Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Polymer Name
- Technologies
- Product Families
- Chemical Composition
Synthetic rubber based on ether/TDI polyurethane.
Features & Benefits
Applications & Uses
- Applications
- Cure Method
- Plastics & Elastomers End Uses
- Product Applications
- A major application of Millathane E40 is in military and aeronautical applications, due to its very good, strength properties, abrasion resistance and low temperature properties.
- It is also used in rollers, belting, footwear and other applications.
Properties
- Appearance
- Pale to dark amber solid sheets
- Typical Properties
- Product Properties
- Vulcanizates based on Millathane E40 can be produced in hardnesses ranging from about 45 to 90 Shore A, and offer high strength properties, excellent abrasion resistance, water resistance and good oil resistance.
- Compounds have low brittle points, and are more resistant to low temperature hardening, due to crystallization, than Millathane E34 or Millathane CM.
- Low Temperature Properties
- Millathane® Millable urethanes have good low temperature properties.
- Compounds based upon polyether grades having brittle points down to as low as -68°C (-90°F), and compounds based upon polyester grades down to as low as -60°C (-76°C).
- Low temperature flexibility is important for applications such as airplane deicing bladders, automotive parts, and hose for cold temperature use.
- Some grades of both polyether and polyester millable urethanes can stiffen considerably at low temperatures due to crystallization of the polymer.
- Grades that are the most resistant to low temperature hardening are the polyether grades Millathane CM and E40 and the polyester grades Millathane HT and 66.
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Specific Gravity | approx. 1.07 | — | — |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
- Chemical Inventories
Technical Details & Test Data
- Processing Information
- Millathane E40 is processed by techniques which are common to the rubber industry.
- Compounds can be mixed on an open mill or in an internal mixer.
- The Premilled sheet physical form makes for easy mill mixing.
- Molded articles can be produced via compression, transfer or injection molding; calendered sheets can be press or rotocured.
- Compounding Information
- Reinforcing Fillers
- Reinforcing fillers like N330 carbon black or precipitated silica increase the mechanical strength of Millathane E40 compounds.
- Fumed silicas such as Wacker HDK N20 or Cabosil M-5 will give somewhat higher reinforcement than precipitated silicas and will give translucent cured compounds (depending on other ingredients).
- Clay, talc and calcium carbonate can also be used as fillers to modify properties and processing, but are less reinforcing than silicas and blacks.
- Coupling Agents
Silane coupling agents like Si 69 or Silquest A-189 for sulfur cures, or Silquest Y-15866, RC-1, or A172 for peroxide cures, will generally improve the tear strength and set properties of silica reinforced compounds and are typically used at about 2% of the mineral filler content.
- Plasticizers
- TP-95 is a plasticizer that is very compatible with Millathane E40, with compounds containing 25 phr and more will usually not show signs of bleeding or incompatibility.
- Other plasticizers such as Mediaplast NB-4 and Benzoflex 9-88SG can also be used to plasticize and soften compounds.
- The antistatic plasticizer Struktol AW-1 can be used to a limited extent, to lower surface resistivity, but may tend to bleed at levels over 10 parts.
- Antidegradants
Polyurethanes are generally very resistant to ozone and oxygen attack because of their saturated polymer backbones (like EPDM). Small amounts (0.5-2 phr) of antioxidants like Naugard 445 and Irganox 1010 can provide some benefit to the heat aging characteristics of peroxide-cured Millathane E40 compounds.
- Process Aids
- Small amounts of process aids are normally used to prevent sticking to processing equipment and to improve flow during molding.
- For sulfur-cured compounds, the 0.5 phr of zinc stearate used as an activator is usually adequate.
- For more release, 0.5 - 2 phr of another process aid such as Struktol WB222 or Vanfre AP-2 can be used.
- For peroxide cures, 0.2-0.5 phr of stearic acid is use in place of the zinc stearate. A low molecular weight polyethylene like AC617A, added at 1 - 4 phr, gives good release for calendering and molding.
- Curing Agents
- The best physical properties and abrasion resistance are achieved with sulfur cures, while the best compression set, heat aging and reversion resistance comes from peroxide cures.
- The sulfur cure system is a combination of MBTS (4 phr), MBT (2 phr), Thanecure® ZM (1 phr) and sulfur (1.5 - 2.0 phr), along with zinc stearate (0.5 phr), used as an activator. Peroxide cures can be used for better set and heat aging characteristics.
- Typical peroxides used are dicumyl peroxide and DBPH, typically used at about 0.6 - 1.2 phr active peroxide (1.5 - 3.0 phr of 40% active).
- The use of low levels of coagents such as triallyl cyanurate (TAC) and trifunctional methacrylates like SR350 (TMTPMA) increase the crosslink density and improve compression set.
- Blends of the difunctional methacrylate SR231 (DEGDMA) with the trifunctional methacrylate SR350 are recommended for high hardness compounds, as the blend gives a good balance of strength properties, elongation and set.
- High crosslink densities, seen with high peroxide and/or coagent levels, will improve compression set but strength properties and elongation may be adversely affected.
Vulcanization Conditions
- Sulfur-cured Millathane E40 compounds are typically molded at temperatures of 150 - 165°C; higher temperatures can give poor cures due to reversion.
- Peroxide-cured compound can be cured from 145 - 175°C, depending on the peroxide, dimensions of the part etc.
- Rubber covered rollers are often cured in steam or electric autoclaves, under pressure, at 140 -155°C for 1 - 6 hours (very large rolls for longer times at lower temperatures), depending on the compound and roll geometry.
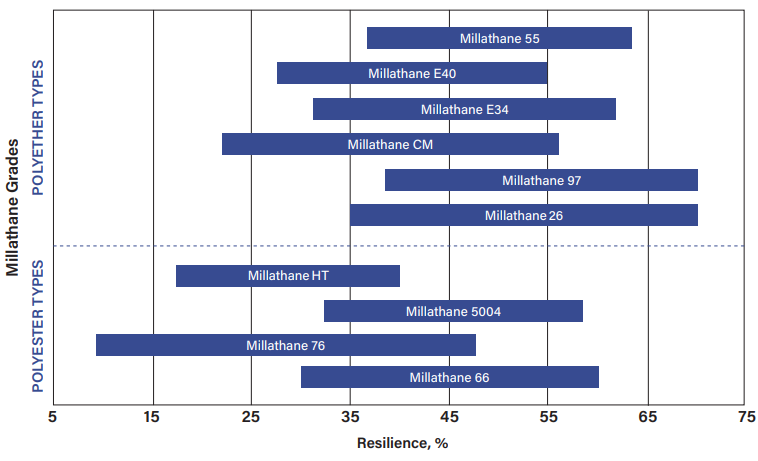
- Resilience/Damping
Millathane millable urethanes can have resilience (rebound) values varying from below 10%, as seen with some Millathane 76 compounds, to over 60%, as seen with several polyether grades.
Low resilience compounds generally have excellent vibration damping characteristics and are used in instrument packaging and other vibration damping applications.
High resilience compounds tend to have lower heat build-up in dynamic applications such as rubber-covered rollers.
Generally, resilience will be higher with low filler loadings than with higher filler loadings. Peroxide cures will tend to give higher resilience than sulfur cures.
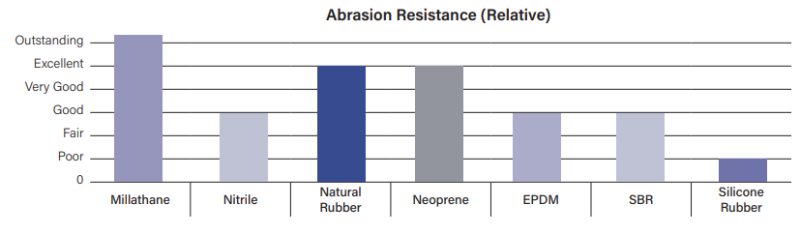
- Abrasion Resistance
- Abrasion resistance is the ability of a surface to resist wearing due to contact with another surface moving with respect to it.
- High resistance to abrasion is important in applications like rollers, belting, and helicopter dust covers.
- The DIN Abrasion Test (ASTM D5963) is one of the most common tests for measuring abrasion resistance.
- It's where a rotating cylindrical sample is passed across a rotating drum of abrasive and the amount of sample volume lost is measured.
- Typical abrasion resistance values for Millathane millable urethane compounds is 50-80 mm³.
- Some compounds can have abrasion resistance values as low as 25 mm³, depending on the polymer, cure system, and formulation.
- Polyurethane rubber provides the highest abrasion resistance of any rubber, synthetic or natural.
- Laboratory tests do not always predict the advantage of Millathane compounds over other rubbers, but field experience often shows a tremendous improvement in product lifetime when millable urethane replaces conventional rubber.
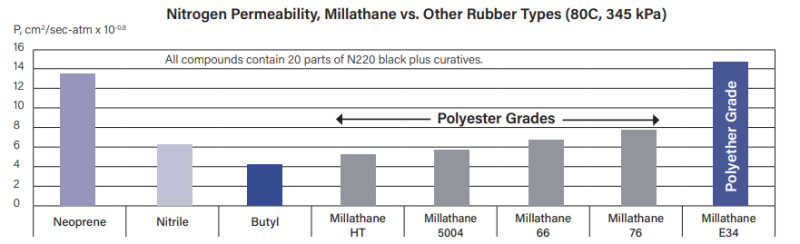
- Gas Permeability
- Millathane millable urethanes have very good resistance to gas permeability, with polyester grades approaching that of butyl rubber.
- A comparison of the nitrogen permeability of several Millathane grades vs. neoprene (CR), nitrile (NBR), and butyl (IIR) rubber is shown in the chart below.
- Polyester millable urethanes have very low gas permeability, comparable to or slightly better than nitrile rubber and slightly defensive to butyl rubber.
- Millathane E34, a polyether polyurethane, had higher (poorer) nitrogen permeability, similar to that of neoprene rubber.
Packaging & Availability
- Packaging Information
Package size/carton: 50 pounds (22.7 kg).
Storage & Handling
- Shelf Life
- 3 years
- Storage Information
Stored under dry and cool conditions.

