Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Carrier
- INCI Name
- Cosmetic Ingredients Functions
- Technologies
- Product Families
Features & Benefits
- Benefit Claims
- Labeling Claims
- Benefits
- Skin barrier regeneration;
- Cellular renewal;
- Photoaging prevention;
- Blue light protection;
- Acne vulgaris treatment;
- Antioxidant properties;
- Standardizes skin tone and reduces pallor;
- Adjuvant in the care of atopic dermatitis and rosacea.
- Product Background
The Niacinamide encapsulation (Figure 1) through Nanovetores Technology enables the smart and safe delivery of the active ingredient, with a significant increase in stability, ensuring greater cosmetic products efficiency.
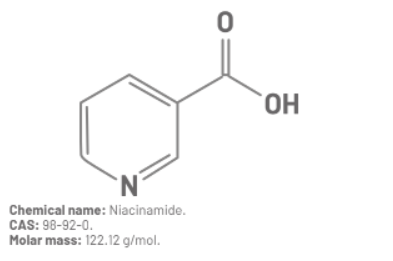
Figure 1: Chemical information and molecular structure of Niacinamide.
Niacinamide, also known as nicotinamide, is the active form of vitamin B3, which is water- soluble. It has several biological effects, as it is essentially involved in metabolism, transcription processes and DNA synthesis regulation. This vitamin is essential in cellular energy supply, acts as a precursor of the coenzymes NADH and NADPH (Figure 2), and is thus involved in more than 200 enzymatic reactions in the body, including ATP3 formation. When topically applied, niacinamide has been shown to be useful in improving cutaneous homeostasis and barrier function, and acts as a therapeutic adjuvant in the treatment of various skin conditions. Niacinamide stimulates the synthesis of collagen and proteins involved in the formation of keratin, filaggrin and involucrin, thus improving the skin's hydration, elasticity and general structure. Furthermore, studies have observed the positive impact of niacinamide on the synthesis of ceramides, free fatty acids and cholesterol contained in the intercellular spaces of the stratum corneum.
The intercellular spaces of the stratum corneum contain mainly non-polar lipids represented by free fatty acids, cholesterol and ceramides. Lipids are formed by multi- layer bilamellar structures separated by a hydrophilic phase, which form fundamental barriers for maintaining the stratum corneum hydration. There is a correlation between impaired epidermal barrier function and skin conditions such as rosacea, atopic dermatitis, aging and winter xerosis, which can be observed by an increase in transepidermal water loss and reduced stratum corneum hydration. In addition to the rebalancing of lipid production, niacinamide has been shown to decrease skin dehydration through a regulatory action on aquaporin 3, which plays a significant role in restoring the skin's barrier function.
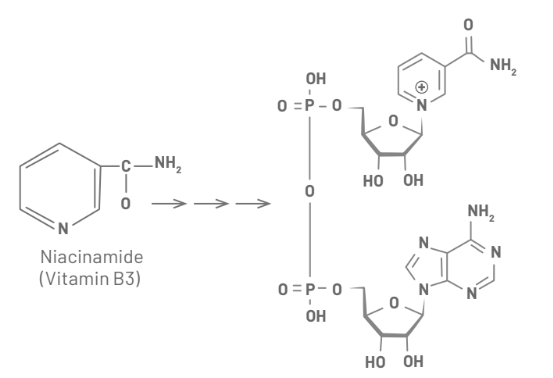
Figure 2: Adapted from niacinamide is an energy cofactor precursor.
The effect of niacinamide on the skin surface structure can be seen to improve its appearance, including reduction of fine lines and wrinkles, hyperpigmented spots, paleness and improved skin elasticity. Since NADH and NADPH are antioxidants, a possible effect of topically applyed niacinamide is to increase the levels of these antioxidants, and conse- quently to inhibit oxidative processes, such as collagen glycation. These oxidative processes play a significant role in skin aging, in addition to impacting the yellowish or pale appearance of the skin, due to the Maillard reaction, which forms yellow compounds. Niacinamide increases the rate of cell renewal and has a stimulating effect on the synthesis of collagen, keratin from epidermal biopolymers (proteins), filaggrin and involucrin. Decreased skin pigmentation can also be observed by the suppressive effect of niacinamide, transfer of melanosomes from melanocytes to keratinocytes and photoprotective effect related to the reduction of oxidative stress, reducing damage caused by blue light.
In the treatment of acne vulgaris, niacinamide can contribute with its seborregulatory effect, anti-inflammatory and curative properties, decrease in the number of pustules, comedones and papules. It significantly reduces the expression of inflammatory mediators produced by keratinocytes such as: IL-6, IL-10, MCP-1 and TNF-a mRNA responsible for tissue damage. Furthermore, niacinamide may exert direct control over Propionibacterium acne as a result of inhibi- tion of Sir2 10,11,12 enzymes. Due to its numerous benefits, niacinamide has proved to be a versatile active for cosmetic application (Figure 3).
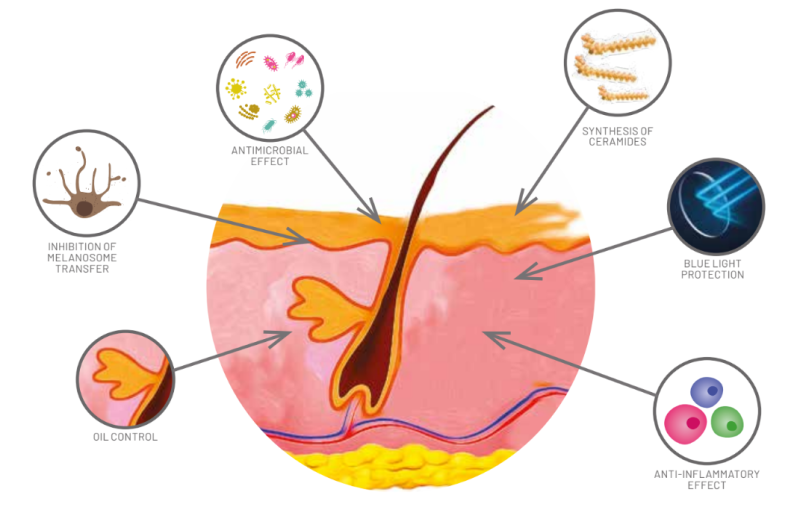
Figure 3: Overview of all niacinamide skin effects
- Remarks
The product is a suspension of nanoparticles, shake before incorporating into the formula. For fluid formulations the use of a suspending agent is recommended.
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Bath & Shower Applications
- Color Cosmetic Applications
- Skin Care Applications
- Treatment Product Applications
- Use Level
- 1 - 10%.
- Applications
Primers, creams, masks, serums, gels, face and eye cream gels, liquid soaps, makeup removeres and skin tone standardizing products.
- Usage Instructions
Add to the formulation below 40°C under mild to moderate agitation, in the desired concentration.
Properties
- Physical Form
- Odor
- Characteristic
- Appearance
- Clear Liquid
- Typical Properties
- Compatibility
Anionic product, compatible with non-ionic and anionic bases.
- Incompatibility
Incompatible with organic solvents such as ethanol.
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| pH Value | 4.0 - 6.0 | — | — |
| Relative Density | 0.9 - 1.1 | g/mL | — |
| pH Stability | 4.0 - 8.0 | — | — |
Regulatory & Compliance
Technical Details & Test Data
- Melanin Production Comparison
The objective of this test was to evaluate the production of melanin granules by melanocytes after exposure to samples of hydroquinone, NV Niacinamide, and positive control (kojic acid).
To evaluate the whitening potential, the samples were tested in order to obtain their cyto- toxicity levels. Hydroquinone showed cytotoxicity at concentrations greater than 0.001 mg/mL, while NV Niacinamide and kojic acid at concentrations greater than 10 mg/mL and 0.1 mg/mL, respectively. Therefore, the analyzes were performed at these non-cytotoxic concentrations.
For analyzing the effectiveness of the samples, the control group (cell culture medium) was normalized to 100%. The positive control reduced 17.93% (±0.91) of melanin granules. The Hydroquinone sample showed a reduction of 46.8% (±0.69) while NV Niacinamide had a reduction of 39.51% (±1.14) when compared to the control group. These results can be seen in Figure 4.
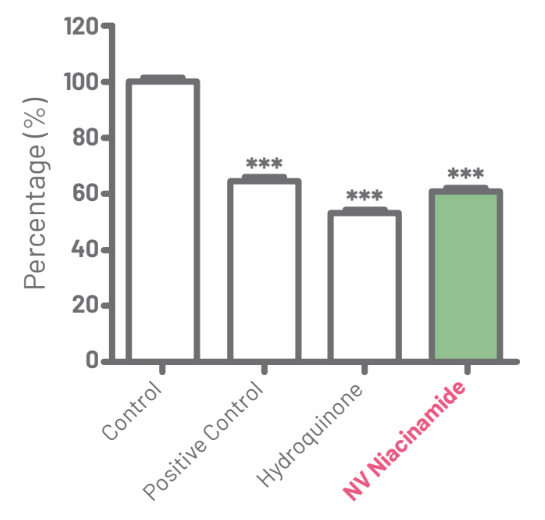
Figure 4: Quantitative chart of the results observed in the study, with the control group normalized to 100% for the respective non-cytotoxic concentrations of the evaluated samples (***p<0.001).
Additionally, the samples were subjected to staining of the treated cells with the respective non-cytotoxic concentrations. Fontana-Masson staining highlights melanin granules within the cell. As shown in Figure 5, it is possible to observe that there was a reduction in melanin granules when comparing the NV Niacinamide sample with the control group, on the other hand, it can be seen that compared to Hydroquinone, the reduction of melanin granules is not significant, but their level is decreased.
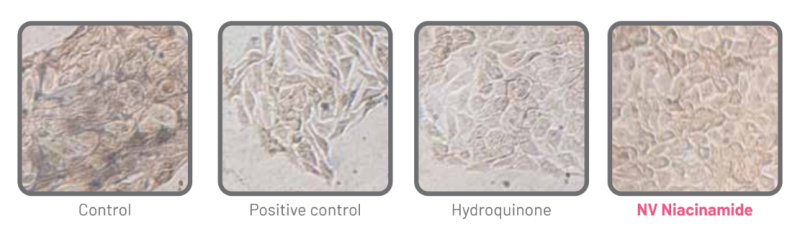
Figure 5: Representative images of the indicated groups with Fontana-Masson staining to highlight the melanin granules.
With the results obtained, it can be stated that the NV Niacinamide sample presented better results compared to the hydroquinone sample, in the reduction of melanin granules, which is associated with the skin whitening potential. It is worth mentioning that the NV Niacinamide sample is presented in this study in its encapsulated form (10% of the active ingredient in the sample) while the hydroquinone sample is in its free form (100%), that is, NV Niacinamide is 10X more effective in redu- cing melanin granules compared to hydroquinone. In addition, hydroquinone was shown to be 10000X more cytotoxic than NV Niacinamide.
- Inflammatory Markers
For the related study, the relative expression of markers related to the inflammatory process was compared among the control, positive control (sodium lauryl sulfate) and NV Niacinamide and Hydroquinone sample groups, at the same concentration assessed of 0.01 mg/mL. The objective of the study was to evaluate the interleukin-6 (IL-6), inter- leukin-8 (IL-8) markers and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) using human keratinocyte cell culture.
IL-6 analysis
Figure 6 shows the analysis of IL-6 expression. It is possible to observe that the positive con- trol increased 2.2X (±0.22) in relation to the control. The hydroquinone sample showed a 4.24X (±0.32) increase in IL-6 expression while the NV Niacinamide sample showed a 0.67X (±0.09) reduction in expression, that is, hydroquinone had an inflammatory potential 6X greater than NV Niacinamide.
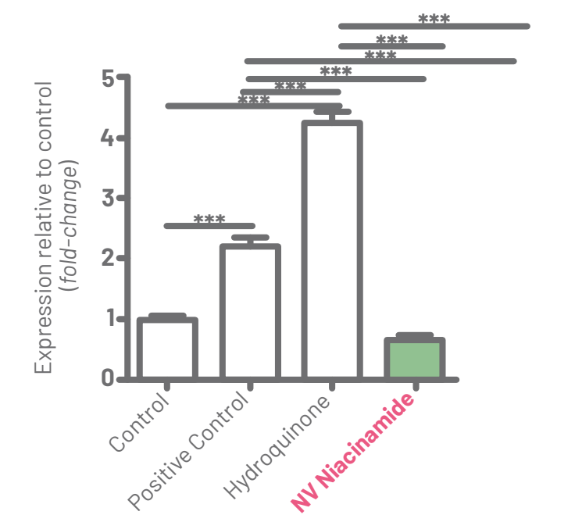
Figure 6: Result of the analysis of the relative IL-6 expression among groups. Horizontal bars connect groups to demonstrate level of statistical difference (***p<0.001).
IL-8 analysis
For IL-8 analysis, it was observed that the positive control showed an increase of 1.63X (±0.32) relative to control. The sample of hydroquinone showed an increase of 4.91X (±0.48) in the expression of IL-8 and the sample of NV Niacinamide showed a 1.38X (±0.27) increase in the expression. Therefore, Formahydroquinone was nearly 4X more inflammatory than NV Niacinamide. The results are shown in Figure 7.
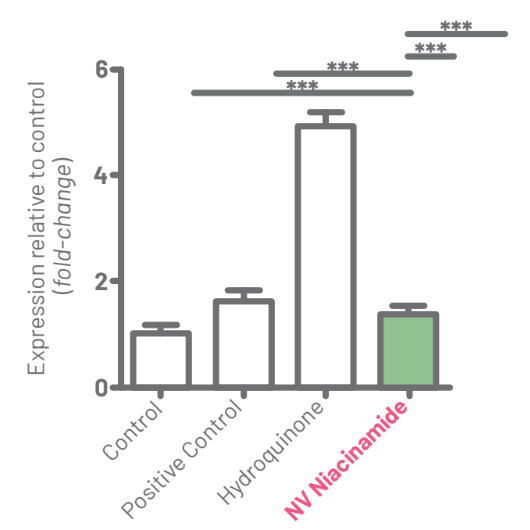
Figure 7: Result of the analysis of relative IL-8 expression among groups. Horizontal bars show the level of statistical difference (***p<0.001).
TNF-α analysis
For TNF-α analysis, it was possible to verify that the positive control showed an increase of 2.26X (±0.35) in relation to the control. A Hydroquinone sample showed a level of 0.99X (±0.08) in the expression of TNF-α related to the control group and the sample of NV Niacinamide showed a 0.21X (±0.01) reduction in the expression, that is, hydroquinone was almost 5X more inflammatory than NV Niacinamide. Results are presented in Figure 8.
With these results, it is possible to state that hydroquinone had a very significant inflammatory potential compared to NV Niacinamide. Hydroquinone also has adverse effects in the regions where the product is applied, causing exogenous ochronosis (asymptomatic bluish-black or gray-brown hyperpigmentation), irritation, dermatitis, occupational vitiligo depigmentation, among others.
Thus, NV Niacinamide becomes the best option for people with sensitive skin, since it has the benefit of whitening potential and simultaneously low inflammatory potential for the skin compared to other lighteners on the market.
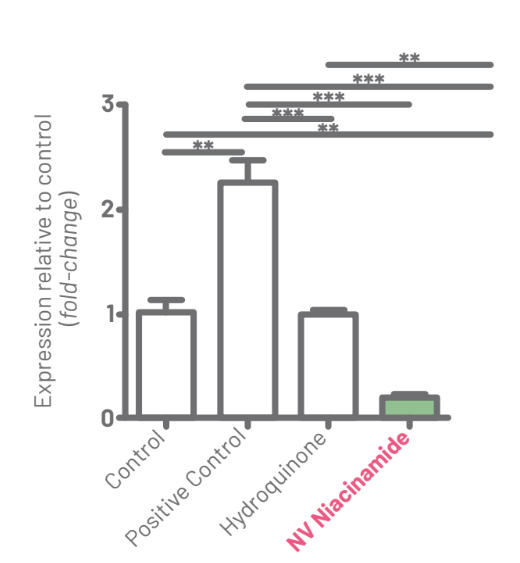
Figure 8: Result of the analysis of the relative TNF-α expression among groups. The horizontal bars show the level of statistical difference (**p<0.01; ***p<0.001).
Storage & Handling
- Storage
Keep in a well-ventilated place, away from light and heat.

