Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Industrial Additives Functions
- CAS No.
- 127087-87-0
- EC No.
- 500-315-8
- Technologies
- Chemical Structure
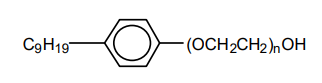
- Surfactant Type
Nonionic.
Features & Benefits
- Labeling Claims
- Industrial Additives Features
- Biodegradability
POLYSTEP F products are biodegradable.
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applicable Processes
- Applications
POLYSTEP® F-9 surfactants are nonionic in nature; they neither ionize in water nor hydrolyze in aqueous acid or alkaline solutions. Chemically, they are the reaction products of nonylphenol and ethylene oxide. They differ in the mole ratio of hydrophilic ethylene oxide to hydrophobic nonylphenol. POLYSTEP® F-9 surfactants offer a broad range of properties. In combination with other surfactants POLYSTEP F products tend to increase latex particle size and contribute to freeze-thaw and mechanical stability.
Properties
- Physical Form
- Appearance
- Clear viscous liquid
- Typical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| pH (in 5% in water) | 6.5 | — | — |
| Actives Content | 70 | % | — |
| Color | max. 150 | — | Apha Scale |
| Pour Point | 3 | °C | — |
| Cloud Point (in 1% in 10% NaCl in water) | 76 | °C | — |
| Hydroxyl Number | 38 | — | — |
| HLB | approx. 17 | — | — |
| Average Moles of EO | 30 | — | — |
| Viscosity (at 25°C) | 700 | cPs | — |
| Flash Point | min. 94 | °C | — |
| Density | 1.06 | g/ml | — |
| Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC) | 42 | mg/L | — |
| Regulated Volatile Organic Chemicals (Ethanol) | 0 | % | U.S. EPA |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
- Clearances
- All components of POLYSTEP F surfactants are listed in the following countries; the registration numbers for the active ingredients are included in parentheses: United States (TSCA 127087-87-0), Australia (AICS 127087-87- 0), Canada (DSL 127087-87-0), China (IECSC 127087-87-0), Europe (NLP 500-315-8), Japan (ENCS 7-172), Korea (ECL Serial No. KE-26246), New Zealand (NZIoC 127087-87-0), and Philippines (PICCS 127087-87-0). It is the responsibility of the end user to review the chemical control regulations for each country. It is the responsibility of the formulator to review the chemical control regulations for each country where the end product is intended to be sold or used.
- POLYSTEP® F-9 is available as Kosher certified.
Safety & Health
- Health Effects
These products are relatively harmless orally (LD50 >16,000 mg/kg b.w.) and mildly to non-irritating to skin and eyes.
Packaging & Availability
- Standard Packaging
: POLYSTEP F-9 is made-to-order materials available in drums and in bulk quantities.
Storage & Handling
- Storage & Handling
Normal safety precautions (i.e., gloves and safety goggles) should be employed when handling POLYSTEP F products. Contact with the eyes and prolonged contact with the skin should be avoided. Wash thoroughly after handling material. It is recommended that POLYSTEP F products be stored in sealed containers and kept in a cool, dry place. If material has been frozen it should be heated gently and stirred to ensure it is homogeneous before use.
Bulk Storage Information
POLYSTEP F surfactants can be stored in vessels of 316 stainless steel. Material should be stored between 29 – 43 °C (85 – 110 °F). An internal hairpin coil of carbon steel with low pressure steam (under 50 psig) should be used if heating is required. Mild agitation is required if the tank is heated. Heating may not be required for inside storage if the tank is turned over frequently. Stainless steel 316 is preferred for pumps, pipes, and transfer lines.
- Workplace Exposure
Occupational exposure can occur primarily through skin contact or via inhalation of vapors and mists Engineering controls, personal protective equipment, and other workplace practices should be used to control these exposures.

