Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Agrochemical Functions
- Technologies
- Product Families
Features & Benefits
- Features
- Suppresses adult EAB populations before they mate and lay eggs
- Economical option for ash dense sites
- Tree size does not affect performance
- No acute toxicity to bees or parasitic wasps
- BT, a time tested tool for forest insect control
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Application Technique
- Insecticide Target Species
- Applications
boreGONE! is an H2O dispersible formula containing 76.5% activeingredient. It is to be mixed with water and sprayed using hand‐held, commercial ground or aerial application equipment. Upon fullEPA registration, it is expected that boreGONE! will meet require‐ments of the USDA National Organic Program (NOP) for use in pro‐duction of organic crops. All boreGONE! inert ingredients were se‐lected from those commonly used in food applications.
No harmful effects against mammals, birds or fish
EPA registration tests & decades of BT use against forest and munici‐pal insect pests lead to the conclusion that Bacillus thuringiensis bio‐insecticides are not likely to cause harm to man or the environmentwhen used according to directions.
Compatible with EAB parasitic wasp release
The toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis galleriae to EAB parasitoid wasps was evaluated by the USDA Forest Ser‐vice/Michigan State University*. Wasps were exposed to Bacillus thuringiensis paste suspended in honey at 0.4 micrograms protein toxin per microliter honey, and % survival was evaluated after 7 days exposure. Re‐sults, shown below, confirmed that the parasitoid wasps were unaffected by Bacillus thuringiensis galleriae.Parasitoid Family Origin insects Number of insects % Survival Tetrastichus planipennisi Eulophidae China 20 100% Spathius agrili Braconidae China 20 100% Oobius agrili Encyrtidae China 20 100% Atanycolus spp. Braconidae Michigan 12 100%
Other Non‐Target Insects
Tests have shown that Bacillus thuringiensis galleriae does not affect Honey Bees (Apis mellifera, Hymenop‐tera Apidae); lady bird beetles (Hippodamia convergens, Coleoptera, Coccinellidae); wire worms (Melanotuscommunis, Coleoptera Elateridae), silkworms (Bombyx mori, Lepidoptera, Bombycidae); nor was it toxic against cutworms (Spodoptera litura, Lepidoptera Noctuidae). No toxicity is expected against any Hymenop‐teran spp.
Technical Details & Test Data
- Details
Bacillus thuringiensis galleriae
Used by organic gardeners, mosquito control districts and foresters for decades, Bacillus thuringiensis (BT) is natural and widespread in nature, thriving in soil and sediments. The insect toxicity of BT is attributable to crystalline proteins (Cry proteins) produced during spore formation. Each BT strain produces a unique Cry protein. Each Unique Cry protein is toxic to specific groups of insects. Phyllom’s BT galleriae strain produces Cry proteins which are toxic to certain species of insects in the order Coleoptera (beetles). BT must be in‐ gested by insects for control. Once ingested, the insect’s digestive enzymes cleave the BT protein to form a stable insect toxin. The protein then progresses through the insect’s diges‐ tive system, where the protein causes the formation of pores, which leads to toxicity as manifested by the cessation of insect feeding and gut paralysis, fol‐ lowed by the formation of midgut le‐ sions and then leading to the death of the Emerald Ash Borer.
boreGONE!
boreGONE! was tested against adults of the Emerald Ash Borer (Agrilus planipennis) on potted green ash at the Morton Arboretum, Lisle, IL. The high rate gave 100% cumulative mortality after 8 days.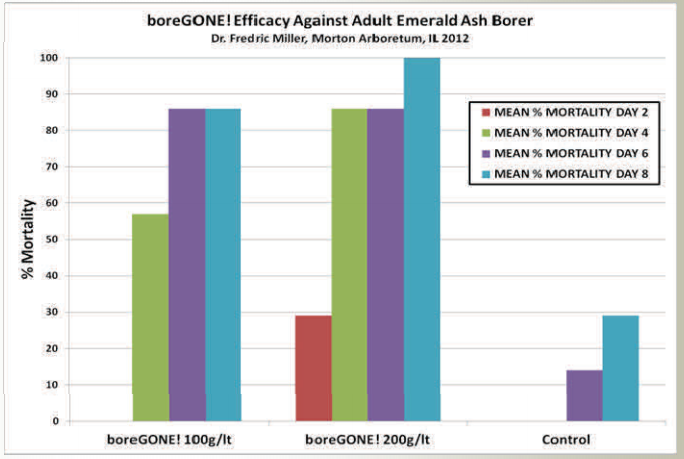
Application Timing
To help prevent or slow tree and forest mortality and to manage adult beetle populations, apply boreGONE! from after adult emergence to during the peak of adult flight for the targeted tree species as determined by degree day models, pest surveys or pest trapping programs. Repeat as often as needed to reduce beetle popu‐ lations to threshold levels through the season. Consult with local, state and federal foresters and arborists or cooperative extension to access information related to predictive models and or surveys which predict the best timing of applications against Emerald Ash Borer.

