Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Fillers Included
- Polymer Name
- Plastics & Elastomers Functions
- Technologies
Features & Benefits
- Labeling Claims
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Plastics & Elastomers End Uses
- Plastics & Elastomers Processing Methods
- Application Development Capabilities and Expertise
In addition to material development, SABIC offers expertise and resources for testing, design and application development for additive manufacturing. From material chemistry, to material formulation, to print expertise, SABIC integrates design, processing and materials, much like we have done with traditional polymer processes over the past decades, to help solve problems for our customers.
Our application development expertise has now expanded to include capabilities specific to pellet-fed additive manufacturing technology. This unique position enables us to produce innovative offerings for this space to help drive greater adoption of additive manufacturing for end use production.
Traditional Application Method Capabilities Added for Pellet-Fed
Additive ManufacturingIndustrial
Design- Application teardowns
- Concept designs
- Prototype development
- Access to industrial engineers and designers to create parts
- Reverse engineering to recreate tools and redesign parts
- specific to additive manufacturing
Predictive
Engineering- Computer aided engineering
- Computer aided design
- Process simulation
- Life cycle analysis
- Processing simulation to screen ideas for efficient test runs
- Fracture analysis to understand failure mode to improve process and materials feed simulation
- Warp analysis
- FEA to study printed parts to solve performance issues
Process
Development- Conversion processes
- Material development
- Technical scoping and validation
- Training and consultation
- Expertise on a variety of 3D printing equipment to optimize
- processing parameters enabling faster setup and transition for customers
- Access to the broad portfolio of LNPTM specialty compounds
- 3D laser scanner to perform quality checks on printed parts
- Thermal imaging to monitor processing consistency
Application
Performace- Secondary operations
- Painting and decoration
- Part testing and end use simulation
- Regulatory standards
- Microscopy for fiber orientation
- CTE analysis for thermally cycled parts
- Mechanical properties testing of printed parts to aid customers in material selection
- Water jet for consistent cutting of printed parts for testing
- Autoclave, thermoform, vac-form and environmental chamber for tooling validation
- Non-destructive testing to check for voids or layer adhesion issues
- Composite testing equipment
- Post processing
Properties
- Mechanical Properties
- Physical Properties
- Thermal Properties
- Processing Information (Extrusion)
- Note
ⁿ Tensile Stiffness (K) is a structural property defined as the stress/strain in the linear region of the stress/strain curve. Value depends on the geometry/shape and boundary/surrounding conditions.
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Tensile Stress (at 5mm/min, XZ Orientation) | 89 | MPa | ASTM D638 Modified |
| Tensile Stress (at 5mm/min, ZX Orientation) | 18 | MPa | ASTM D638 Modified |
| Tensile Strain (at 5mm/min, XZ Orientation) | 1 | % | ASTM D638 Modified |
| Tensile Strain (at 5mm/min, ZX Orientation) | 0.7 | % | ASTM D638 Modified |
| Tensile Stiffness (at 5mm/min, XZ Orientation) ⁿ | 11.8 | GPa | ASTM D638 Modified |
| Tensile Stiffness (at 5mm/min, ZX Orientation) | 2.9 | GPa | ASTM D638 Modified |
| Flexural Stress (at 5mm/min, XZ Orientation) | 32 | MPa | ASTM D790 Modified |
| Flexural Stress (at 5mm/min, ZX Orientation) | 125 | MPa | ASTM D790 Modified |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Specific Gravity | 1.14 | — | ASTM D792 |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Heat Deflection Temperature (at 1.82 MPa, 3.2 mm, Annealed) | 101 | °C | ASTM D648 |
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Barrel - Zone 1 Temperature | 190 - 230 | °C | — |
| Barrel - Zone 2 Temperature | 200 - 240 | °C | — |
| Extruder Length/Diameter (L/D) | 24 | — | — |
| Barrel - Zone 3 Temperature | 210 - 250 | °C | — |
| Barrel - Zone 4 Temperature | 220 - 260 | °C | — |
| Bed Temperature | 120 - 150 | °C | — |
| Drying Temperature | 80 | °C | — |
| Drying Time | 4 | Hrs | — |
| Extruder Pressure | max. 13.5 | MPa | — |
| Maximum Moisture Content | 0.05 - 0.1 | % | — |
| Melt Temperature | 220 - 260 | °C | — |
| Nozzle Temperature | 210 - 250 | °C | — |
Technical Details & Test Data
- Material Innovations for Pellet-Fed Additive Manufacturing
Mechanical properties and processing information for THERMOCOMP™ AM compounds, including tensile and flexural properties, are developed internally using test specimens printed on our large format equipment (see Figure 1). This insight into process conditions and material performance gives customers confidence in the use of our materials and enables faster machine set up as well as higher print productivity.
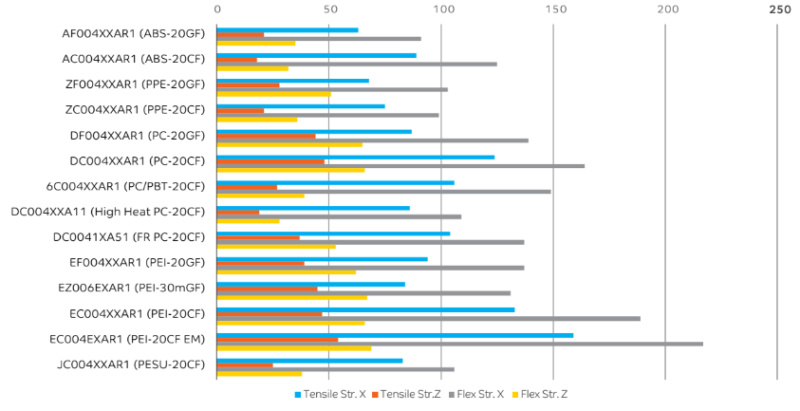
Figure 1: SABIC's PFAM Grades: Strength Comparison Table
SABIC’s access to a wide range of thermoplastics resins and a number of fillers and reinforcements enables development of new compounds to meet customer and application needs for pellet-fed additive manufacturing.
Thermoplastic Resins:
- ABS
- PC, PC/ABS, PC/PBT
- PEI
- PSU
- PA11
- PESU/PES
- PPSU
- PEEK
- PPS
- PA6
- PA66
- PPA
- PPE, PPE/Nylon
- Others
Reinforcements - Fillers:
- Carbon Fiber
- Glass Fiber
- Minerals
- Flame Retardants
- Heat Stabilizers
- UV Agents
- Thermally Conductive Fillers
- Others
- Pellet-Fed Additive Manufacturing - Process Development
Unlike other additive manufacturing processes, pellet-fed additive manufacturing is an open process that allows for adjustment in temperature, speed of laydown, layer height and many more parameters. Proper processing is critical to ensure a quality printed part and can help to avoid issues such as polymer degradation which could lead to loss of some physical properties. SABIC develops process parameters for our pellet-fed dditive manufacturing compounds, to be used as starting guidelines which can save customers time and resources. Following proper printing practices with careful consideration of drying time, extrusion residence times, temperatures and pressure will help create a robust part.
Packaging & Availability
- Country Availability
- Regional Availability

