Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Polymer Name
- Technologies
- Product Families
- Chemical Composition
Synthetic rubber based on ether/aliphatic diisocyanate.
Features & Benefits
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Cure Method
- Plastics & Elastomers End Uses
Properties
- Appearance
- Pale amber to clear solid bales
- Typical Properties
- Product Properties
- Vulcanizates based on Millathane 97 can be produced in hardnesses of 40 to 95 Shore A, with tensiles up to 4300 psi (30 MPa).
- Properly formulated compounds offer excellent clarity and abrasion resistance, with good chemical resistance and hydrolysis resistance.
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Specific Gravity | approx. 1.02 | — | — |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
- Chemical Inventories
Technical Details & Test Data
- Processing Information
- Millathane 97 is processed by techniques which are common to the rubber industry.
- Compounds can be mixed on an open mill or in an internal mixer; molded articles can be produced via compression, transfer or injection molding.
- Calendered sheets can be press-cured or rotocured, or vulcanized in steam or hot air autoclaves (with protection from contact with steam and oxygen).
- Cleanliness Information
- Compounds are best mixed in areas away from black-compound mixing, mixing equipment cleaned before mixing and ingredients protected against ambient dust contamination.
- If transparent, clear compounds are being made, it is extremely important to avoid all possible sources of contamination.
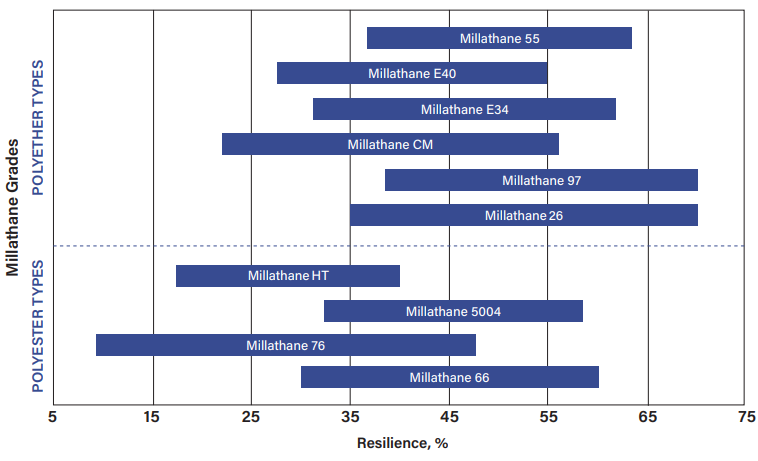
- Resilience/Damping
Millathane millable urethanes can have resilience (rebound) values varying from below 10%, as seen with some Millathane 76 compounds, to over 60%, as seen with several polyether grades.
Low resilience compounds generally have excellent vibration damping characteristics and are used in instrument packaging and other vibration damping applications.
High resilience compounds tend to have lower heat build-up in dynamic applications such as rubber-covered rollers.
Generally, resilience will be higher with low filler loadings than with higher filler loadings. Peroxide cures will tend to give higher resilience than sulfur cures.
- Compounding Information
- Fillers
- Millathane 97 requires reinforcing fillers to achieve hardness and high mechanical strength. Fumed silica (e.g., Wacker HDK N20 and Aerosil 200) is the filler of choice for transparent applications.
- Precipitated silicas can also be used for translucent or non-black compounds.
- Other conventional fillers like carbon blacks can also be used with Millathane 97.
- A small amount (0.25 - 0.5 parts) of a silane coupling agent such as Silquest Y-15866, Silquest RC-1 or Silquest A-172 will improve abrasion resistance, tear, and compression set properties of mineral filled compounds. Sulfur-containing coupling agents (e.g., Si69) should not be used.
- The effect of varying the level of fumed silica is show in the table below.
- As expected, hardness, tensile strength, and tear strength increase as the level of fumed silica increases.
- Plasticizers
- Moderate amounts of plasticizer can be incorporated into Millathane 97 to aid in processing and/or to reduce hardness.
- For the best compound transparency, the plasticizer should also be clear, or very close to clear.
- Mediaplast NB-4 has been shown to have good compatibility, color and properties with Millathane 97. Other plasticizers such as TP-90B (DBEEF) and TP-95 (DBEEA) can also be used.
- The antistatic plasticizer Struktol AW-1 can be used to a limited extent, but may tend to bleed at levels over 10 parts.
- Antidegradants / UV Stabilizers
- A small amount, approximately 0.25 phr, of antioxidant1 should be used in all compounds.
- For good weather and UV resistance, especially for clear compounds, a UV absorber2 and a Hindered Amine Light Stabilizer3 (HALS) should be used at ~0.25 phr each.
- For higher heat resistance, 2 phr of antioxidant1, along with the two UV stabilizers noted, should be used, although some yellowing may be a result.
- Curing Agents: Peroxides and Coagents
- Millathane 97 must be cured with peroxides and, optionally, coagents.
- The choice of peroxide depends on the cure conditions desired for curing the part.
- For the best transparency, a neat (not on a filler) peroxide should be used. Luperox (or Varox) 231 is typically used for cures at 145 –-155°C, while Di-Cup R (dicumyl peroxide) is used for cures at 155 - 170°C
- Vulcanization Conditions
- Curing conditions are dependant on the molded part configuration as well as the peroxide used.
- Compounds based on Millathane 97 using Luperox 231 are typically vulcanized for 5-10 minutes at 145 - 155°C.
- If dicumyl peroxide is used, cures of 5 - 20 minutes at 155 - 170°C are typical for compression or transfer molding, 2 - 5 minutes at 170o - 180°C for injection molding. Note that higher
- temperatures can tend to yellow the cured parts slightly, so lower cure temperatures will give the best transparency.
- The small wheels, below, were injection molded for 2 minutes at 180°C in a REP injection molding machine.
- Varox DBPH can be used for cures at 160 - 180°C. Coagents typically used in Millathane 97 are the liquid methacrylate types, such as SR-231 (DEGDMA) and SR-350 (TMPTMA) from Sartomer.
- Difunctional methacrylates, such as SR-231 and SR-297 (BGDMA), give improvements in abrasion and tear resistance, while the trifunctional methacrylates such as SR-350 give a greater increase in hardness than the difunctional types.
- The liquid methacrylate coagents also give the benefit of reducing compound viscosity, which improves processing and mold flow.
- High hardness Millathane 97 compounds can be made with blends of di- and tri-functional methacrylates, resulting in good processing compounds with excellent cured properties. Most scorch-retarded liquid coagents should not be used for clear compounds as their scorch-retarding ingredients will tend to yellow the cured parts.
- Liquid polybutadiene, such as Ricon 153, can be used as a coagent but it can tend to make compounds cloudy and less transparent. TAC and TAIC can also be used as coagents, although only at low levels (< 2 phr) as high levels tend to give high crosslink densities which can result in low elongation and tensile and tear strengths.
- Colorants
- For transparent compounds, a very small amount of ultramarine blue (0.002 - 0.005 parts) will minimize any slight yellowing of the compound and give the compound a brighter appearance.
- For brightly colored transparent compounds, 0.005 - 0.1 part of various organic colors can be used. Examples of these are Akrochem 97AA Red, Akrochem 802 Yellow, and Akrochem 414 Green.
- For opaque compounds, a rutile grade of titanium dioxide should be used.
- Vulcanization Conditions
- Curing conditions are dependant on the molded part configuration as well as the peroxide used.
- Compounds based on Millathane 97 using Luperox 231 are typically vulcanized for 5-10 minutes at 145 - 155°C.
- If dicumyl peroxide is used, cures of 5-20 minutes at 155 - 170°C are typical for compression or transfer molding, 2-5 minutes at 170 - 180°C for injection molding.
- Note that higher temperatures can tend to yellow the cured parts slightly, so lower cure temperatures will give the best transparency. The small wheels, below, were injection molded for 2 minutes at 180°C in a REP injection molding machine.
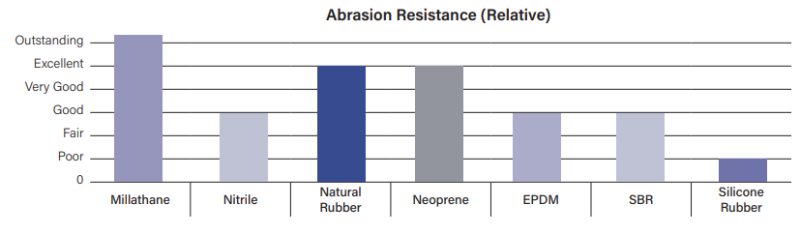
- Abrasion Resistance
- Abrasion resistance is the ability of a surface to resist wearing due to contact with another surface moving with respect to it.
- High resistance to abrasion is important in applications like rollers, belting, and helicopter dust covers.
- The DIN Abrasion Test (ASTM D5963) is one of the most common tests for measuring abrasion resistance.
- It's where a rotating cylindrical sample is passed across a rotating drum of abrasive and the amount of sample volume lost is measured.
- Typical abrasion resistance values for Millathane millable urethane compounds is 50-80 mm³.
- Some compounds can have abrasion resistance values as low as 25 mm³, depending on the polymer, cure system, and formulation.
- Polyurethane rubber provides the highest abrasion resistance of any rubber, synthetic or natural.
- Laboratory tests do not always predict the advantage of Millathane compounds over other rubbers, but field experience often shows a tremendous improvement in product lifetime when millable urethane replaces conventional rubber.
Packaging & Availability
- Packaging Information
Package size/carton: 38 pounds (17.2 kg).
Storage & Handling
- Shelf Life
- 3 years
- Storage Information
Stored under dry and cool conditions.

