Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Name
- Agrochemical Functions
- Industrial Additives Functions
- CAS No.
- 9038-95-3
- EC No.
- 618-542-7
- Technologies
Features & Benefits
- Product Features
- Nonionic surfactant used to emulsify systems heavy in chlorinated solvents and pesticides
- Used as emulsifier, dispersant or wetting agent
- Low pour point to reduce handling problems
- Soluble in water, methanol and xylene
- Good sticker and wetter
- Nonionic emulsifier, adjuvant and wetting agent
- Hydrophilic properties promote uniform dispersion of the concentrate when diluted in a broad spectrum of waters and fertilizers
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applicable Processes
- Applications
- TOXIMUL 8320 is 100% active nonionic surfactant used to emulsify systems heavy in chlorinated solvents and pesticides. This surfactant has a lowered pour point to reduce handling problems.
- Emulsifiable Concentrates
- Microemulsions
- Suspension Concentrates
- Suspoemulsions
- Oil Dispersants
Properties
- Formulation Type
- Physical Form
- Appearance
- Hazy liquid (at 25°C)
- Soluble in
- Water, Methanol, Xylene
- Insoluble in
- Kerosene
- Typical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Cloud Point (1% in 10% NaCl) | 50 | °C | — |
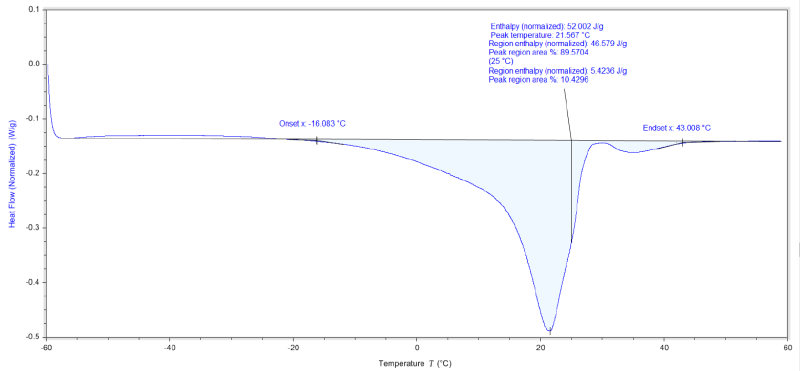
| Melt Range | -16.08 to 43.01 | ºC | — |
| Density (at 25°C) | 1.05 | g/ml | — |
| Melted Quantity (at 25ºC) | 89.57 | % | — |
| Flash Point | min. 94 | °C | PMCC Flash Point Tester |
| Hydrophobe | Butanol | — | — |
| HLB | 12 | — | — |
| Base | Butyl | — | — |
| Moisture Content | max. 0.25 | % | — |
| Average Molecular Weight | 5500 | — | — |
| pH (in 1% aqueous) | 6 | — | — |
| Surface Tension (0.1% Aqueous) | 45 | dynes/cm | — |
| Pour Point | 21 | °C | — |
| Regulated Volatile Organic Chemicals | 0 | % | U.S. EPA |
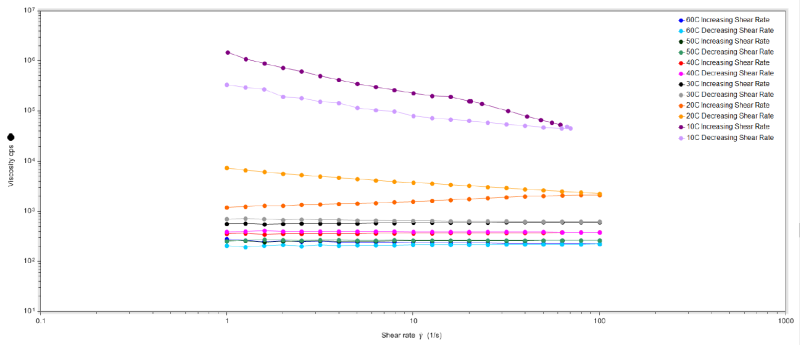
| Viscosity (at 25°C) | 2000 | cPs | — |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
- Chemical Inventories
- Clearances
- The international inventories (country clearances) of TOXIMUL 8320 can be found in Section 15 of the Safety Data Sheet (SDS). It is the responsibility of the formulator to review the chemical control regulations for each country where the end-product is intended to be sold or used.
- TOXIMUL 8320 is approved for use as an inert ingredient under U.S. EPA 40 CFR 180.960.
Technical Details & Test Data
- Melt Point Determination of TOXIMUL® 8320
- Rheology of TOXIMUL® 8320
Packaging & Availability
- Packaging Type
- Standard Packaging
TOXIMUL 8320 is available in drums, totes, and bulk quantities.
Storage & Handling
- Storage & Handling
- Normal safety precautions (e.g., gloves and safety goggles) should be employed when handling TOXIMUL 8320. Contact with eyes, nose or prolonged contact with skin should be avoided. Wash thoroughly after handling TOXIMUL 8320. See SDS for more information.
- Non-Bulk Storage Recommendations: TOXIMUL 8320 should be stored in closed containers and kept in a cool, dry place away from incompatible materials (see Section 10 of the SDS). Temperatures below 75°F (24°C) may thicken or solidify. It may be fluidized by warming with a drum heater or in a steam room, by heating gently and mixing to ensure it is homogenous prior to use. Drums should be vented prior to heating to avoid excessive pressure build up. Product temperatures over 130°F (54°C) are not recommended.
- Bulk Storage Recommendations: TOXIMUL 8320 should be stored in vessels of stainless steel and glass fiber-reinforced polyester tanks. Many oven-cured phenolic and epoxy/phenolic linings may also be used. Elevated storage temperature may be desirable to maintain ease of pumping. Temperatures up to 130°F (54°C) can be maintained for long periods of time without degradation of the product.
- Workplace Exposure
Occupational exposure can occur primarily through skin contact or via inhalation of vapors and mists. Engineering controls, personal protective equipment, and other workplace safety practices should be used to control these exposures. See SDS for more information.

