Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Additives Included
- Chemical Family
- Polymer Name
- Plastics & Elastomers Functions
- Technologies
Features & Benefits
- Materials Features
- Wear and Friction Solutions Lubriloy Alloy Technology
The recently introduced LUBRICOMP DX19519H compound exhibits good flow in thin-wall parts and reduces frictional forces associated with squeak generation during operation of buttons and sliders. It joins a family of PFPE lubricated grades embraced by drug delivery device and surgical tool manufactures as a reliable way to get improved friction performance from tight tolerance parts.
- Features
Improved “slip-stick”, low friction, low squeak, thin wall molding.
Applications & Uses
- Applications
- Plastics & Elastomers End Uses
- Plastics & Elastomers Processing Methods
- Possible Applications in Thin-Wall Healthcare
Thin wall medical drug delivery, lab equipment, injector pens/pump.
Properties
- Physical Properties
- Mechanical Properties
- Thermal Properties
- Impact Properties
- Injection Molding
- Note
- ᵍ Measurements made from Laboratory test Coupon. Actual shrinkage may vary outside of range due to differences in processing conditions, equipment, part geometry and tool design. It is recommended that mold shrinkage studies be performed with surrogate or legacy tooling prior to cutting tools for new molded article.
- ⁷ Injection Molding parameters are only mentioned as general guidelines. These may not apply or may need adjustment in specific situations such as low shot sizes, large part molding, thin wall molding and gas-assist molding.
- ¹¹ The information stated on Technical Datasheets should be used as indicative only for material selection purposes and not be utilized as specification or used for part or tool design.
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Melt Flow Rate (at 300°C, 1.2 kgf) ¹¹ | 27.7 | g/10 min | ASTM D1238 |
| Melt Volume Rate (at 300°C, 1.2 kg) ¹¹ | 24.19 | cm³/10 min | ISO 1133 |
| Melt Volume Rate (at 300°C, 1.2 kg) ¹¹ | 24.5 | cm³/10 min | ASTM D1238 |
| Water Absorption (at 23°C, 24hrs) ¹¹ | 0.07 | % | ISO 62-1 |
| Specific Gravity ¹¹ | 1.2 | — | ASTM D792 |
| Mold Shrinkage (flow, 24 hrs) ᵍ ¹¹ | 0.83 | % | ASTM D955 |
| Mold Shrinkage (xflow, 24 hrs) ᵍ ¹¹ | 0.94 | % | ASTM D955 |
| Wear Factor Washer ¹¹ | 211.5 | 10^-10 in^5-min/ft-lb-hr | ASTM D3702 Modified: Manual |
| Dynamic COF ¹¹ | 0.3495 | — | ASTM D3702 Modified: Manual |
| Moisture Absorption (at 23°C, 50% RH) ¹¹ | 0.28 | % | ISO 62 |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Tensile Modulus (at 50 mm/min) ¹¹ | 2135 | MPa | ASTM D638 |
| Tensile Strain (Break, 50 mm/min) ¹¹ | 45.24 | % | ISO 527 |
| Tensile Strain (Break, Type I, 50 mm/min) ¹¹ | 45.86 | % | ASTM D638 |
| Tensile Strain (Yield, 50 mm/min) ¹¹ | 5.9 | % | ISO 527 |
| Tensile Strain (Yield, Type I, 50 mm/min) ¹¹ | 5.97 | % | ASTM D638 |
| Tensile Stress (Break, 50 mm/min) ¹¹ | 45.24 | MPa | ISO 527 |
| Tensile Stress (Break, Type I, 50 mm/min) ¹¹ | 45.85 | MPa | ASTM D638 |
| Tensile Stress (Yield, 50 mm/min) ¹¹ | 57.69 | MPa | ISO 527 |
| Tensile Stress (Yield, Type I, 50 mm/min) ¹¹ | 57.65 | MPa | ASTM D638 |
| Flexural Modulus (at 1.3 mm/min, 50 mm span) ¹¹ | 2085 | MPa | ASTM D790 |
| Flexural Stress (Break, 1.3 mm/min, 50 mm span) ¹¹ | 79 | MPa | ASTM D790 |
| Tensile Modulus (at 1 mm/min) ¹¹ | 2091.4 | MPa | ISO 527 |
| Flexural Modulus (at 2 mm/min) ¹¹ | 2160 | MPa | ISO 178 |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (at -40°C to 95°C, flow) ¹¹ | 0.0000753 | 1/°C | ASTM E831 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (at -40°C to 95°C, xflow) ¹¹ | 0.0000751 | 1/°C | ASTM E831 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (at 23°C to 80°C, flow) ¹¹ | 0.0000808 | 1/°C | ISO 11359-2 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (at 23°C to 80°C, xflow) ¹¹ | 0.0000795 | 1/°C | ISO 11359-2 |
| Vicat Softening Temperature (Rate B/50) ¹¹ | 145.95 | °C | ISO 306 |
| Heat Deflection Temperature (at 1.82 MPa, 3.2mm, Unannealed) ¹¹ | 123 | °C | ASTM D648 |
| Heat Deflection Temperature/Af (at 1.8 Mpa, Flatw 80*10*4, sp=64mm) ¹¹ | 119.8 | °C | ISO 75/Af |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Charpy Impact (at -30°C, Unnotch Edgew 80*10*4 sp=62mm) ¹¹ | 304.27 | kJ/m² | ISO 179/1eU |
| Charpy Impact (at -30°C, V-notch Edgew 80*10*4 sp=62mm) ¹¹ | 16.86 | kJ/m² | ISO 179/1eA |
| Charpy Impact (at 23°C, Unnotch Edgew 80*10*4 sp=62mm) ¹¹ | 223.51 | kJ/m² | ISO 179/1eU |
| Charpy Impact (at 23°C, V-notch Edgew 80*10*4 sp=62mm) ¹¹ | 43.79 | kJ/m² | ISO 179/1eA |
| Izod Impact (Notched, 80*10*4, at -30°C) ¹¹ | 16.09 | kJ/m² | ISO 180/1A |
| Izod Impact (Notched, at -30°C) ¹¹ | 156 | J/m | ASTM D256 |
| Izod Impact (Unnotched, 80*10*4, at -30°C) ¹¹ | 28.62 | kJ/m² | ISO 180/1U |
| Izod Impact (Notched, at 23°C) ¹¹ | 614 | J/m | ASTM D256 |
| Izod Impact (Unnotched, 80*10*4, at 23°C) ¹¹ | 168.55 | kJ/m² | ISO 180/1U |
| Izod Impact (Notched, 80*10*4, at 23°C) ¹¹ | 44.75 | kJ/m² | ISO 180/1A |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Drying Time (Cumulative) ⁷ | 48 | Hrs | — |
| Drying Time ⁷ | 3 - 4 | Hrs | — |
| Nozzle Temperature ⁷ | 290 - 310 | °C | — |
| Vent Depth ⁷ | 0.025 - 0.076 | mm | — |
| Drying Temperature ⁷ | 120 | °C | — |
| Maximum Moisture Content ⁷ | 0.02 | % | — |
| Melt Temperature ⁷ | 295 - 315 | °C | — |
| Front - Zone 3 Temperature ⁷ | 295 - 315 | °C | — |
| Middle - Zone 2 Temperature ⁷ | 280 - 305 | °C | — |
| Rear - Zone 1 Temperature ⁷ | 270 - 295 | °C | — |
| Mold Temperature ⁷ | 70 - 95 | °C | — |
| Back Pressure ⁷ | 0.3 - 0.7 | MPa | — |
| Screw Speed ⁷ | 40 - 70 | rpm | — |
| Shot to Cylinder Size ⁷ | 40 - 60 | % | — |
Technical Details & Test Data
- Lubricomp for Thin-Wall Healthcare Applications
As designers miniaturize drug delivery devices (insulin pens, inhalers) for improved portability, they are often faced with a difficult dilemma. How do you design for smooth, repeatable, and quiet actuation in parts created with thin walls and maintain the tight dimensional tolerances required? Semicrystalline resins will generally flow better and provide better wear and lower friction compared to amorphous resins, but they can’t always hold the tolerances needed.
Dimensional Accuracy and Low Friction
To get dimensional accuracy and good tribological performance, a common technic is to add an internal lubricant into an amorphous resin. But adding traditional lubrication packages like PTFE and silicone generally reduces the flow of a thermoplastic resin. One possible solution is compounding a high-flow PC Copolymer resin for use in healthcare applications, with PFPE, a fluorinated synthetic oil.
PFPE as Internal Lubricant and Flow Promoter
Perfluoropolyether (PFPE) is available as a USP Class VI material, and it can act as both an internal lubricant, reducing wear and friction, and as a flow aid to improve filling of thin wall parts. The chart below illustrates the effect of adding various lubrication packages on melt viscosity of a high flow PC Copolymer. The PFPE lubricated formulation showed significant improvement in flow and has been shown to reduce assembly and actuation forces in some applications. Based on these results, anew grade LUBRICOMP™ DX19519H compound was created.
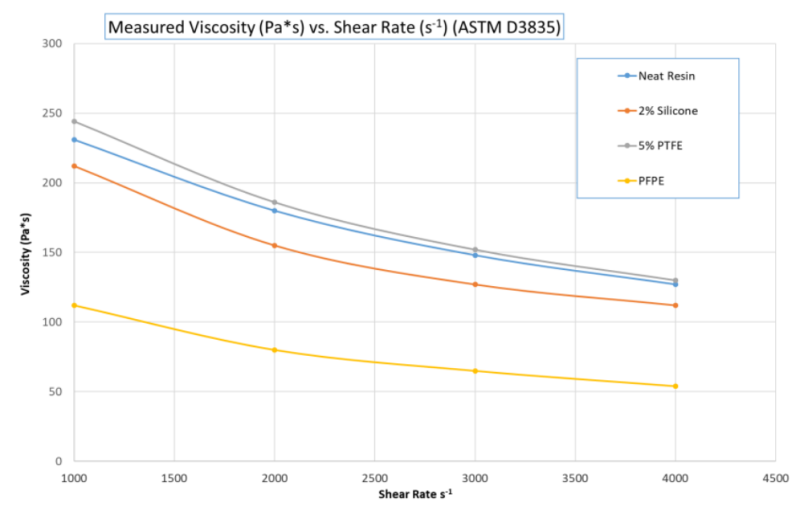
Fig: Viscosity vs shear for a high flow PC copolymer resin with various internal lubrication types.
Packaging & Availability
- Regional Availability

