Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Name
- Base Chemicals Functions
- CAS No.
- 108-78-1
- EC No.
- 203-615-4
- Technologies
- Product Families
Features & Benefits
- Product Highlights
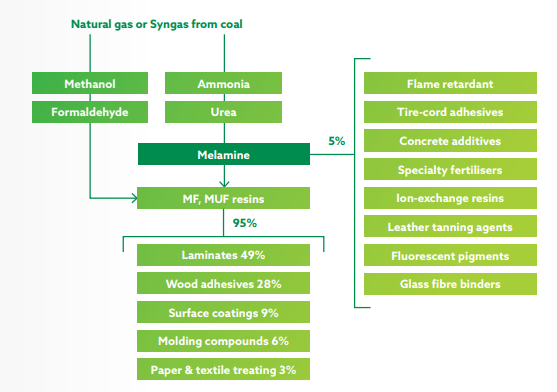
Melamine resins are produced by the condensation polymerization reaction of melamine with formaldehyde to yield melamine-formaldehyde (MF) resins. Continued efforts to reduce formaldehyde emissions have a positive effect on melamine consumption, since melamine is a strong formaldehyde binding agent.
Melamine is a constant presence in everyday life. Dinnerware, laminates, flooring, and medium density fibreboards owe their hardness, flame-resistance, mar-resistance and waterproofing to melamine. Being able to form strong stable bonds with formaldehyde, melamine confers MF and MUF resins unique features thanks to the high nitrogen content (66% wt) of the molecule, which is essential for the flame retardant and fire-resistant properties in the finished goods. If exposed to intense heat they give off nitrogen without producing toxic gasses, diluting oxygen and inhibiting the combustion. New aircrafts interiors, for instance, make use of melamine-based flame-retardants in order to comply with the most stringent safety requirements.
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Base Chemicals End Uses
- Applications
- Household items such as flooring and dinnerware
- As a flame retardant
- As a concrete plasticiser
- Process Flow Chart
Regulatory & Compliance
- Regulatory
Implementation of stricter limits on formaldehyde emissions by the California Air Resources Board (CARB) set lower emission levels for the formaldehyde in composite wood products (such as plywood, particleboard, medium-density fibreboard MDF). CARB Phase 1, followed by stricter Phase 2, has been taken as reference by Japan and Europe, which are enforcing similar laws. Class E1 boards have become the industry standard in Europe; they are defined as panels having a limit of ≤ 0.1 ppm formaldehyde content/emission. E0 boards, featuring emissions which are one-tenth those of E1, are also becoming available.

