Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Fillers Included
- Polymer Name
- Reinforcement Form
- Reinforcement Material
- Composite Materials Functions
- Plastics & Elastomers Functions
- Technologies
Features & Benefits
- Labeling Claims
- Materials Features
- Product Highlights
As OEMs continue to downsize high-performance engines, cooling systems need to be smaller and more efficient. Coolant expansion tanks contain a volume reserve to compensate for volume differences of the liquid and cooling components due to thermal expansion. The coolant expansion tank is also known as the coolant reservoir, or overflow canister.
As the engine heats up, the coolant inside it expands. Without the expansion tank, the coolant would flow out of the overflow tube and be lost from the cooling system onto the street. Instead, the coolant flows into the expansion tank and remains in the system.
The requirements for the materials used in these parts are high.
The material must withstand:
• Under-the-hood temperatures of 105°C to 150°C
• Exposure to water glycol
• Internal coolant temperatures of 120°C to 137°C
• Internal pressure levels of more than 2.3 bar
• Vibration from the chassis or engineThe material must also demonstrate good welding properties, with high strength at the weld line at under-the-hood temperatures. Under these conditions, materials such as polypropylene (PP) and polyamide 66 (PA66) are at the limit of their performance capabilities. Manufacturers using these materials have increased wall thicknesses to meet the higher specifications required for the part. As the specifications for the materials continue to increase with smaller spaces and higher engine temperatures,
manufacturers can no longer improve the part’s performance by increasing wall thicknesses, as the materials have reached their limit due to manufacturing constraints.
A drop-in solution when PA66 fails
EcoPaXX® is a bio-based high-performance polyamide 410 (PA410) that provides outstanding performance across a broad range of applications. EcoPaXX® can be used as a drop-in solution without the need for retooling or costly tool modifications in cases where PA66 fails to meet changing requirements. EcoPaXX® demonstrates superior chemical stability and weld-line strength after aging, resulting in a part that lasts up to three times longer, with higher safety margins. This eliminates the need to replace the part during the lifetime of the vehicle, and reduces the risk of hazardous or explosive failure.
Designing for EcoPaXX®
When the coolant expansion tank is designed for production in EcoPaXX®, it can be optimized to fulfill functionality and application requirements at the lowest possible weight and cost. The material’s superior performance, especially for weld-line stability, is so high that the part can be produced with thinner walls, resulting in a 30% reduction in weight and 50% reduction in cooling times versus PA66. This thinner, lighter part design is technically superior, yet cost neutral compared with PA66.
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Plastics & Elastomers End Uses
- Composites Processing Methods
- Plastics & Elastomers Processing Methods
- Potential Applications
Envalior's polyamide-based UD tapes with endless carbon or glass fiber reinforcements are viable, lightweight alternatives to metals in several applications. UD tapes, tape-based 2D fabrics and crossplies are used in structural and semi-structural applications, as well as in the selective reinforcement of injection molded parts.
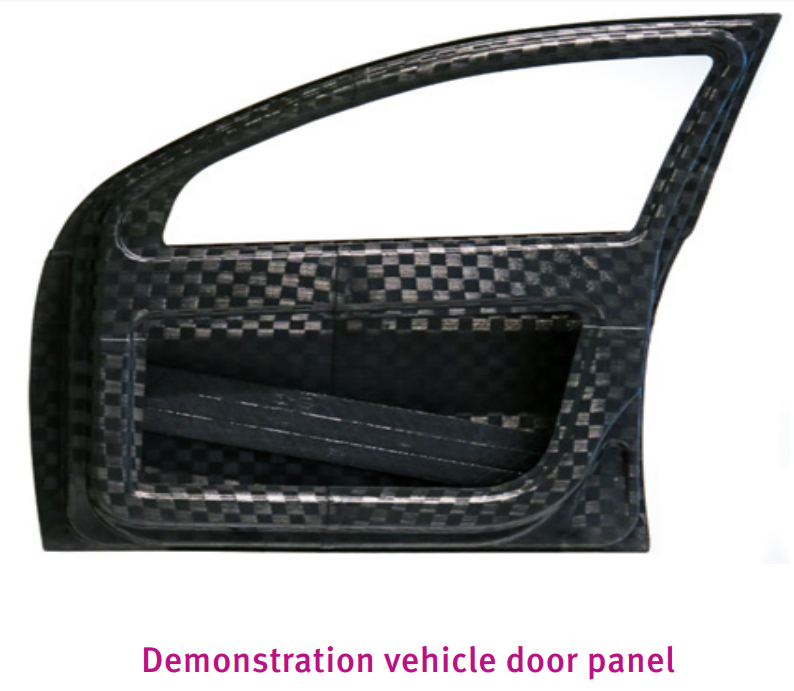

A demonstration vehicle door panel made by JLR from carbon fiber-reinforced PA410, as well as fabric sheets woven from the same UD tape (EU-sponsored ENLIGHT project). The UD tape products were thermo-formed and glued to make the panel, which is 60% lighter than state- of-the-art, steel-based designs, while still fulfilling safety requirements. The full composite door consists of structural panels and a tape-wound side impact beam over an extruded, permanent mandrel.
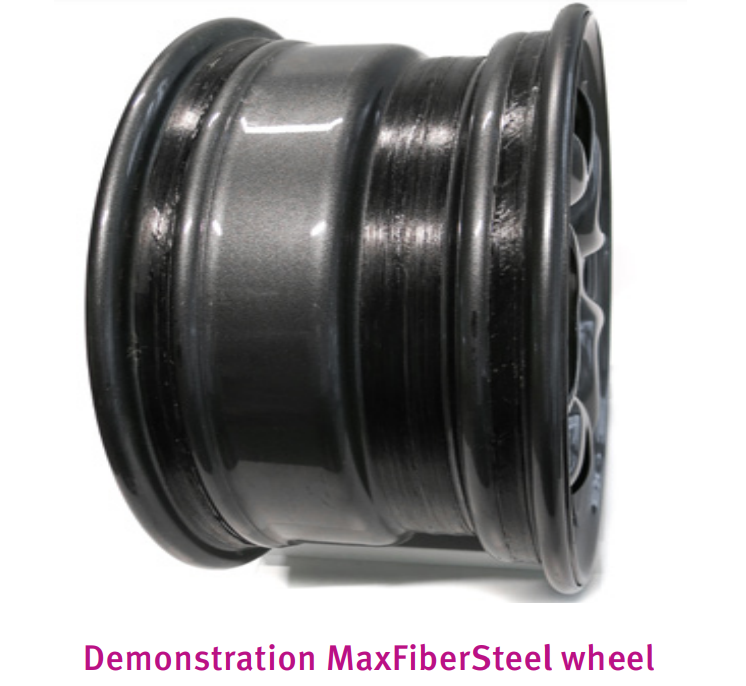

Maxion Wheels and Envalior successfully manufactured and tested (Rim Rolling Fatigue) thin-walled hybrid, steelcomposite automotive wheel-rim reinforced with UD tape (tape-winding) made from glass fiber-reinforced PA410. The hybrid wheel-rim is 2Kg lighter and 30% more fatigue-resistant than state-ofthe- art, steel design, whilst inert to road salts and battery acids.
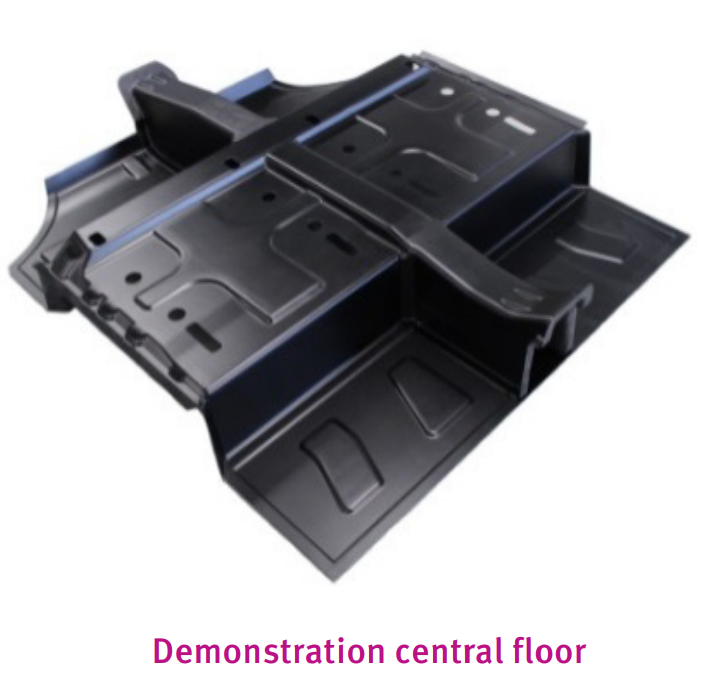

A vehicle central-floor module from carbon fiber-reinforced PA410 made by FCA (EU-sponsored ENLIGHT project). The UD tapes based ply-books were thermoformed to the final shape. The composite part is 18% lighter than state-of-the-art, steel-based designs, while still fulfilling safety requirements. The composite strength and dimensional stability are not affected by the E-coating process, a requirement of BIW parts.
Properties
- Mechanical Properties
- Thermal Properties
- Electrical Properties
- Other Properties
- Rheological Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Tensile Modulus | 9500 / 7000 | MPa | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Tensile Modulus (120°C) | 4600 / - | MPa | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Tensile Modulus (160°C) | 3700 / * | MPa | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Tensile Modulus (180°C) | 3200 / * | MPa | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Tensile Modulus (200°C) | 3000 / * | MPa | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Stress at Break | 170 / 115 | MPa | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Stress at Break (120°C) | 85 / - | MPa | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Stress at Break (160°C) | 70 / * | MPa | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Stress at Break (180°C) | 65 / * | MPa | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Stress at Break (200°C) | 60 / * | MPa | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Strain at Break | 4 / 5.8 | % | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Strain at Break (at 120°C) | 8.2 / - | % | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Strain at Break (at 160°C) | 9.4 / * | % | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Strain at Break (at 180°C) | 10 / * | % | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Strain at Break (at 200°C) | 10 / * | % | ISO 527-1/-2 |
| Flexural Modulus | 8500 / 6300 | MPa | ISO 178 |
| Flexural Strength | 260 / 185 | MPa | ISO 178 |
| Charpy Impact Strength (at +23°C) | 80 / 80 | kJ/m² | ISO 179/1eU |
| Charpy Impact Strength (at -30°C) | 60 / - | kJ/m² | ISO 179/1eU |
| Charpy Notched Impact Strength (at +23°C) | 11 / 15 | kJ/m² | ISO 179/1eA |
| Charpy Notched Impact Strength (at -30°C) | 9 / - | kJ/m² | ISO 179/1eA |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Melting Temperature (10°C/min) | 250 / * | °C | ISO 11357-1/-3 |
| Temperature of Deflection Under Load (1.80 MPa) | 215 / * | °C | ISO 75-1/-2 |
| Temperature of Deflection Under Load (0.45 MPa) | 243 / * | °C | ISO 75-1/-2 |
| Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion (parallel) | 0.32 / * | E-4/°C | ISO 11359-1/-2 |
| Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion (normal) | 0.66 / * | E-4/°C | ISO 11359-1/-2 |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Volume Resistivity | >1E13 / 2E12 | Ohm*m | IEC 62631-3-1 |
| Surface Resistivity | - / 1.5E14 | Ohm | IEC 62631-3-2 |
| Electric Strength | 40 / 35 | kV/mm | IEC 60243-1 |
| Comparative Tracking Index | - / 600 | V | IEC 60112 |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Humidity Absorption | 1.5 / * | % | Sim. to ISO 62 |
| Density | 1340 / - | kg/m³ | ISO 1183 |
| Biobased Content | 70 / * | % (Bio C/Total C) | ASTM D6866-12 Method B |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Molding Shrinkage (parallel) | 0.6 / * | % | ISO 294-4 |
| Molding Shrinkage (normal) | 1.1 / * | % | ISO 294-4 |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
Technical Details & Test Data
- Envalior's Automotive Weight Loss Factory
Extreme light weighting of automobiles is the most efficient technology for reducing emissions and enhancing mileage. The Envalior Weight Loss Factory utilizes unidirectional, continuous fiber-reinforced, thermoplastic tapes as the fundamental building block of such light weight composite materials.
Our strategy extends well beyond just manufacturing the composite tapes. We also develop and specify processes such as Automatic Tape Placement (ATP), tape winding and tape-insert over-molding. and the necessary computer aided engineering (CAE) for part design and manufacturing process specifications. Envalior is active in the industry in specifying and standardizing composite material testing and quality specifications.UD tape processes
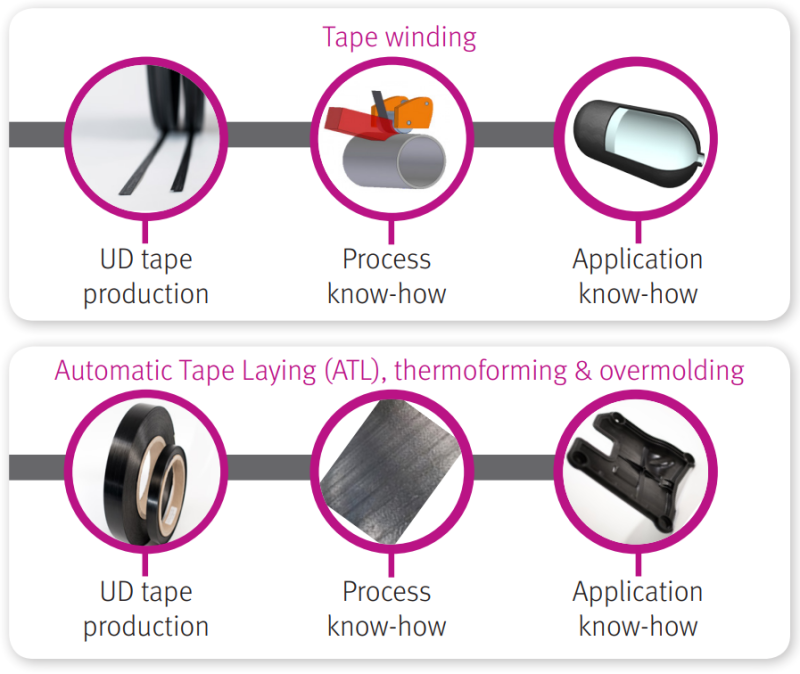
UD tape manfucaturing process
- Tape winding of parts with rotational symmetry (cylinders, tubes, box-beams etc.).
- Automatic Tape Laying (ATL) (panels, sheets, etc.)
- ATL panels are thermoformed to net shape
- ATL panels are over-molded with structural features (ribs, etc.).
- Hybrid metal-composite construction (composite patches glued to metal).
Technology and support
Design and CAE
- FEM analyzes (static & high-strain)
- Thermoforming and over-molding simulation
- UD tape winding and simulation
- Mold flow analyzes (injection-molding)
In-house macro & micro structural analysis of UD tapes
- Material-modeling and micro-mechanics
- Micro CT scans (void content, fiber-filament orientation, fiber-matrix adhesion, etc.)
- SEM micrography
- Tensile, flexural and impact testing.
Bonding
- Composite to plastic
- Composite to metal (with and without adhesives).
- Chemical Resistance
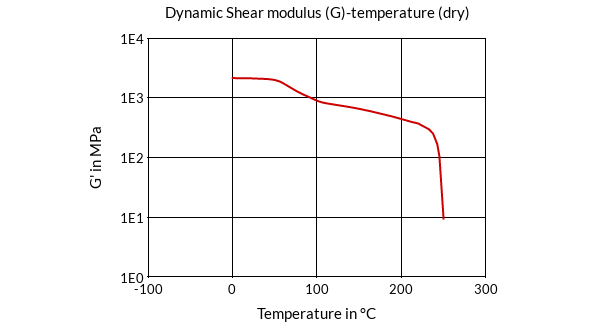
Chemical Type Chemical Name Resistance Other Acetaldehyde (40% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Acetamide (50% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Acetamide (50% by mass) at >140°C not resistant Other Acetic acid (10% by mass) at 100°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Acetic acid (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Acetic acid (95% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Ketones Acetone at 23°C resistant Other Acetophenone at 23°C resistant Other Acetyl chloride at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Acetylene at 23°C resistant Other Acrylic acid at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Aliphatic amines at 23°C resistant Other Aliphatic hydrocarbons at 23°C resistant Other Alkylbenzenes at 23°C resistant Other Allyl alcohol at 23°C resistant Other Aluminum acetate (saturated) at 23°C resistant Other Aluminum chloride (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Aluminum hydroxide (saturated) at 23°C resistant Other Aluminum salts of mineral acids (saturated) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Aluminum trichloride (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Amino acids (saturated) at 23°C resistant Other Ammonia at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Ammonium chloride (35% by mass) at 100°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Ammonium chloride (35% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Ammonium hydroxide (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Ammonium salts of mineral acids (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Ammonium salts of mineral acids (10% by mass) at 50°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Ammonium thiocyanate (saturated) at 23°C resistant Other Amyl acetate at 100°C not resistant Other Amyl acetate at 23°C resistant Other Amyl alcohol at 23°C resistant Other Aniline at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Anodizing liquid (HNO3/H2SO4) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Antimony trichoride (saturated) at 23°C not resistant Other Aqua Regia (HCl/HNO3) at 23°C not resistant Other Aromatic hydrocarbons at 23°C resistant Other ASTM 1 at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other ASTM 3 at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Bariumsalts of mineral acids at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Benzaldehyde at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Benzene at 23°C resistant Other Benzene at 80°C resistant Other Benzoic acid (20% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Benzoic acid (saturated) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Benzyl alcohol at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Beverages at 23°C resistant Other Bleaching agent (NaOCl) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Blood at 23°C resistant Other Boric acid (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Boron trifluoride at 23°C not resistant Other Brake fluids (DOT 3/4) at 23°C resistant Other Bromine water (saturated) at 23°C not resistant Other Bromobenzene at 23°C resistant Other Bromochlorodifluoromethane at 23°C resistant Other Bromotrifluoromethane at 23°C resistant Other Burnishing oil at 23°C resistant Other Butadiene at 23°C resistant Other Butane at 23°C resistant Other Butanediols at 23°C resistant Other Butanediols at >140°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Butanols at 23°C resistant Other Butene glycol at 23°C resistant Other Butene glycol at >160°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Butene-1 at 23°C resistant Other Butter at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Butyl acetate at 23°C resistant Other Butyl acrylate at 23°C resistant Other Butyl glycolate at 23°C resistant Other Butyl phthalate at 23°C resistant Other Butyric acid (20% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Butyrolactone at 23°C resistant Other Butyrolactone at >90°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Calcium chloride (10% by mass) at 100°C resistant Other Calcium chloride (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Calcium chloride (alcoholic) (20% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Calcium chloride (saturated) at 100°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Calcium chloride (saturated) at 23°C resistant Other Calcium chloride (saturated) at 60°C resistant Other Calcium hydroxide (saturated) at 23°C resistant Other Calcium hypochloride (saturated) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Camphor (alcoholic) (50% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Caprolactam (50% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Caprolactam (50% by mass) at >150°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Carbon disulfide at 23°C resistant Other Carbon disulfide at 60°C not resistant Other Carbon tetrachloride at 23°C resistant Other Casein at 23°C resistant Other Castor oil at 23°C resistant Other Chloral hydrate at 23°C not resistant Other Chloramines (10% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Chlorinated biphenyls at 80°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Chlorine water at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Chloroacetic acid (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Chlorobenzene at 23°C resistant Other Chlorobenzene at 50°C resistant Other Chlorobromomethane at 23°C resistant Other Chlorodifluoroethane at 23°C resistant Other Chlorodifluoromethane at 23°C resistant Other Chlorofluoroethylene at 23°C resistant Other Chloroform at 23°C not resistant Other Chlorosulfonic acid (10% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Chromic acid (1% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Chromic acid (10% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Chromyl chloride at 23°C not resistant Other Cinnamon at 23°C resistant Other cis-2-butene at 23°C resistant Other Citric acid (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Citric acid (20% by mass) at 80°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Cobalt salt (20% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Copper sulfate (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Copper(II) salt (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Cresols at 23°C not resistant Other Cycloalcohols (incl their esters) at 23°C resistant Other Cycloalkanes at 23°C resistant Other Cycloalkanones at 23°C resistant Other Cyclohexanol at 23°C resistant Other Decalin at 23°C resistant Other Developer (photografic) at 23°C resistant Other Diamyl phthalate at 23°C resistant Other Dibutyl phthalate at 23°C resistant Other Dibutyl phthalate at 60°C resistant Other Dichlorobenzene at 23°C resistant Other Dichloroethane at 23°C resistant Other Dichloroethylene at 23°C resistant Other Dichlorofluoromethane at 23°C resistant Other Dichlorotetrafluoroethane at 23°C resistant Ethers Diethyl ether at 23°C resistant Other Diethylene glycol at 23°C resistant Other Diethylene glycol at >140°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Difluoromethane at 23°C resistant Other Dimethyl acetamide at 23°C resistant Other Dimethyl acetamide at >150°C not resistant Other Dimethyl ether at 23°C resistant Other Dimethylamine at 23°C resistant Other Dimethylformamide at 23°C resistant Other Dimethylformamide at 90°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Dimethylsilane at 23°C resistant Other Dimethylsulfoxide at 125°C not resistant Other Dimethylsulfoxide at 23°C resistant Other Dioctyl phtalate at 23°C resistant Other Dioxan at 23°C resistant Other Dioxan at 60°C resistant Other Diphenyl ether at 80°C resistant Other Dipropyl ether at 23°C resistant Other Drilling oil at 23°C resistant Other Duck grease at 23°C resistant Other Edible fats waxes and oils at 100°C resistant Other Electroplating bath (acidic) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Electroplating bath (alkali) at 23°C resistant Other Essential oil at 23°C resistant Other Ethane at 23°C resistant Alcohols Ethanol at 23°C resistant Other Ethyl Acetate at 23°C resistant Other Ethyl amine at 23°C resistant Other Ethyl bromide at 23°C resistant Other Ethyl chloride at 23°C resistant Other Ethylene at 23°C resistant Other Ethylene carbonate at 100°C not resistant Other Ethylene carbonate at 50°C resistant Other Ethylene chlorohydrin at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Ethylene glycol at 100°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Ethylene glycol at 23°C resistant Other Ethylene oxide at 23°C resistant Other Ethylene oxide at >80°C not resistant Other Ethylenediamine at 23°C resistant Other Fatty acids at 23°C resistant Other Fatty alcohols at 23°C resistant Other Ferric chloride (2,5% by mass) at 100°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Ferric chloride (2,5% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Fish oil at 23°C resistant Other Fixer (photografic) at 23°C resistant Other Fluorinated hydrocarbons at 70°C resistant Other Fluorine at 23°C not resistant Other Formaldehyde (30% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Formamide at 23°C resistant Other Formamide at >150°C not resistant Other Formic acid (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Formic acid (10% by mass) at 50°C not resistant Other Fruit juices at 23°C resistant Other Fuel; Diesel at 85°C resistant Other Fuel; FAM 1A at 23°C resistant Other Fuel; FAM 2A at 23°C resistant Other Fuel; Gasoline at 85°C resistant Other Fuel; LPG at 23°C resistant Other Furfural at 23°C resistant Other Furfuryl alcohol at 23°C resistant Other Glucose at 23°C resistant Other Glycerol at 170°C not resistant Other Glycerol at 23°C resistant Other Glycolic acid (30% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Glycols at 23°C resistant Other Grease (based on ester oils) at <100°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Grease (based on metal soaps) at <100°C resistant Other Grease (based on polyphenylester) at <100°C resistant Other Hardening oils at 23°C resistant Other Heating oils at 23°C resistant Other Heptane at 23°C resistant Other Hexachlorobenzene at 80°C resistant Other Hexachloroethane at 23°C resistant Other Hexafluoroisopropanol at 23°C not resistant Other Hexane at 23°C resistant Other Hydraulic fluids at 100°C resistant Other Hydrobromic acid (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Hydrochloric acid (10% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Hydrochloric acid (20% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Hydrochloric acid (conc.% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Hydrofluoric acid (40% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Hydrofluoric acid (5% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Hydrogen at 23°C resistant Other Hydrogen peroxide (0.5% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Hydrogen peroxide (1% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Hydrogen peroxide (3% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Hydrogen peroxide (30% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Hydrogen sulfide (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Hydroiodic acid at 23°C not resistant Other Hydroquinone (5% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Impregnating oils at 23°C resistant Other Ink at 23°C resistant Other Iodine (alcoholic) at 23°C not resistant Other Iron(III)chloride (acidic) (10% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Iron(III)chloride (neutral) (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Iron(III)chloride (saturated) at 23°C not resistant Other Iron(III)thiocyanate (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other isoamylalcohol at 23°C resistant Other Isocyanates (aromatic) at 23°C resistant Other Isooctane at 80°C resistant Other Isopropanol at 23°C resistant Other Isopropanol at 60°C resistant Other Ketones (aliphatic) at 23°C resistant Other Lactic acid at 10°C resistant Other Lactic acid at 90°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Lead acetate (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Linseed oil at 23°C resistant Other Lithium bromide (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Lithium chloride (20% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Lithium hydroxide (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Lithium hydroxide (10% by mass) at 80°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Lubricating oil (gear) at <130°C resistant Other Lubricating oil (hydraulics) at <130°C resistant Other Lubricating oil (transformers) at <130°C resistant Other Magnesium hydroxide (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Magnesium salts (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Maleic acid (25% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Maleic acid (saturated) at 23°C resistant Other Manganese salts (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Mercury at 23°C resistant Other Mercury(II)chloride (saturated) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Methane at 23°C resistant Alcohols Methanol at 23°C resistant Other Methyl acetate at 23°C resistant Other Methyl chloride at 23°C resistant Other Methyl ethyl ketone at 23°C resistant Other Methyl formate at 23°C resistant Other Methyl glycol at 23°C resistant Other Methylamine at 23°C resistant Other Methylaniline at 23°C resistant Other Methylbromide at 23°C resistant Other Methylene chloride at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Methylpyrrolidone at 23°C resistant Other Milk at 23°C resistant Other n-Butyl ether at 23°C resistant Other n-Butyl glycol at 23°C resistant Other Naphtha at 23°C resistant Other Naphthalene at 23°C resistant Other Naphthalenesulfonic acids at 23°C not resistant Other Naphthenic acids at 23°C resistant Other Naphthols at 23°C not resistant Other Nickel nitrate (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Nickel salts (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Nitric acid (10% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Nitric acid (2% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Nitric acid (20% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Nitric acid (conc.% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Nitrobenzene at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Nitrobenzene at >100°C not resistant Other Nitrocellulose lacquers (alcoholic) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Nitrocellulose lacquers (non-alcoholic) at 23°C resistant Other Nitrogen oxides at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Nitromethane at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Nitropropane at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Nitrotoluene at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Nitrotoluene at >100°C not resistant Other Nitrous fumes at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Nitrous oxide at 23°C resistant Other Octane at 23°C resistant Other Octene at 23°C resistant Other Oil (Burmah TAF 21) at 23°C resistant Other Oil (Castrol TAF) at 23°C resistant Other Oil (Shell 10W40) at 23°C resistant Other Oil (Shell Dexron ATF) at 23°C resistant Other Oil (Shell Spirax EP90) at 23°C resistant Other Oil (transformers, switchgear) at 50°C resistant Other Oils (vegatable, mineral, ethereal) at 23°C resistant Other Oleic acid at 23°C resistant Other Oleum (H2SO4+SO3) at 23°C not resistant Other Oxalic acid (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Oxalic acid (10% by mass) at 80°C not resistant Other Ozone at 23°C not resistant Other Paint solvents at 23°C resistant Other Palmatic acid at 80°C resistant Other Paraffin at 23°C resistant Other Pentane at 23°C resistant Other Pentasin CHF 11 (S) at 23°C resistant Other Pentasin CHF 7.1 at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Peracetic acid at 23°C not resistant Other Perchloric acid (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Petroleum at 23°C resistant Other Petroleum ether and solvents at 80°C resistant Other Phenol (alc. sol.) (70% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Phenol (conc.% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Phenol at >40°C not resistant Other Phenyl ether at 23°C not resistant Other Phenyl ethyl alcohol at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Phenyl ethyl alcohol at >160°C not resistant Other Phosphate sol. (neutral, alkaline) (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Phosphine at 23°C resistant Other Phosphoric acid (10% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Phosphoric acid (3% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Phosphoric acid (conc.% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Phthalic acid (saturated) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Polyols at 23°C resistant Other Potassium bromide (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Potassium chloride (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Potassium chloride (10% by mass) at 70°C resistant Other Potassium dichromate (5% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Potassium hydroxide (50% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Potassium nitrate (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Potassium permanganate (1% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Potassium thiocyanate (saturated) at 23°C not resistant Other Propane at 23°C resistant Other Propanol at 23°C resistant Other Propanol at >100°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Propene at 23°C resistant Other Propionic acid (5% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Propionic acid (50% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Pyridine at 23°C resistant Other Pyridine at 80°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Pyrrolidone at 23°C resistant Other Pyruvic acid (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Rainwater (acidic) at 23°C resistant Other Refrigerator oil at 23°C resistant Other Resorcinol (alcoholic) (50% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Road salts at 23°C resistant Other SAE 80 at 23°C resistant Other Salicylic acid (saturated) at 23°C resistant Other Seawater at 23°C resistant Other Silane at 23°C resistant Other Silicone oils at <80°C resistant Other Silicone oils at >100°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Silver nitrate (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Soap solution (10% by mass) at 80°C resistant Other Sodium bichromate (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium bichromate (5% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium bromide (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Sodium cabonate (20% by mass) at 100°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Sodium carbonate (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium chlorate (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium chloride (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium chlorite (10% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Sodium cyanide (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium dichromate (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate at 23°C resistant Other Sodium hydrogen carbonate (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium hydrogen sulfate (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium hydrogen sulfite (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium hydroxide (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium hydroxide (10% by mass) at 80°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Sodium hydroxide (50% by mass) at 23°C limited resistant, tests necessary to verify Other Sodium hypochlorite (10% by mass) at 23°C not resistant Other Sodium hypophosphite (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium lauryl sulfate (30% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium lignosulfonate at 23°C resistant Other Sodium nitrilotriacetate (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium oleate at 23°C resistant Other Sodium pentachlorophenolate at 23°C resistant Other Sodium pyrosulfite (10% by mass) at 23°C resistant Other Sodium salts (nitrate, sulfate) (10% by mass) at 23°C r - Dynamic Shear Modulus (G)-Temperature (dry)
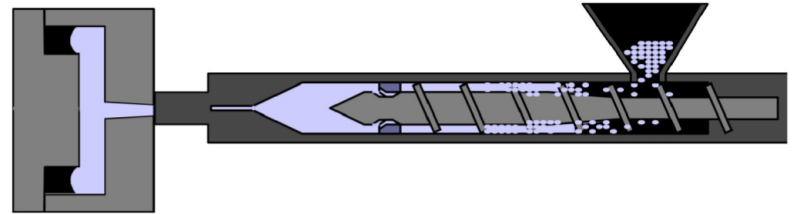
- Machinery for Injection Molding
EcoPaXX® grades can be processed on general injection molding machines.
Screw geometry- Typically 3-zone screw designs with volumetric compression ratios of approximately 2.5 work fine.
Steel type
- Abrasive resistant tool steels which are normally used for glass and/or mineral reinforced materials are also to be used for EcoPaXX® polymers in tools, nozzles and screws.
Nozzle temperature control
- The use of an open nozzle with good temperature control and an independently-controlled thermocouple nearby the tip and heater bands with sufficient output is recommended.
Hot runner layout
- Try to achieve a close contact with your hot runner supplier and Envalior as the material supplier, to be sure that the right hot runner system is chosen.
- When processing EcoPaXX® with hot runners, keep in mind these basic rules:
- Central bushing heated separately
- Only use external heated system
- Manifold heated from both sides
- Tip with thermocouple in front (near gate)
- Very accurate temperature control in the gate area
- Temperature Settings For Injection Molding
Mold Temperature
- EcoPaXX® can be used with a wide range of tool temperatures (80 - 140°C / 176 - 284°F). However, we recommend a low mold temperature for parts with thick walls and a high mold temperature for good dimensional stability, flow properties and surface esthetics.
Barrel Temperature
- Optimal settings are governed by barrel size and residence time. Furthermore, the level of glass and/or mineral reinforcement and the presence or absence of flame retardant have to be taken into account
Mold/Tool Measured melt Nozzle Front Center Rear 80 - 140°C
176 - 284°F275-310°C
527-590°F270-300°C
518-572°F270-290°C
518-554°F260-280°C
500-536°F250-270°C
482-518°FMelt Temperature
- To generate a good and homogeneous melt, the melt temperature should always be above 275°C / 527°F. Optimal mechanical properties will be achieved at melt temperatures between 275-310°C / 527-590°F.
- We advise to frequently measure the melt temperature by pouring the melt in a Teflon cup and inserting a thermo probe into the melt.
Hot Runner Temperature
- A hot runner temperature set to the same level as the nozzle temperature should work fine and not lead to excessive overheat of the EcoPaXX® grade. When starting up, an increased tip temperature may be necessary to overcome a frozen nozzle.
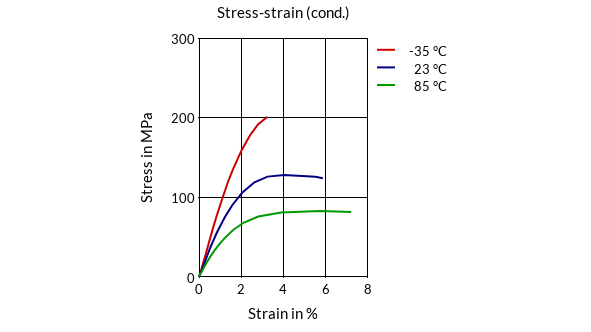
- Stress-Strain (cond.)
- General Processing Settings For Injection Molding
Screw Rotation Speed
- To realize a good and homogeneous melt, it is advised to set a screw rotation speed resulting in a plasticizing time that is just within the cooling time.
- The rotational speed of the screw should not exceed 6500 / D RPM (where D is the screw diameter in mm).
Back Pressure
- Back pressure should be between 30-100 bars effective. Keep it low in order to prevent nozzle-drooling, excessive shear heating and long plasticizing times.
Decompression
- In order to prevent nozzle drool after plasticizing and retracting the nozzle from the mold, a short decompression stroke can be used. However, to prevent oxidation of the melt, which may result in surface defects on the parts, it is recommended to keep this as short as possible.
Injection Speed
- Moderate to high injection speeds are required in order to prevent premature crystallization in the mold during injection phase and to obtain a better surface finish. Adequate mold venting is required to avoid burning at the end of the flow path (due to diesel effect).
Injection Pressure
- The real injection pressure is the result of the flowability of the material (crystallization rate, flow length, wall thickness, filling speed). The set injection pressure should be high enough to maintain the set injection speed (use set injection pressure higher than the peak pressure if possible). Tooling air vents must be effective to allow optimum filling pressure and prevent burn marks.
Holding Time
- Effective holding time is determined by part thickness and gate size. Holding time should be maintained until a constant product weight is achieved.
Holding Pressure
- The most adequate holding pressure is the level whereby no sinkmarks or flash are visible. A too high holding pressure can lead to stresses in the part.
Cooling Time
- Actual cooling time will depend on part geometry and dimensional quality requirements as well as the tool design (gate size).
- Stress-Strain (dry)
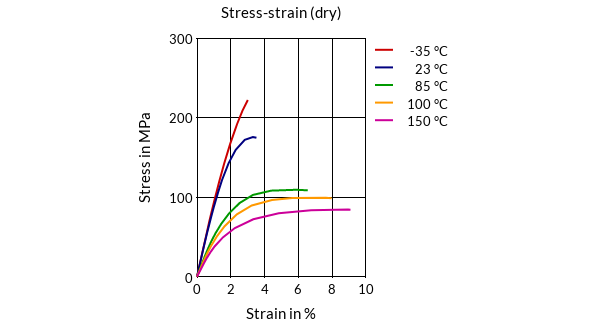
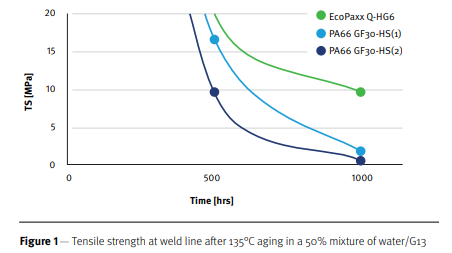
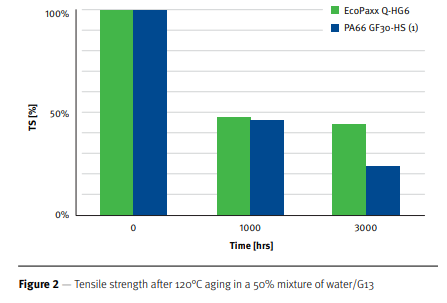
- Test Data
EcoPaXX® vs. PA66
- High strength after aging enables thin-walled parts that reduce weight by 30% over PA66
- Reliable weld line for tanks that live up to three times longer
- Cost neutral compared with PA66 for a tank designed for production in EcoPaXX®
EcoPaXX® vs. PPA
- Unlike PPA, EcoPaXX® can be used as a drop-in solution for PA66, using the same tools and processing settings
EcoPaXX®
- Reduces carbon footprint by more than 60%
- Weight reduction achieves a savings of more than €6 per vehicle in saved CO2 penalties
- Drop-in solution for PA66-GF tooling if PA66 fails to meet requirements
- 60% Reduction of carbon footprint
- Weight reduction achieves more than €6 per vehicle in saved C02 penalties
- Melt Residence Time For Injection Molding
The optimal Melt Residence Time (MRT) for EcoPaXX® Q-KG6 is ≤ 6 minutes with preferably at least 50% of the maximal shot volume used. The MRT should not exceed 10 minutes.
A formula to estimate the MRT is described below:
𝑀𝑅𝑇 = (∏D³ρ/m) * (t/60)
Whereas:
MRT = Melt Residence Time [minutes]
D = Screw Diameter [cm]
p = Melt Density [g/cm3)
m = Shot Weight [g]
t = Cycle Time [s]
Please note: In the calculation above, the hotrunner volume has not been taken into account. When a hotrunner is part of the setup, please add the hotrunner volume to the calculation.- Startup/Shut Down/Cleaning For Injection Molding
- Production has to be started and stopped with a clean machine. Cleaning can be done with EcoPaxx® Q-KG6, applicable cleaning agents or HDPE. Hot runners can also be cleaned and put out of production cleaning them with EcoPaXX® Q-KG6.
- Production Breaks For Injection Molding
- During production breaks longer than a few minutes, we advise emptying the barrel. The temperature of the barrel and the hot runner [if applicable) should be reduced to a level far enough below the melting point of the compound in order to stop decomposition of the compound.
- When the hot runner, nozzle, or even the screw is blocked, be aware that under these conditions a sudden outburst of molten material can take place. Always wear personal safety protections for hand/eye/body.
Packaging & Availability
- Packaging Type
Storage & Handling
- Material Handling For Injection Molding
Storage
- In order to prevent moisture pick up and contamination, supplied packaging should be kept closed and undamaged. For the same reason, partial bags should be sealed before re-storage.
- Allow the material that has been stored elsewhere to adapt to the temperature in the processing room while keeping the bag closed.
Packaging
- EcoPaXX® grades are supplied in airtight, moisture-proof packaging.
Moisture content as delivered
- EcoPaXX® grades are packaged at a moisture level ≤ 0.15 w%.
Conditioning before molding
- To prevent moisture condensing on granules, bring cold granules up to ambient temperature in the molding shop while keeping the packaging closed.
Moisture content before molding
- EcoPaXX® is delivered at molding moisture specification (≤ 0.15 w%). We advise to pre-dry to overcome the fluctuation from package to package (see drying section below). Furthermore, pre-drying is required in case the material is exposed to moisture before molding (prolonged storage or open/damaged packaging).
- Moisture content can be checked by water evaporation methods or manometric methods (ISO 15512).
Drying
- EcoPaXX® grades are hygroscopic and absorb moisture from the air relatively quickly. Moisture absorption is fully reversible under the following drying conditions without compromising material quality. Preferred driers are dehumidified driers with dew points maintained between -30 and -40°C / -22 and -40°F. Vacuum driers with N, purge can also be used. Hot air ovens or hopper driers are not suitable for pre-drying EcoPaXX® grades; the use of such driers may result in non-optimum performance.
Moisture content Time Temperature [%] [h] [°c] [°F] 0.1-0.2
and as delivered2-4 80 176 0.2-0.5 478 80 176 Regrind
- Regrind can be used taking into account that this regrind must be clean/low dust content/not thermally degraded/dry, of same composition and similar particle size as the original material. The acceptable level of regrind depends on the application requirements (e.g. UL Yellow Card). Be aware that regrind can cause some small color deviations.

