Knowde Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Chemical Name
- INCI Name
- CASE Ingredients Functions
- Cosmetic Ingredients Functions
- CAS No.
- 112926-00-8
- EC No.
- 601-214-2
Features & Benefits
- Benefit Claims
- CASE Ingredients Features
- Materials Features
Applications & Uses
- Applications
- Application Format
- Compatible Polymers & Resins
- AP/Deo Applications
- Plastics & Elastomers End Uses
Properties
- Physico-Chemical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| Tamped Density (ex plant) | approx. 60 | g/l | — |
| Specific Surface Area (BET), Multipoint | 195 - 245 | m²/g | — |
| SiO₂ Content (based on ignited material) | min. 99.8 | wt % | — |
| pH Value (in 4% dispersion) | 5.5 - 9.0 | — | ISO 787-9 |
| Loss on Drying* (at 105 °C, 2 hours) | max. 0.5 | wt % | ISO 787-2 |
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
- Chemical Inventories
Technical Details & Test Data
- Sedimentation Stability of Defoamer Formulations
To prepare the model defoamer formulations, 2 weight-% each of the silica products listed above were incorporated in a mixture consisting of polyethersiloxane (38 weight-%, TEGO 5861, Evonik Goldschmidt GmbH and mineral oil (60 weight-%, ONDINA® 913, Shell). For incorporation of the silica we used a rotor-stator system Ultra-Turrax® at 10.000 rpm for 1 minute. The quality of dispersion and the sedimentation stability of the defoamer formulations obtained was recorded at intervals of 7, and 31 days and 6 months by means of a) microscopic evaluation and /or b) rheological measurements (see Figure 2 and 4) and subsequently visual inspection.
Figure 2 Methods used for evaluation of the dispersion and sedimentation stability of the model defoamer formulation a Microscopy for checking the quality of the dispersion b Rheology for viscosity measurements
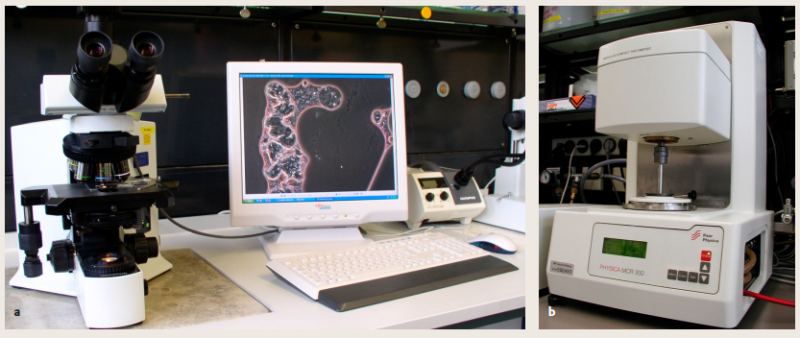
Figure 3 Sedimentation stability of hydrophobic AEROSIL* and SIPERNAT® containing model defoamer formulations. The higher the number of an isoline, the more stable the model defamer formulation is expected to be against settling. The relative position of the black dots in this and the following figures represent the same silica grades as shown in Figure 1
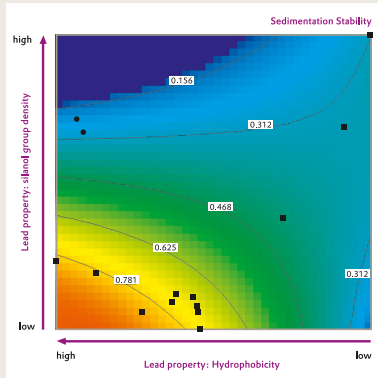
On the other hand, the rather hydrophobic precipitated silica products SIPERNAT® D 10 and SIPERNAT® D 17, the structure modified fumed silica grades AEROSIL* R 9200 and AEROSIL R 7200, and the slightly hydrophilic AEROSIL* R 816 are located in the upper (green and blue colored) part of the diagram in Figure 3. They are therefore not expected to have sufficient sedimentation stability in the tested model defoamer formulation. Combinations of precipitated and fumed silica may improve the stability of the formulation considerably; however, this is beyond the scope of this brochure and will be explored in the future.
Every black dot represents the same silica grade as shown in Figure 1. The higher the number of an isoline, the more stable the respective model defoamer formulation is expected to be against settling. For example, a silica grade positioned in the red or yellow area means that the model defamer it is based on should have very good or good sedimentation stability. The following hydrophobic AEROSIL* fumed silica products were actually found to have good or very good sedimentation stability:
Packaging & Availability
- Packaging Type
- Regional Availability

