strength | 23.0 | N/m | — |
| Volume Resistivity | max. 1E9 | ohms-cm | — |
| Surface Resistivity | max. 1E9 | Ohm/sq | — |
| Temperature Profile of the Cylinder | 190 ÷ 220 | °C | — |
| Maximum Processing Temperature | 240.0 | °C | — |
| Mold Temperature | 20 ÷ 30 | °C | — |
| Pre-drying (80°C for 4 h) | Mandatory | — | — |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
Technical Details & Test Data
- Resistivity Range Of Different Materials