Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Chemical Name
- Plastics & Elastomers Functions
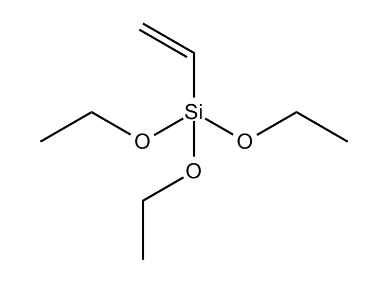
- Molecular formula
- C₈H₁₈O₃Si
- Technologies
- Product Families
- Chemical Structure
Features & Benefits
- Product Highlights
Olefin Functional Trialkoxy Silane
Silane coupling agents have the ability to form a durable bond between organic and inorganic materials to generate desired heterogeneous environments or to incorporate the bulk properties of different phases into a uniform composite structure. The general formula has two classes of functionality. The hydrolyzable group forms stable condensation products with siliceous surfaces and other oxides such as those of aluminum, zirconium, tin, titanium, and nickel. The organofunctional group alters the wetting or adhesion characteristics of the substrate, utilizes the substrate to catalyze chemical transformations at the heterogeneous interface, orders the interfacial region, or modifies its partition characteristics, and significantly effects the covalent bond between organic and inorganic materials.
Alkenylsilane Cross-Coupling Agent
The cross-coupling reaction is a highly useful methodology for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds. It involves two reagents, with one typically being a suitable organometallic reagent - the nucleophile - and the other a suitable organic substrate, normally an unsaturated halide, tosylate or similar - the electrophile.
- Product Attributes
- Relative hydrolysis rate versus SIV9220.0, vinyltrimethoxysilane; 0.05
- Forms copolymers with ethylene for moisture induced coupling of polyethylene
- Couples fillers or fiberglass to resins
- See VEE-005 for polymeric version
- Reacts with enamines to give (E)-β:-silylenamines, which cross-couple with aryl iodides to give β-aryl enamines
- Employed as a coupling agent, adhesion promoter, and crosslinking agent
- Used in microparticle surface modification for fillers
- Compatible with sulfur and peroxide cured rubber, polyester, polyolefin, styrene, and acrylic based materials
- For vinylations
- Available as an oligomeric hydrolysate, SIV9112.2
Applications & Uses
- Compatible Polymers & Resins
- Product Applications
Reacts with enamines to give (E)-?-silylenamines, which cross-couple w/ aryl iodides to give ?-aryl enamines.1
Extensive review on the use in silicon-based cross-coupling reactions.2Reference
1. Marciniec, B. et al. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 8550.
2. Denmark, S. E. et al. Organic Reactions, Vol. 75, Denmark, S. E. ed., John Wiley and Sons, 233, 2011.
Properties
- Physical Form
- Chemical Properties
- Thermal Properties
- Typical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Delta H Vaporization | 6.8 | kcal/mole | — |
| Boiling Point | 160 - 161 | °C | — |
| Enthalpy of Formation | -463.5 | kcal/mole | — |
| Enthalpy of Evaporation | 6.8 | kcal/mole | — |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Auto-ignition Temperature | 268.0 | °C | — |
| Specific Heat | 0.25 | cal/gm/°C | — |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Density | 0.903 | g/ml | — |
| Flash Point | 44.0 | °C | — |
| Refractive Index (at 20°C) | 1.396 | — | — |
| Dipole Moment | 1.69 | debye | — |
| Molecular Weight | 190.31 | g/mol | — |
| Purity | 97.0 | % | — |
| Specific Wetting Surface Area | 412.0 | m²/g | — |
| Copolymerization Parameters (e) | -0.42 | — | — |
| Vapor Pressure (at 20°C) | 5.0 | mmHg | — |
| Surface Tension (of treated glass surface) | 25.0 | mN/m | — |
| Copolymerization Parameters (Q) | 0.028 | — | — |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Chemical Inventories
Packaging & Availability
- Standard Packaging
25 g, 2 kg, 16 kg, 180 kg