Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Additives Included
- Chemical Family
- Polymer Name
- Plastics & Elastomers Functions
- Technologies
Features & Benefits
- Labeling Claims
- Materials Features
- Lubriloy Compounds Feature
- Improved impact over PTFE filled materials
- Lower mold deposits
- Excellent surface finish & colorability
- Lower S.G. vs. PTFE filled materials
- Non-halogenated lubrication
Applications & Uses
- Applications
- Plastics & Elastomers End Uses
- Plastics & Elastomers Processing Methods
- Recommended Applications
- Surgical stapler internals
- Laparoscopic surgical tool internals
- Trocar latches
- Insulin pen dials, screw, and sleeve
- Inhaler dose counter buttons
- Fluid coupling quick disconnect
- Lubriloy Compounds Applications
PC based LUBRILOY alloys are widely used in consumer electronics and medical applications for combination of low wear and friction, tight dimensional tolerances and nonhalogenated FR systems. They have also been used in automotive interiors for BSR reduction.
Properties
- Mechanical Properties
- Physical Properties
- Thermal Properties
- Impact Properties
- Injection Molding
- Note
- ᵍ Measurements made from Laboratory test Coupon. Actual shrinkage may vary outside of range due to differences in processing conditions, equipment, part geometry and tool design. It is recommended that mold shrinkage studies be performed with surrogate or legacy tooling prior to cutting tools for new molded article.
- ⁷ Injection Molding parameters are only mentioned as general guidelines. These may not apply or may need adjustment in specific situations such as low shot sizes, large part molding, thin wall molding and gas-assist molding.
- ¹¹ The information stated on Technical Datasheets should be used as indicative only for material selection purposes and not be utilized as specification or used for part or tool design.
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Tensile Stress (Yield) ¹¹ | 53 | MPa | ASTM D638 |
| Tensile Stress (Yield) ¹¹ | 54 | MPa | ISO 527 |
| Tensile Stress (Break) ¹¹ | 53 | MPa | ISO 527 |
| Tensile Stress (Break) ¹¹ | 60 | MPa | ASTM D638 |
| Tensile Strain (Yield) ¹¹ | 6.5 | % | ASTM D638 |
| Tensile Strain (Yield) ¹¹ | 6.2 | % | ISO 527 |
| Tensile Strain (Break) ¹¹ | 125 | % | ASTM D638 |
| Tensile Strain (Break) ¹¹ | 138 | % | ISO 527 |
| Tensile Modulus (at 50 mm/min) ¹¹ | 1860 | MPa | ASTM D638 |
| Flexural Stress ¹¹ | 78 | MPa | ISO 178 |
| Flexural Stress ¹¹ | 82 | MPa | ASTM D790 |
| Flexural Modulus ¹¹ | 2130 | MPa | ASTM D790 |
| Flexural Modulus ¹¹ | 2130 | MPa | ISO 178 |
| Tensile Modulus (at 1 mm/min) ¹¹ | 1980 | MPa | ISO 527 |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Density ¹¹ | 1.17 | g/cm³ | ASTM D792 |
| Density ¹¹ | 1.17 | g/cm³ | ISO 1183 |
| Moisture Absorption (at 23°C, 50% RH, 24hrs) ¹¹ | 0.13 | % | ASTM D570 |
| Mold Shrinkage (flow, 24 hrs) ᵍ ¹¹ | 0.7 - 0.9 | % | ASTM D955 |
| Mold Shrinkage (flow, 24 hrs) ᵍ ¹¹ | 0.7 - 0.9 | % | ISO 294 |
| Mold Shrinkage (xflow, 24 hrs) ᵍ ¹¹ | 0.8 - 1 | % | ASTM D955 |
| Mold Shrinkage (xflow, 24 hrs) ᵍ ¹¹ | 0.8 - 1 | % | ISO 294 |
| Wear Factor Washer ¹¹ | 50 | 10^-10 in^5-min/ft-lb-hr | ASTM D3702 Modified: Manual |
| Dynamic COF ¹¹ | 0.32 | — | ASTM D3702 Modified: Manual |
| Static COF ¹¹ | 0.22 | — | ASTM D3702 Modified: Manual |
| Moisture Absorption (at 23°C, 50% RH) ¹¹ | 0.19 | % | ISO 62 |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Heat Deflection Temperature (at 0.45 MPa, 3.2 mm, Unannealed) ¹¹ | 140 | °C | ASTM D648 |
| Heat Deflection Temperature (at 1.82 MPa, 3.2mm, Unannealed) ¹¹ | 126 | °C | ASTM D648 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (at -40°C to 40°C, flow) ¹¹ | 0.0000741 | 1/°C | ASTM E831 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (at -40°C to 40°C, flow) ¹¹ | 0.0000742 | 1/°C | ISO 11359-2 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (at -40°C to 40°C, xflow) ¹¹ | 0.0000738 | 1/°C | ASTM E831 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (at -40°C to 40°C, xflow) ¹¹ | 0.0000738 | 1/°C | ISO 11359-2 |
| Heat Deflection Temperature/Bf (at 0.45 Mpa, Flatw 80*10*4, sp=64mm) ¹¹ | 140 | °C | ISO 75/Bf |
| Heat Deflection Temperature/Af (at 1.8 Mpa, Flatw 80*10*4, sp=64mm) ¹¹ | 126 | °C | ISO 75/Af |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Izod Impact (Unnotched, at 23°C) ¹¹ | No break | J/m | ASTM D4812 |
| Izod Impact (Notched, at 23°C) ¹¹ | 715 | J/m | ASTM D256 |
| Instrumented Dart Impact Energy (Peak, at 23°C) ¹¹ | 40 | J | ASTM D3763 |
| Multi-Axial Impact ¹¹ | 48 | J | ISO 6603 |
| Izod Impact (Unnotched, 80*10*4, at 23°C) ¹¹ | 137 | kJ/m² | ISO 180/1U |
| Izod Impact (Notched, 80*10*4, at 23°C) ¹¹ | 56 | kJ/m² | ISO 180/1A |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Drying Temperature ⁷ | 100 | °C | — |
| Drying Time ⁷ | 4 | Hrs | — |
| Maximum Moisture Content ⁷ | 0.02 | % | — |
| Melt Temperature ⁷ | 290 - 315 | °C | — |
| Front - Zone 3 Temperature ⁷ | 280 - 310 | °C | — |
| Middle - Zone 2 Temperature ⁷ | 280 - 300 | °C | — |
| Rear - Zone 1 Temperature ⁷ | 275 - 300 | °C | — |
| Mold Temperature ⁷ | 65 - 95 | °C | — |
| Back Pressure ⁷ | 0.2 - 0.3 | MPa | — |
| Screw Speed ⁷ | 30 - 60 | rpm | — |
Technical Details & Test Data
- LNP™ Compounds Wear and Friction Solutions Medical Devices
For a medical device, whether it be a drug delivery pen or a laparoscopic surgical tool, repeatable and efficient motion is critical to performance. The friction between moving parts plays a large role in how a device is perceived and accepted by both consumers and healthcare professionals. LUBRICOMP™ and LUBRILOY™ compounds can help deliver the performance required.
Growing List of Demands
The demands on wear and friction materials for medical devices grow as sterilization and cleaning techniques evolve, parts get smaller and thinner, and market trends move towards more consumer friendly styling and colors. Add the heightened emphasis on system cost optimization and the need for innovative internally lubricated thermoplastic solutions expands.
Internally Lubricated Compounds
The addition of an internal lubricant to a thermoplastic material can reduce the coefficient of friction between two plastic parts, allowing them to slide past each other smoothly with minimal wear. Traditional lubricants like medical grade silicone and PTFE can be combined with advanced PC copolymer technology to deliver the required performance in thin wall parts.
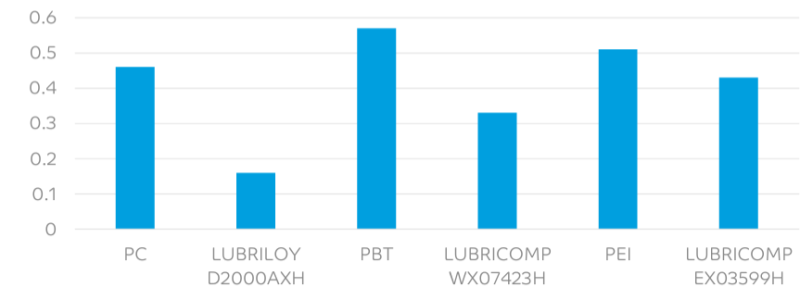
- Dynamic Cof Vs Steel
Packaging & Availability
- Regional Availability

