Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Chemical Name
- Base Chemicals Functions
- CASE Ingredients Functions
- Molecular formula
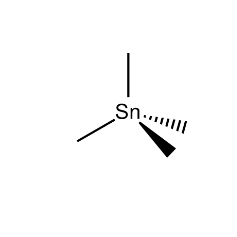
- C₄H₁₂Sn
- Technologies
- Product Families
- Chemical Structure
Features & Benefits
- Product Highlights
This material can be deposited without the vacuum requirements of sputtering techniques. Alternative material technologies that eliminate indium include zinc, antimony and tin based oxides that can be fluorine doped.
- Product Benefits
- In combination with WCl6 catalyzes olefin metathesis for synthesis of terpenoids from 1-methylcyclobutene.
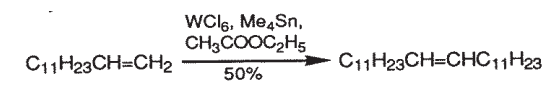
- Allows synthesis of even numbered alkanes.
- Converts acid chlorides to methyl ketones with benzylchlorobis(triphenyl phosphine)palladium.
- Forms aryl methyl ketones from aryl halides and CO in the presence of dicarbonylbis(triphenylphosphine)nickel.
- Product Features
- Catalyst for rearrangement and cleavage of epoxy alcohols.
- Catalyst for cyclization of ω-amino acids to lactams.
- In combination with lead alkyls yields PZT films by MOCVD.
- Review of reactions in combination with Grignard reagents and various organic substrates.
- In combination with triethylamine and trimethylchlorosilane extends aldehydes to two carbons to enals.
- Product Attributes
- For CVD of tin oxide transparent conductive electrodes on glass for photovoltaics and sensors
- Pyrolyzed in vacuum to tin at 600-750°C
- Pyrolyzed oxidatively to SnO at 350-600 °C
- Forms transparent conductive oxides for photovoltaics by Plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD)
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applicable Processes
- Base Chemicals End Uses
- Coating Type
- Product Applications
Forms transparent conductive oxides for photovoltaics by PECVD.10
Safety and handling considerations.11
In combination with WCl6 catalyzes olefin metathesis.2
Allows synthesis of even numbered alkanes.3
Converts acid chlorides to methyl ketones with benzylchlorobis(triphenyl phosphine)palladium.4,5
Forms aryl methyl ketones from aryl halides and CO in the presence of dicarbonylbis(triphenylphosphine)nickel.6
For CVD of tin oxide transparent conductive electrodes on glass for photovoltaics and sensors.7
Pyrolyzed in vacuum to tin at 600-750°.8
Pyrolyzed oxidatively to SnO at 350-600°.Reference
1. Scott, W. J.; Jones, J. H.; Moretto, A. F. in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis 1995, Volume 8, 4823-4825.
10. Chandra, H. et al. Am. Vac. Soc. 2008, 55, TFThA10.
11. Kalb, P. et al. Report BNL-52123, 1987 Order NTIS #DE89005936.
2. van Dam, P. et al. J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun. 1972, 1221.
3. Gibson, T. et al. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 1821.
4. Milstein, D. et al. J. Org. Chem. 1979, 44, 1613.
5. Labadie, J. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 6129.
6. Tanaka, M. Synthesis 1981, 47.
7. Inagaki, N. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1989, 37, 2341.
8. Svoboda, G. et al. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1992, 31, 19.
9. Borman, C. et al. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1989, 136, 3820.
Properties
- Chemical Properties
- Typical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Delta H Vaporization | 6.8 | kcal/mole | — |
| Boiling Point | 74 - 75 | °C | — |
| Melting Point | -54.0 | °C | — |
| Enthalpy of Combustion | 903.5 | kcal/mole | — |
| Enthalpy of Formation (gas at 27°C) | -13.6 | kcal/mole | — |
| Enthalpy of Evaporation | 6.8 | kcal/mole | — |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Flash Point | -12.0 | °C | — |
| Refractive Index (at 20°C) | 1.441 | — | — |
| Purity | 97.0 | % | — |
| Vapor Pressure (at -21 °C) | 10.0 | mmHg | — |
| Molecular Weight | 178.83 | g/mol | — |
| Density (at 20°C) | 1.291 | g/ml | — |
| Vapor Pressure (at 20°C) | 90.0 | mmHg | — |
| Dissociation Energy (Sn-Me Bond) | 227.0 | kJ/mole | — |
| Ethylene Acrylate Copolymer (pyrolysis) | 41.1 | kcal/mole | — |
Regulatory & Compliance
Technical Details & Test Data
- LEDs (Organic, Polymer, Phosphorescent)
They are utilized to modify a variety of surfaces that include glass, metal oxides, plastics and nano-crystals. Plastic substrates are critical in the manufacture of flexible electronic displays. Gelest offers a multitude of materials for metallization via low temperature vapor deposition techniques such as CVD and ALD to yield conductive coatings and dielectric coatings for light emitting diodes to include OLEDs, PLEDs and Phosphorescent OLEDs. The ability to customize the refractive index of Group IV materials makes them ideal candidates for cladding fiber optic cables and planar wave guides. Gelest offers an extensive range of materials for antireflective and refractive index coatings.
- Extraction Process
- Atomic layer deposition (ALD) is a chemically self-limiting deposition technique that is based on the sequential use of a gaseous chemical process. In most cases, ALD reactions use two chemical precursors which react with a surface one at a time in a sequential, self-limiting, manner.
- A thin film results from repeating the deposition sequence as many times as needed to reach a certain thickness. The major characteristic of the films is their conformality and the tact that the amount of control provided by an ALD arrangement (where the reacting precursors are spatially separated) allows to obtain very thin deposited layers (as fine as 0.1 A per cycle).
- Precursor selection is key in ALD processes, namely finding molecules which will have enough reactivity to produce the desired films, but are stable enough to be handled and safely delivered to the reaction chamber.
Packaging & Availability
- Standard Packaging
25 g, 100 g,1.5 kg, 20 kg