Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Chemical Name
- Plastics & Elastomers Functions
- Formula
- (NH4)2S2O8
- CAS No.
- 7727-21-1
- EC No.
- 231-781-8
- Technologies
Features & Benefits
- Materials Features
Applications & Uses
- Applications
- Compatible Polymers & Resins
- Plastics & Elastomers End Uses
- Applications
Persulfates are key components in many industrial processes and commercial products. The polymer industry uses aqueous solutions of persulfates as initiators in the polymerization of latex and synthetic rubber. The electronics industry considers sodium persulfate an efficient microetchant in the manufacture of printed circuit boards. The following examples further illustrate the chemical versatility of persulfates.
Polymerization
- PLASTICS AND RUBBER: Ammonium, potassium, and sodium persulfates are used as initiators for emulsion polymerization reactions in the preparation of acrylics, polyvinyl chlorides, polystyrenes, and neoprene. They are used as polymerization initiators in the manufacture of synthetic rubber (styrene butadiene and isoprene) for automobile and truck tires. Persulfate initiation is used to prepare latex polymers for paints, coatings, and carpet backing.
- STRUCTURAL MATERIALS: Persulfates are used as initiators in polymeric concrete formulations.
- INORGANIC CHEMICALS AND MINERALS: Persulfates are also initiators for the polymeric coating of graphite filaments.
- SOIL STABILIZATION: Ammonium persulfate is used as a curing agent in chemical grout systems used to stabilize soil near dams, tunnels, and buildings.
- Oxidation SURFACE PREPARATION: The oxidation power of persulfates is used to clean and microetch a variety of printed circuit board substrates. Persulfates are important oxidants in plating and coating processes. They are also etchants for nickel, titanium, and zinc alloys. Persulfates are used to clean and mill aluminum, brass, copper, and many other metal surfaces prior to plating or adhesive bonding. Persulfates are used to clean and activate carbon and charcoal before and after their use as absorbents
- COSMETICS: The cosmetic industry has developed formulations which use persulfates to boost hair bleaching performance.
- ORGANIC SYNTHESIS: Persulfates are oxidizing agents in the preparation of aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, quinones, and a variety of other compounds. The pharmaceutical industry uses sodium persulfate as a reagent in the preparation of antibiotics. Other Applications
- ADHESIVE: Persulfates are used in the preparation of adhesive films and metal bonding adhesives.
- GAS AND OIL PRODUCTION: In enhanced oil recovery, persulfates are used “down hole” for gel forming and breaking.
- INKS, PIGMENTS, AND DISPERSANTS: Persulfates are used to graft substrates to polymers (for example, carbon black to sodium acrylate). Persulfates are used in the preparation of dispersants for ink jetting and toner formulations.
- MINING: Persulfates can be used in nickel and cobalt separation processes.
- PEROXYMONOSULFATE: PeroxyChem developed a process using ammonium and sodium persulfates to prepare peroxymonosulfate solutions. This patented process allows fast, efficient, on-site production of an alternative to Caro’s acid and potassium caroate.
- PHOTOGRAPHY: Persulfates are used in many photographic applications, including bleaching solutions, solution regeneration, equipment cleaning, and wastewater treatment.
- PULP AND PAPER: Persulfates are used in the sizing of paper, preparation of binders and coatings, and production of special papers. An activated alkali metal persulfate effectively repulps neutral/ alkaline wetstrength broke and decolorizes dyes and optical brightener.
- TEXTILES: Ammonium and sodium persulfates are used in the desizing and bleaching of textiles and the development of dyestuffs.
- ENVIRONMENTAL: Persulfates are very strong oxidants, have excellent shelf life when stored properly, and are economical to use. These properties make persulfates suitable for a variety of environmental applications, such as soil remediation and wastewater/groundwater cleanup.
Properties
- Odor
- None
- Typical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Molecular Weight | 228.2 | — | — |
| pH Value (1% Solution) | 5.2 | — | — |
| Crystal Density | 1.98 | g/cc | — |
| Loose Bulk Density | 1.05 | g/cc | — |
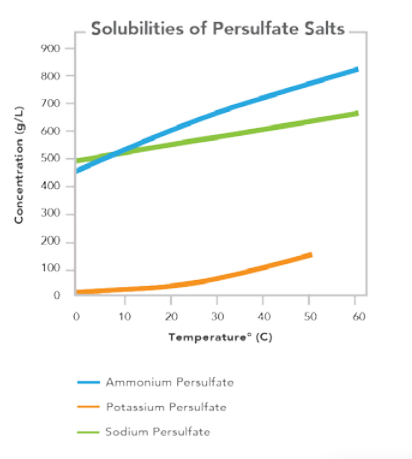
| Solubility (g/100g of H2O,25°C) | 85 | — | — |
| Solubility (g/100g of H2O,50°C) | 116 | — | — |
| Purity | 99.5 | % | — |
| Active oxygen | 6.98 | % | — |
| Moisture | 0.02 | % | — |
| Iron | 1 | ppm | — |
| Insolubles | 21 | ppm | — |
| Copper | max. 0.3 | ppm | — |
| Chloride | max. 10 | ppm | — |
| Heavy metals, as lead | max. 1 | ppm | — |
| Manganese | max. 0.5 | ppm | — |
| Chromium | max. 0.5 | ppm | — |
| Sodium | 20 | ppm | — |
| Potassium | 50 | ppm | — |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Quality Assurance
PeroxyChem persulfate products are produced under an ISO-9002 certified quality system. Statistical Process Control (SPC) and a distributed control system combine to provide consistent process control. PeroxyChem operators monitor key parameters to ensure consistent quality for all products. All materials–raw, intermediate and final–are checked and tested in a new, modern laboratory employing the latest analytical technology. Quality test results are maintained on each batch of product. Certificates of Analysis and other end-product information can be customized to meet your system requirements. Our production facility uses SPC methods to improve and assure the quality of persulfate chemical products. PeroxyChem operators chart key operating parameters to maintain process control; this assures that quality is built in to each customer’s order. The SPC system is designed to meet your specific quality standards. Product is analyzed and identified as it leaves the packaging areas. Product quality is maintained by batch number. The information is then stored in a computer database, enabling PeroxyChem to issue Certificates of Analysis that are specific to each batch of materials received by our customers. PeroxyChem is the only persulfate producer that uses cutting edge technology to ensure that our products are stable for storage or transport and use. We have established new product safety standards for thermal stability to ensure a high-quality, stable persulfate.
Technical Details & Test Data
- Test Data
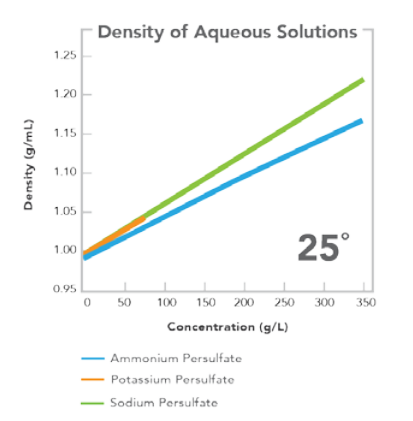
EQUATION FOR CALCULATION OF DENSITY Density (g/mL) = density H2O + (A/1000)X + (B/1000)X1.5, where X = solution concentration in grams per liter (g/L).
Salt Constant 25°C 35°C 45°C Ammonium
A 0.4903 0.486 0.4789 B 2.6730x10-4 -7.6254x10-4 -5.0971x10-4 Potassium
A 0.6368 0.6273 0.6294 B 1.4934x10-3 -8.1965x10-4 -1.6472x10-3 Sodium
A 0.6709 0.6727 0.661 B 1.4934x10-3 -1.4909x10-3 -1.0038x10-3 DENSITY OF WATER
25°C 35°C 45°C Density H2O 0.99707 0.99406 0.99025 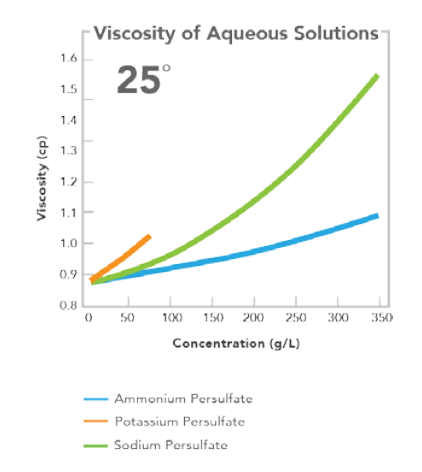
EQUATION FOR CALCULATION OF VISCOSITY
Viscosity (cp) = viscosity H2O + CX0.5 + DX + EX1.5, where X = solution concentration in grams per liter (g/L).Salt Constant 25°C 35°C 45°C Ammonium
C -1.0686x10- 6.8050x10-3 5.3134x10-3 D 1.7140x10-4 -9.4542x10-4 -5.8450x10-4 E 2.4670x10-5 5.9785x10-5 4.5080x10-5 Potassium
C 0 5.9187x10-3 3.5413x10-3 D 1.0661x10-3 -1.0551x10-3 -9.5623x10-5 E 9.8884x10-5 1.0674x10-4 1.2477x10-5 Sodium
C 4.3857x10-3 6.1743x10-3 1.3461x10-2 D -1.2218x10-3 -4.6619x10-4 -1.9741x10-3 E 1.5146x10-4 8.1093x10-5 1.3540x10-4 VISCOSITY OF WATER
25°C 35°C 45°C Viscosity of H2O 0.8904 0.7194 0.596 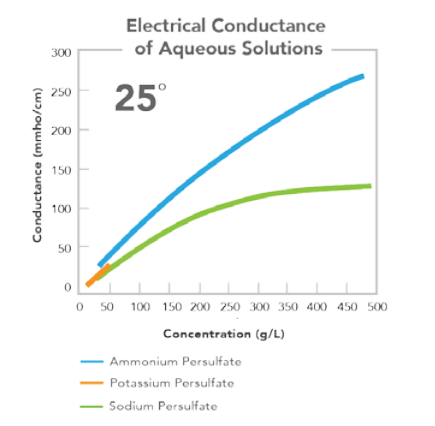
EQUATION FOR CALCULATION OF ELECTRICAL CONDUCTANCE
Conductance (mmho/cm) = F + GX + HX2, where X = solution concentration in grams per liter (g/L).
Salt Constant 25°C 35°C 45°C Ammonium
F 3.9016 6.6081 6.2538 G 0.8568 0.9804 1.1578 H 6.2904x10-4 -7.1312x10-4 -8.8912x10-4 Potassium
F 2.9603 3.7314 4.1673 G 0.6704 0.7972 0.9525 H -1.0456x10-3 -1.1982x10-3 -1.9173x10-3 Sodium
F 5.9501 7.1826 8.1825 G 0.588 0.6967 0.8123 H -6.6193x10-4 -7.5821x10-4 -8.6226x10-4 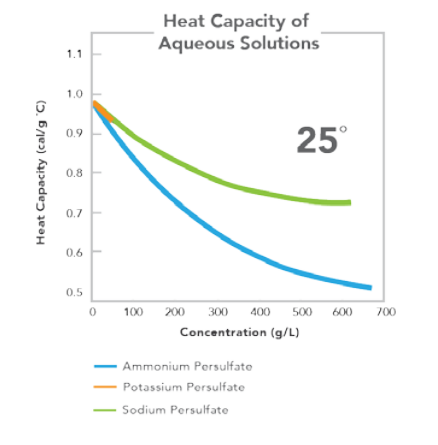
EQUATION FOR CALCULATION OF HEAT CAPACITY
Heat capacity (cal/g °C) = K - LX + MX1.5, where X = solution concentration in grams per liter (g/L).
Salt Constant 25°C Ammonium
K 0.994 L -1.863x10-3 M 4.531x10-5 Potassium
K 0.997 L 1.150x10-3 M 2.670x10-5 Sodium
K 0.997 L 1.190x10-3 M 3.112x10-5 
G/L 25°C 35°C 45°C 25°C 35°C 45°C 25°C 35°C 45°C 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 25 2.477 2.485 2.495 2.468 2.476 2.486 2.466 2.474 2.484 50 4.895 4.911 4.931 4.861 4.877 4.896 4.854 4.868 4.888 75 7.256 7.281 7.311 7.183 7.208 7.237 7.167 7.187 7.219 100 9.562 9.598 9.635 — 9.47 9.51 9.41 9.435 9.479 125 11.815 11.863 11.912 — 11.668 11.719 11.586 11.616 11.672 150 14.017 14.077 14.136 — — 13.868 13.699 13.733 13.801 175 16.17 16.244 16.311 — — 15.959 15.751 15.79 15.87 200 18.275 18.364 18.44 — — 17.994 17.745 17.788 17.88 250 22.349 22.471 22.564 — — — 21.572 21.62 21.738 300 26.251 26.411 26.519 — — — 25.197 25.25 25.394 350 29.993 30.194 30.316 — — — 28.634 28.695 28.864 400 33.583 33.831 33.964 — — — 31.91 31.969 32.164 450 37.031 37.329 37.473 — — — 35.026 35.087 35.307 500 40.346 40.699 40.85 — — — 37.998 38.06 38.305 550 Safety & Health
- Persulfate Safety
Persulfates are oxidizing chemicals that require careful attention to all aspects of handling and use. Personal Protective Equipment When handling persulfate chemicals, follow the guidelines listed here and in the SDS.
- PROTECT YOUR EYES: Wear chemical-type goggles or a face mask whenever splashing, spraying, or any eye contact is possible.
- PROTECT YOUR RESPIRATORY SYSTEM: Use dust respirators approved by NIOSH/MSA whenever exposure may exceed the established standard listed in the current SDS.
- PROTECT YOUR HANDS: Wear general purpose neoprene gloves.
- PROTECT YOURSELF WITH PROPER CLOTHING: Wear ordinary work clothes with long sleeves and full-length pants.
- PROTECT YOURSELF WITH PROPER FOOTWEAR: Wear shoes with neoprene soles.
- First Aid
- EYE CONTACT: Flush with water for at least 15 minutes. If irritation occurs and persists, obtain medical attention. SKIN CONTACT: Wash with plenty of soap and water. If irritation occurs and persists, obtain medical attention. Wash clothing before reuse.
- INHALATION: Get fresh air. If breathing difficulty or discomfort occurs, call a physician.
- INGESTION: Drink one to two glasses of water. Do not induce vomiting. Do not give anything by mouth to an unconscious individual. Call a physician immediately. When properly handled and stored, persulfates and their solutions do not present serious health hazards. The SDS provides information concerning exposure, emergency, first aid, and disposal of persulfates.
Packaging & Availability
- Containers And Packaging
PeroxyChem packages and ships crystalline persulfate chemicals in three different container types, according to customer requests.
Type Construction Persulfate wt/container Containers per pallet Persulfate wt/pallet
Bag PolyethyleneFiber drums, 55 lbs/25kg 40 2,200 lbs/1,000kg
Drum polyethylene liner 225 lbs/102kg 8 1,800 lbs/896kg IBC* Polypropylene sack 2,200 lbs/1,000kg 1 2,200 lbs/1,000kg
Storage & Handling
- Storage
Persulfates should be stored in accordance with the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 400 Hazardous Materials Code. PeroxyChem personnel can provide additional support in reviewing storage facilities.
- GENERAL PRECAUTIONS: Persulfates should be kept in a cool, dry storage area, in a configuration that is appropriate for the sprinkler capacity of the building per NFPA 400. Personnel should be trained to handle persulfates safely, properly dispose of spilled materials and prevent contamination. If material gets wet or spills, it must be isolated and disposed of properly.
- HANDLING: To remove and transport persulfates from the shipping containers, use clean plastic or stainless steel scoops, shovels, pails, etc. Cleanliness is essential.
- SOLUTION STORAGE: Aqueous solutions of ammonium persulfate are more susceptible to decomposition than the solid product. The recommended materials of construction for storage and conveyance equipment (tanks, pipelines, etc.) are 304 and 316 stainless steel. Other acceptable materials include polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene, Plexiglas® plastic (or other suitable generic), Teflon® resin (or other suitable generic), chemical stoneware, and glass. Metals other than 304 and 316 stainless steel cause decomposition of the persulfate solutions or may be corroded by them. This is particularly true of Monel, copper, brass, and iron. Do not store or process persulfate solutions in sealed or closed containers or vessels. Normal solution decomposition will release oxygen gas which may overpressurize a sealed container and cause rupture. Storage of persulfate solutions above 25°C will accelerate the rate of decomposition. See data on decomposition hazard and decomposition prevention.
- Disposal Persulfate crystals should never be discarded to trash bins. Contact with moisture, contaminants, and/or reducing agents can initiate a chemical reaction or a persulfate decomposition. Persulfate crystals which become a waste material are classified as hazardous waste because they are oxidizers. Persulfates that are spilled on the floor, or otherwise contaminated, are best dissolved in copious quantities of water.An acceptable disposal method for spent persulfate solutions is to dilute with large quantities of water and dispose via a treatment system. Any disposal method must be in full accordance with all local, state and federal regulations.
- Shipping U.S. and international transportation regulations classify persulfates as OXIDIZERS and regulates their transport by air, water, and rail. These regulations detail the specific requirements for packaging, marking, labeling and describing persulfates for shipment.
- Decomposition Hazard Overheating or contamination of persulfates can lead to a runaway decomposition. The persulfate salt will begin to effervesce with an acid-like odor. Persulfates decompose to form solid sulfate salts and emit noxious fog or fumes of SOx and NOx. This decomposition may form a high temperature melt. The material will flow like magma and may ignite nearby combustible materials such as wood or paper. Oxygen produced by persulfate decomposition can increase the intensity of the fire. The only way to halt a decomposition event is to apply LARGE quantities of water to the reacting material. Eight pounds of water per pound of decomposing materials is recommended, but no less than two pounds of water should be applied. Insufficient amounts of water will intensify the reaction and increase the acid mist concentration. Please note that carbon dioxide (CO2) or other gas-filled extinguishers will have NO effect on decomposing persulfate. The use of water as an extinguishing agent is emphasized. Control of the melt and firefighting efforts are enhanced if persulfates are stored within containment areas. Persulfate decomposition will require emergency responders wearing full protective rubber clothing, face and head protection, plus self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA).
- Decomposition Prevention OBSERVE THE FOLLOWING PRECAUTIONS TO PREVENT DECOMPOSITION: Do not expose persulfates or their containers to moisture. Moisture significantly lowers the decomposition temperature. Do not store persulfates near incompatible materials such as reducing agents, acids, bases, halide salt solutions, organics, ammoniacal solutions, alkaline cleansers, or other oxidizers. These materials can initiate decomposition. Do not store near point sources of heat such as steam pipes, electrical appliances, heating vents, gas flames, welding sparks, or radiant heaters. Do not store at ambient temperatures above 113°F or 45°C. Do not return spilled or unused portions of persulfates to the original container. Dirt, metal, moisture, or other contaminants can induce the decomposition of persulfates. Do not cross-contaminate with scoops, cups, or stirrers that may have been exposed to or used with other chemicals. Use only dedicated clean, dry plastic or stainless steel scoops and utensils for transfer. Do not grind or dry mix in equipment or machines that develop frictional heat.

